Spring(一)—— Spring IOC
文章目录
-
- Spring简介
- Spring IOC
-
- IOC的使用(基于配置)
-
- Spring创建对象的方式
- Spring依赖注入的方式
- IOC的使用(基于注解)
Spring简介
Spring是一个轻量级、开源的框架,核心功能如下:
- IOC:控制反转,对象额创建不是通过 new 的形式,而是交给Spring配置创建对象;
- AOP:面向切面编程,扩展功能而不用修改代码;(通常用于日志监控、登陆操作等);
IOC是典型的工厂模式,通过工厂去注入对象,AOP则是代理模式的体现。
Spring提供了一站式的框架,Java EE三层结构中,每一层Spring都提供了解决方案:
- Controller(Web服务层):Spring MVC;
- Service(业务处理层):Spring IOC、AOP;
- Dao:Mybatis、jdbcTemplated、Mybatis-Spring整合;
Spring IOC
IOC即控制反转,把对象的创建交给了Spring管理,IOC的使用有两种方式:
- 通过配置文件;
- 通过注解;
IOC的底层原理:
- XML配置文件;
- dom4j解析XML配置文件,得到需要创建对象的全路径名;
- 利用工厂设计模式,通过反射产生对象;
- 创建XML配置文件,配置要创建的对象的类;
示例 - 创建工厂类,利用dom4j解析配置文件,通过反射创建对象;
//大概原理
public class UserFactory {
public static User getBean() {
//利用dom4j解析配置文件,通过id属性值来获取到类的全路径名
String path = "com.tulun.bean.Student1";
//通过反射创建对象
Class c = Class.forName(path);
//创建对象
User user = (User) c.newInstance();
return user;
}
}
IOC的使用(基于配置)
使用步骤:
- 引入依赖;
- 创建类,在类中添加方法;
- 创建Spring的XML配置文件,配置需要创建对象的类;
- 使用;
需要引入的Spring的基本依赖包:
org.springframework
spring-beans
4.1.7.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-core
4.1.7.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-context
4.1.7.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-expression
4.1.7.RELEASE
Spring创建对象的方式
Spring通过配置文件创建对象的方式(即bean实例化的方式)主要有三种:
- 通过无参构造;
- 通过静态工厂创建;
- 通过一般工厂创建;
代码示例:
这三种方式需要创建的对象都是Student1的对象:
public class Student1 {
public void show() {
System.out.println("Student1.show()...");
}
}
一、通过无参构造
配置文件 bean1.xml:
测试:
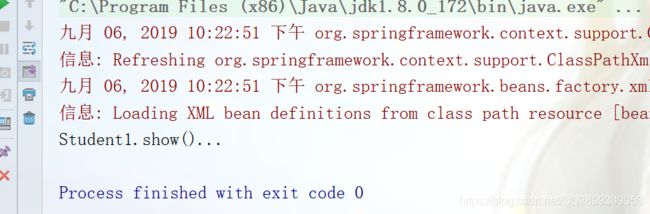
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//加载Spring配置文件,创建对象
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean实例化/bean1.xml");
Student1 student = (Student1) context.getBean("student"); //参数是id
student.show();
}
}
添加静态工厂类:
public class StaticFactory {
public static Student1 getBean() {
return new Student1();
}
}
配置文件需要这样写,bean2.xml:
测试:
public class TestDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean实例化/bean2.xml");
Student1 student = (Student1)context.getBean("student1");
student.show();
}
}
三、通过一般工厂创建:
添加一般工厂类:
public class Factory {
public Student1 getBean() {
return new Student1();
}
}
这个方法实例化bean的时候,我们需要先得到工厂类对象,所以这个时候的配置文件bean3.xml是:
测试:
public class TestDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean实例化/bean3.xml");
Student1 student = (Student1)context.getBean("student1");
student.show();
}
}
Spring依赖注入的方式
以上是Spring创建对象的方式,现在来说说Spring如何给属性赋值,也就是依赖注入(DI);
Java中给属性赋值的方式有主要三种:
- 通过有参构造函数;
- 通过set方法;
- 通过接口;
在Spring里面我们主要使用的给属性赋值的方式有两种:
- 有参构造;
- set方法;
代码示例:
依赖注入主要是给Student2对象进行属性注入:
public class Student2 {
private String name;
//通过set方法个属性赋值的时候,先创建的是一个无参的对象
public Student2() {}
public Student2(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void show() {
System.out.println("Student2.show()...");
}
}
一、通过有参构造
配置文件nature1.xml:
测试:
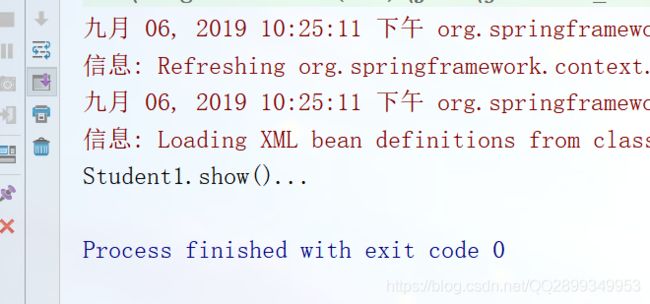
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("属性的注入/nature1.xml");
Student2 student = (Student2)context.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student.getName());
student.show();
}
}
这个被创建对象的类一定要有set方法,不然报错;
nature2.xml:
测试:
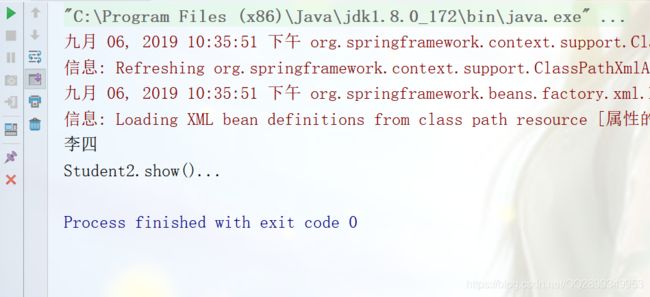
public class TestDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("属性的注入/nature2.xml");
Student2 student = (Student2)context.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student.getName());
student.show();
}
}
上述我们是对简单数据类型的属性进行依赖注入,那么接下来就是复杂属性的依赖注入,复杂属性包括对象、数组、map、List、Properties(配置文件);
先来说说对象的注入:
先创建一个dao层的类:
public class User {
public void add() {
System.out.println("User.dao()");
}
}
再来一个Service层的对象:
public class UserService {
private User user;
//需要添加set方法才可以给属性赋值
public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}
public void add(){
user.add();
}
}
现在来写配置文件nature3.xml:
其实只要注意对象的注入的时候,后面那个标签不是value,而是 ref 就好了!
