DispatcherServlet初始化和请求处理过程
1.DispatcherServlet的继承关系
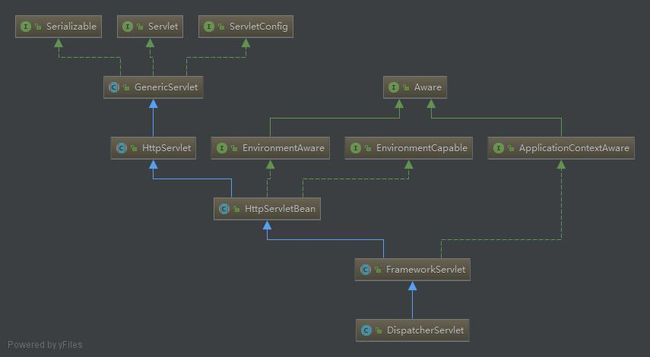
在idea中,右键选择DispatcherServlet的Diagrams可以查看类的继承关系,如图所示
可以看到,DispatchServlet继承子FrameworkServlet,而FrameworkServlet继承子HttpServletBean;
2.HttpSerlvetBean初始化过程分析
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
try {
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
throw ex;
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}
分析:
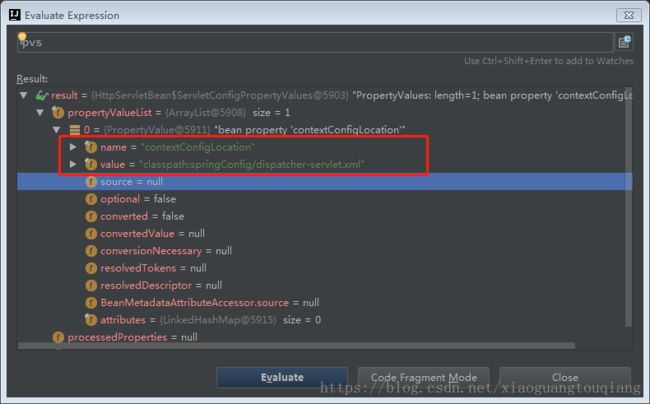
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
获取web.xml的参数,构造PropertyValues对象;这里的psv值通过debug可以观察到实际是servlet的名称和具体的配置路径;
之后设置DispatcherServlet的属性;其实这段代码的目的就是获取servlet的context参数,设置为DispatcherServlet的contextConfigLocation参数,构造spring mvc的容器上下文;最后
initServletBean();
protected void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
}
该方法是占位方法,子类可以重写该方法,来做更多的事情;
3.FrameworkServlet
源代码如下所示,省略部分日志代码
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
重要的方法有initWebApplicationContext,代码
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}
首先判断WebApplicationContext是否为空,因为DispatcherServlet有一个构造函数webApplicationContext
public DispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext) {
super(webApplicationContext);
}
所以要先进行判断,当使用该构造函数来生成DispatcherServlet的时候执行这段逻辑;
之后调用
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
以contextAttribute为key从ServletContext中找WebApplication。一般不会设置contextAttribute属性,所以这里返回值为null;然后调用
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
来创建上下文,具体的代码如下
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
wac.setParent(parent);
wac.setConfigLocation(getContextConfigLocation());
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
设置跟上下文为父上下文,然后配置ServletConfig,ServletContext等实例到这个上下文中;
最后onRefresh(wac);模板方法,子类DispatcherServlet会覆盖这个方法;
之后将创建的容器上下文设置到ServletContext中;
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
4.DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet覆盖了父类FrameworkServlet中的方法,代码如下
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
这里主要初始化各种策略接口的实现类,比如常用的异常处理初始化initHandlerExceptionResolvers,视图处理初始化initViewResolvers,请求映射初始化方法initHandlerMappings;
