tensorflow实现卷积神经网络CNN
卷积神经网络是目前深度学习的核心网络结构,被广泛的应用于计算机图像识别。
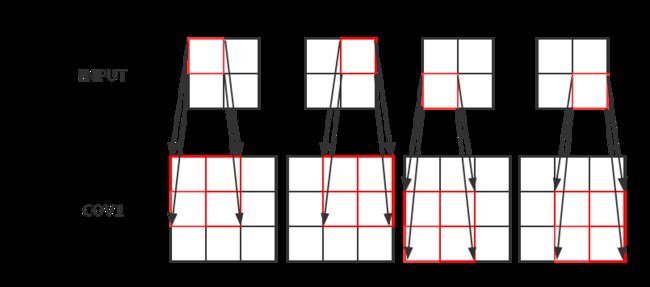
输入数据会通过多个卷积层及激活函数来获得输入数据的特征,每层之间的传递如下图:
在上面的图例中,每一个输入层的一格对应卷积层的四格,也可以更多。当然,一个输入层往往对应了很多个卷积层,比如RGB图片就有三个输入层,R图层,G图层与B图层,然后输入到大于3层或小于3层或刚好3层的卷积层中。卷积层后往往会有池化层,比如每2X2的格子里挑出最大的一个值出来,完成池化层后继续输入到新的卷积层中,再是池化层,再是卷积层…这样构成深度学习的网络,最后输出数据特征。
接下来上代码,先随意下载一些图片,比如猫和狗的图片,想分类什么都可以试试。
读取图片的函数,我下载了一些待分类的图片,一类放在set1文件夹,另一类放在set2文件夹:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import glob
def load_data(my_label="set1"):
def read_pic(pic_path):
image_raw_data = tf.gfile.FastGFile(pic_path, 'rb').read()
img_data = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_raw_data)
img_data = img_data.eval().reshape(100, 100, 3) # 所有图片都需要转换成相同大小
return img_data.eval()/255.0 # 图片数值控制在0到1之间,方便训练
# 用glob模块获取图片路径
paths = glob.glob("./%s/*.png" % my_label)
if my_label == "set1":
my_label = [0, 1]
elif my_label == "set2":
my_label = [1, 0]
# 分成测试集和训练集
pictures = []
pictures_test = []
labels = []
labels_test = []
check_num = 0
for path in paths:
check_num += 1
if check_num % 2 == 0:
pictures_test.append(read_pic(path))
labels_test.append(my_label)
else:
pictures.append(read_pic(path))
labels.append(my_label)
return pictures, labels, pictures_test, labels_test
def datas():
# 处理得粗狂了一些,生成set1及set2所有的数据。建议先转换好保存成数据直接读取,不然调参时每次转换图片过于耗时
pictures, labels, pictures_test, labels_test = load_data("set1")
pictures1, labels1, pictures_test1, labels_test1 = load_data("set2")
pictures = np.array(pictures+pictures1)
pictures_test = np.array(pictures_test+pictures_test1)
labels = np.array(labels+labels1)
labels_test = np.array(labels_test+labels_test1)
print(np.shape(pictures), np.shape(pictures_test)) # 打印看下数据是什么样子
print(np.shape(labels), np.shape(labels_test))
return pictures, labels, pictures_test, labels_test
接下来就是CNN网络了,先定义输入的数据shape,输出节点数等:
INPUT_SHAPE = [None, 100, 100, 3]
OUTPUT_NODE = 2
TRAIN_STEP = 3000
定义变量weights及biases:
def weight_variable(shape):
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape, stddev=0.1))
return Weights
def biases_variable(shape):
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
Biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape, mean=0.1, stddev=0.1))
return Biases
卷积神经网络由卷积层,池化层及最后的全连接层构成,所以需要定义这三种,首先是卷积层,这里的striders是定义的在卷积层上的扫描模式,第一和第四位都是1,第二位和第三位代表水平方向和竖直方向一次跳多少格,另外可以对输出层周围进行填充,'SAME’就是不填充,'VALID’是第一列第一行都加一行:
def conv_layer(layername, inputs, Weights_shape, biases_shape, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='VALID', activation_function=None):
# add one more layer and return the output of this layer
with tf.name_scope(layername):
Weights = weight_variable(Weights_shape)
biases = biases_variable(biases_shape)
with tf.name_scope("h_conv"):
h_conv = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.nn.conv2d(inputs, Weights, strides=strides, padding=padding), biases)
if activation_function is None:
outputs = h_conv
else:
outputs = activation_function(h_conv)
return outputs
然后是池化层,ksize是在2X2内处理,strides也和卷积层的意义一样,这里默认每次跳两格
def pool_layer(layername, conv, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME', pooling_function=None):
with tf.name_scope(layername):
if pooling_function is None:
outputs = conv
else:
outputs = pooling_function(conv, ksize=ksize, strides=strides, padding=padding)