测试:
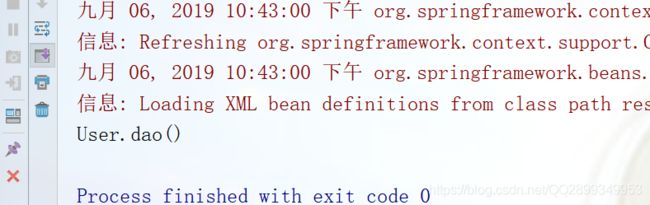
public class TestDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("属性的注入/复杂属性的注入/nature3.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService)context.getBean("userService");
userService.add();
}
}
下来就是数组、List、map和properties属性的注入了:
需要创建对象的类是Student3:
public class Student3 {
private String name;
private String[] str;
private List list;
private Map map;
private Properties properties;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setStr(String[] str) {
this.str = str;
}
public void setList(List list) {
this.list = list;
}
public void setMap(Map map) {
this.map = map;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student3{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", 数组=" + Arrays.toString(str) +
", list=" + list +
", map=" + map +
", properties=" + properties +
'}';
}
}
他的配置文件nature4.xml:
1
2
张三
李四
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
测试:
public class TestDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("属性的注入/复杂属性的注入/nature4.xml");
test1(context);
test2(context);
test3(context);
test4(context);
}
//测试数组
private static void test1(ApplicationContext context) {
Student3 student = (Student3)context.getBean("student1");
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
//测试list
private static void test2(ApplicationContext context) {
Student3 student = (Student3)context.getBean("student2");
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
//测试map
private static void test3(ApplicationContext context) {
Student3 student = (Student3)context.getBean("student3");
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
//测试文件
private static void test4(ApplicationContext context) {
Student3 student = (Student3)context.getBean("student4");
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
}
IOC的使用(基于注解)
使用步骤:
- 引入依赖;
- 配置XML文件,开启扫描类;
- 创建对应的类,添加注解,一般用@Component;
- 测试使用;
依赖和上面的一样;
在常用的注解@Component下还衍生了三个注解:
- @Controller(Web层);
- @Service(业务层);
- @Repository(dao层);
他们的作用都是一样的,只是这样是各层之间有了很高的区分度;
依赖注入的方式:
对象的依赖注入:
- @Autowired
- @Resource
简单类型(基本属性)的依赖注入:
- @Value
代码示例:
创建类:
@Component(value = "user")
@Scope(value = "singleton") //设置单例
//相当于配置实现时里面的id 注解实现的配置文件,bean4.xml:
测试,测试我用的额 junit,它的 jar 包如下:
junit
junit
4.12
test
测试代码:
public class TestDemo1 {
@Test
public void test1() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("注解实现/bean4.xml");
User user = (User)context.getBean("user");
user.add();
}
}
创建一个类:
@Component(value = "userService")
public class UserService {
@Autowired
//@Resource //这个也可以 需要添加参数的话就是User那个类注解里面的
private User user; //这个User就是上面示例中的那个
public void add() {
user.add();
}
}
测试:
public class TestDemo2 {
@Test
public void test1() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("注解实现/bean4.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
userService.add();
}
}
所以拿注解来实现的话,就显得特别简单,而在IOC中,配置和注解一般是联合使用的,其中:
- 创建对象(bean的实例化)是通过配置实现的;
- 依赖注入是通过注解实现的;
下面是一个配置和注解联合使用的例子,有三层(Controller、Service、Dao),其中,Controller层中有Service层的对象,Service层中有Dao层对象,那么代码如下:
创建Dao层类:
public class TestDao {
@Value(value = "1")
private int test;
public void setTest(int test) {
this.test = test;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println("TestDao.test()"+test);
}
}
创建Service层类:
public class TestService {
@Autowired
private TestDao testDao;
public void setTestDao(TestDao testDao) {
this.testDao = testDao;
}
public void test() {
testDao.test();
}
}
创建Controlller层类:
public class TestController {
@Resource
private TestService testService;
public void setTestService(TestService testService) {
this.testService = testService;
}
public void test() {
testService.test();
}
}
因为是配置和注解的联合使用,所以需要在配置文件中开启扫描、创建对象,那么bean5.xml如下:
测试:
public class TestDemo3 {
@Test
public void test1() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("配置和注解联合使用/bean5.xml");
TestController testController = (TestController)context.getBean("controller");
testController.test();
}
}