总结:1.HttpServletBean 主要做一些初始化的事情,将web.xml中的配置参数设置到servlet中。比如servlet标签的子标签init-param标签中的参数;
2.FrameworkServlet 将Servlet与Spring容器上下文关联;也就是初始化FarmeworkServlet属性webApplicationContext,这个属性代表springmvc上下文,它有个父类上下文;
3.DispatcherServlet 初始化各个功能的实现,比如异常处理,视图处理,请求映射等功能;
5.DispatcherServlet对http请求的处理过程
首先了解下HttpServlet对于http请求的处理过程;
1.所有的请求都会调用service方法;
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
2.service中,根据请求类型再分别调用以下方法
else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req,resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req,resp);
3.FrameworkServlet子类继承子HttpServlet,并重写了上述方法,代码如下:
@Override
protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
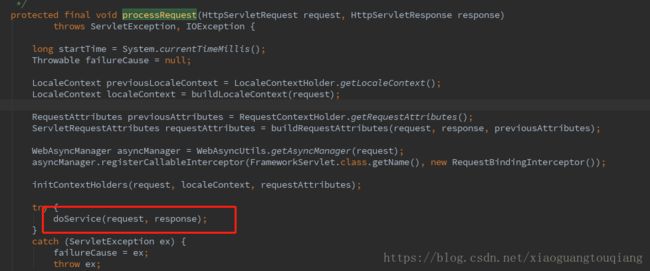
4.FrameworkServlet的processRequest方法代码如下
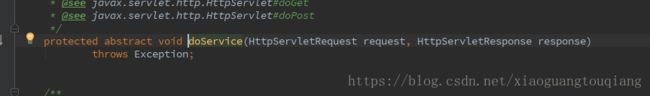
其中doService的具体代码如下,可以看到是抽象方法,具体的实现是在DispatchServlet中,
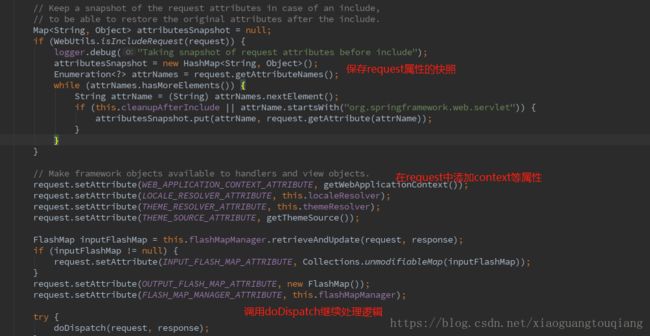
5.doService具体实现逻辑如下
这里判断请求如果是include请求,那么就保存请求的快照,doDispatch方法处理之后,快照中的数据会覆盖新的request中的数据;
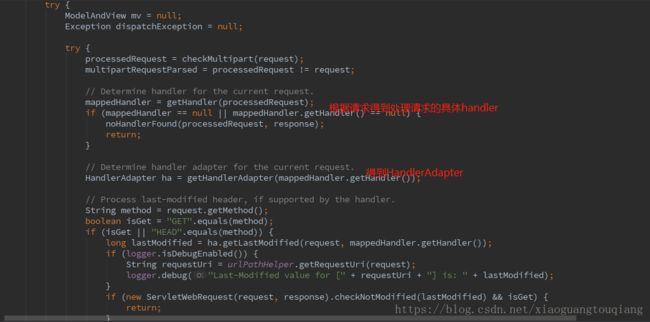
6.doDispatch方法的处理逻辑
这里首先通过getHandler得到当前请求对应的handler;getHandler方法的具体代码如下
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
"Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}
这里的handlerMapping的数据结构其实是个List,里面保存了当前servlet处理请求的映射;
/** List of HandlerMappings used by this servlet */
private List handlerMappings;
根据handler再得到HandlerAdapter,HandlerAdapter是一个接口,其中的handle方法如下所示
/**
* Use the given handler to handle this request.
* The workflow that is required may vary widely.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @param handler handler to use. This object must have previously been passed
* to the {@code supports} method of this interface, which must have
* returned {@code true}.
* @throws Exception in case of errors
* @return ModelAndView object with the name of the view and the required
* model data, or {@code null} if the request has been handled directly
*/
ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception;
处理对应的request请求,返回一个视图;这里就是http请求的处理逻辑;
参考文章:
https://www.cnblogs.com/fangjian0423/p/springMVC-directory-summary.html