return outputs
最后是需要全连接层来降低维数,减少节点数
def fc_layer(layername, inputs, Weights_shape, biases_shape, activation_function=None):
with tf.name_scope(layername):
Weights = weight_variable(Weights_shape)
biases = biases_variable(biases_shape)
with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'):
Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b, name = layername)
tf.summary.histogram(layername+"/outputs", outputs)
return outputs
各种层都定义好了就可以写卷积神经网络的模型了,这里写一个简单一点的,输入层-卷积层-池化层-卷积层-池化层-全连接层
def mode(inputs, keep_prob):
# 需要计算好每层会有多少个节点
# 我的输入层为[None, 100, 100, 3],以2X2的大小进行卷积,第一个卷积层从3层对应到48层,权重的第四个值应该是和偏差的个数相同
# 每一层卷积层是使用relu函数
conv1_layer1 = conv_layer("conv1_layer1", inputs, [2, 2, 3, 48], [48], [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME', tf.nn.relu)
# 池化层1,每2X2的格子里挑出最大值
pool1_layer2 = pool_layer("pooling1_layer2", conv1_layer1, [1, 2, 2, 1], [1, 2, 2, 1], 'VALID', tf.nn.max_pool)
# 第二层卷积层
conv2_layer3 = conv_layer("conv2_layer3", pool1_layer2, [2, 2, 48, 96], [96], [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME', tf.nn.relu)
# 第二层池化层
pool2_layer4 = pool_layer("pooling2_layer4", conv2_layer3, [1, 2, 2, 1], [1, 2, 2, 1], 'VALID', tf.nn.max_pool)
layer4_shape = pool2_layer4.get_shape().as_list()
print(layer4_shape)
# 将数据降维,并用全连接层降低节点数目
pool2_layer4flat = tf.reshape(pool2_layer4, [-1, layer4_shape[1]*layer4_shape[2]*layer4_shape[3]])
fc1_layer5 = fc_layer("fc1_layer5", pool2_layer4flat, [layer4_shape[1]*layer4_shape[2]*layer4_shape[3], 50], [50], tf.nn.relu)
# 训练过程中随机扔掉一些节点,防止过拟合
fc1_layer5_drop = tf.nn.dropout(fc1_layer5, keep_prob)
# 最后通过一个全连接层输出结果
fc2_layer6 = fc_layer("fc2_layer6", fc1_layer5_drop, [50, output_node], [output_node])
return fc2_layer6
然后需要定义损失函数
def loss(outputs, outputs_target, learning_rate=0.001, Optimizer = "Adam"):
end_points = {}
# 计算交叉熵时,tf.log需要加上一个极小值,防止Nan出现
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_mean(outputs_target*tf.log(outputs+1e-10))
if Optimizer == "Adam":
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cross_entropy)
elif Optimizer == "GradientDescent":
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cross_entropy)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(outputs, 1), tf.argmax(outputs_target, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
end_points["accuracy"] = accuracy
end_points["loss"] = cross_entropy
end_points["train_step"] = train_step
end_points["outputs"] = outputs
end_points["outputs_target"] = outputs_target
return end_points
训练的函数跟之前写的全连接神经网络的类似
def train():
##run tf
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, INPUT_SHAPE, name="data")
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, OUTPUT_NODE], name="target")
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name="keep_prob")
outputs = tf.nn.softmax(mode(x, keep_prob), name="op_to_store")
end_points = loss(outputs, y_, 0.035, "GradientDescent")
init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.local_variables_initializer())
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
pictures, labels, pictures_test, labels_test = datas()
sess.run(init_op)
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("./cnv_tbgragh", sess.graph)
for i in range(0, TRAIN_STEP):
_, loss_ = sess.run([end_points["train_step"], end_points["loss"]], feed_dict={x: pictures, y_: labels, keep_prob: 0.5})
print (i, loss_)
saver.save(sess, "./model.ckpt")
loss_, accuracy_, test_y, true_y = sess.run([\
end_points["loss"], end_points["accuracy"], end_points["outputs"], end_points["outputs_target"]], \
feed_dict={x: pictures_test, y_: labels_test, keep_prob: 1.0})
print(accuracy_)
print(test_y.tolist(), true_y.tolist())
下面贴上完整的代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import glob
def load_data(my_label="set1"):
def read_pic(pic_path):
image_raw_data = tf.gfile.FastGFile(pic_path, 'rb').read()
img_data = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_raw_data)
img_data = img_data.eval().reshape(100, 100, 3) # 所有图片都需要转换成相同大小
return img_data.eval()/255.0 # 图片数值控制在0到1之间,方便训练
paths = glob.glob("./%s/*.png" % my_label)
if my_label == "set1":
my_label = [0, 1]
elif my_label == "set2":
my_label = [1, 0]
# 分成测试集和训练集
pictures = []
pictures_test = []
labels = []
labels_test = []
check_num = 0
for path in paths:
check_num += 1
if check_num % 2 == 0:
pictures_test.append(read_pic(path))
labels_test.append(my_label)
else:
pictures.append(read_pic(path))
labels.append(my_label)
return pictures, labels, pictures_test, labels_test
def datas():
# 处理得粗狂了一些,生成set1及set2所有的数据。建议先转换好保存成数据直接读取,不然调参时每次转换图片过于耗时
pictures, labels, pictures_test, labels_test = load_data("set1")
pictures1, labels1, pictures_test1, labels_test1 = load_data("set2")
pictures = np.array(pictures+pictures1)
pictures_test = np.array(pictures_test+pictures_test1)
labels = np.array(labels+labels1)
labels_test = np.array(labels_test+labels_test1)
print(np.shape(pictures), np.shape(pictures_test)) # 打印看下数据是什么样子
print(np.shape(labels), np.shape(labels_test))
return pictures, labels, pictures_test, labels_test
----------------------------------------------------
INPUT_SHAPE = [None, 100, 100, 3]
OUTPUT_NODE = 2
TRAIN_STEP = 3000
def weight_variable(shape):
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape, stddev=0.1))
return Weights
def biases_variable(shape):
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
Biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape, mean=0.1, stddev=0.1))
return Biases
def conv_layer(layername, inputs, Weights_shape, biases_shape, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='VALID', activation_function=None):
# add one more layer and return the output of this layer
with tf.name_scope(layername):
Weights = weight_variable(Weights_shape)
biases = biases_variable(biases_shape)
with tf.name_scope("h_conv"):
h_conv = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.nn.conv2d(inputs, Weights, strides=strides, padding=padding), biases)
if activation_function is None:
outputs = h_conv
else:
outputs = activation_function(h_conv)
return outputs
def pool_layer(layername, conv, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME', pooling_function=None):
with tf.name_scope(layername):
if pooling_function is None:
outputs = conv
else:
outputs = pooling_function(conv, ksize=ksize, strides=strides, padding=padding)
return outputs
def fc_layer(layername, inputs, Weights_shape, biases_shape, activation_function=None):
with tf.name_scope(layername):
Weights = weight_variable(Weights_shape)
biases = biases_variable(biases_shape)
with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'):
Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b, name = layername)
tf.summary.histogram(layername+"/outputs", outputs)
return outputs
def mode(inputs, keep_prob):
conv1_layer1 = conv_layer("conv1_layer1", inputs, [2, 2, 3, 48], [48], [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME', tf.nn.relu)
pool1_layer2 = pool_layer("pooling1_layer2", conv1_layer1, [1, 2, 2, 1], [1, 2, 2, 1], 'VALID', tf.nn.max_pool)
conv2_layer3 = conv_layer("conv2_layer3", pool1_layer2, [2, 2, 48, 96], [96], [1, 1, 1, 1], 'SAME', tf.nn.relu)
pool2_layer4 = pool_layer("pooling2_layer4", conv2_layer3, [1, 2, 2, 1], [1, 2, 2, 1], 'VALID', tf.nn.max_pool)
layer4_shape = pool2_layer4.get_shape().as_list()
# print(layer4_shape)
pool2_layer4flat = tf.reshape(pool2_layer4, [-1, layer4_shape[1]*layer4_shape[2]*layer4_shape[3]])
fc1_layer5 = fc_layer("fc1_layer5", pool2_layer4flat, [layer4_shape[1]*layer4_shape[2]*layer4_shape[3], 50], [50], tf.nn.relu)
fc1_layer5_drop = tf.nn.dropout(fc1_layer5, keep_prob)
fc2_layer6 = fc_layer("fc2_layer6", fc1_layer5_drop, [50, output_node], [output_node])
return fc2_layer6
def loss(outputs, outputs_target, learning_rate=0.001, Optimizer = "Adam"):
end_points = {}
# 计算交叉熵时,tf.log需要加上一个极小值,防止Nan出现
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_mean(outputs_target*tf.log(outputs+1e-10))
if Optimizer == "Adam":
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cross_entropy)
elif Optimizer == "GradientDescent":
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cross_entropy)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(outputs, 1), tf.argmax(outputs_target, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
end_points["accuracy"] = accuracy
end_points["loss"] = cross_entropy
end_points["train_step"] = train_step
end_points["outputs"] = outputs
end_points["outputs_target"] = outputs_target
return end_points
def train():
##run tf
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, INPUT_SHAPE, name="data")
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, OUTPUT_NODE], name="target")
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name="keep_prob")
outputs = tf.nn.softmax(mode(x, keep_prob), name="op_to_store")
end_points = loss(outputs, y_, 0.035, "GradientDescent")
init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.local_variables_initializer())
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
pictures, labels, pictures_test, labels_test = datas()
sess.run(init_op)
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("./model_tbgragh", sess.graph)
for i in range(0, TRAIN_STEP):
_, loss_ = sess.run([end_points["train_step"], end_points["loss"]], feed_dict={x: pictures, y_: labels, keep_prob: 0.5})
print (i, loss_)
saver.save(sess, "./model.ckpt")
loss_, accuracy_, test_y, true_y = sess.run([\
end_points["loss"], end_points["accuracy"], end_points["outputs"], end_points["outputs_target"]], \
feed_dict={x: pictures_test, y_: labels_test, keep_prob: 1.0})
print(accuracy_)
print(test_y.tolist(), true_y.tolist())
def main(_):
train()
if __name__ == "__main__":
tf.app.run()
另外需要说明的是,如果电脑内存不够16g不要随意运行,有一个正经一点的服务器最好,训练图片4000张左右会用到10g以上的内存,当然也可以把图片大小再改小一点,如果只想试试CNN,就少整一些图片。