Spring IOC---invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors源码分析
文章目录
-
- 前言
- 1.概述
-
- 1.1 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
- 1.2 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
- 2.准备工作
- 3.源码调试
-
- invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
-
- 3.1.getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()
- 3.2.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List beanFactoryPostProcessors)
-
- 3.2.1 先来介绍一下这个方法中出现的集合。
- 3.2.2 源码调试分析
-
- 3.2.2.1 处理手动添加的 实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的类
- 3.2.2.2 处理Spring自带的后置处理器ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
- 3.2.2.3 处理spring扫描的并且是实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor和Ordered接口的类
- 3.2.2.4 处理spring扫描的并且实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口没有实现Ordered接口的类
- 3.2.2.5 处理实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的类 的父接口BeanFactoryPostProcessor的逻辑
- 3.2.2.6 处理程序手动添加的并且实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类
- 3.2.2.7 处理Spring扫描的并且实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类
- 4.总结
前言
先提几个问题,如果对以下这几个问题不了解,那么仔细的看看这篇博客,希望可以解决你的疑问。
1.BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的作用是什么?
2.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 方法内 不同类型的后置处理器的执行顺序是怎样的?
3.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 方法内出现的集合各自存储的都是什么,有什么作用?
4.为什么有一段代码需要用到while循环?
5.哪一步完成了扫描,将加了注解的类注册到bdMap中。
1.概述
根据名字就可以知道这个方法的主要作用就是执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor
该方法会实例化并调用所有需要被执行的BeanFactoryPostProcessor(包括它的子类BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor)。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口是spring提供的扩展点,程序员可以实现这个接口或子接口来扩展spring。
那么BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的作用是什么呢?
1.1 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
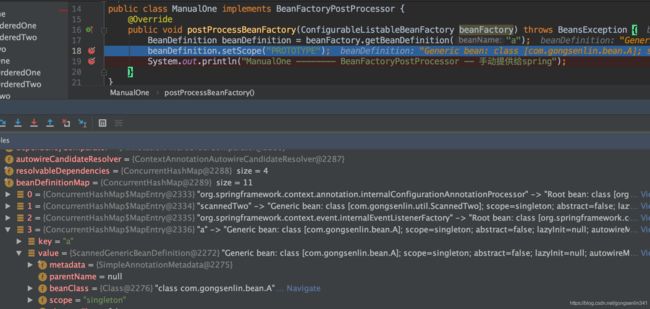
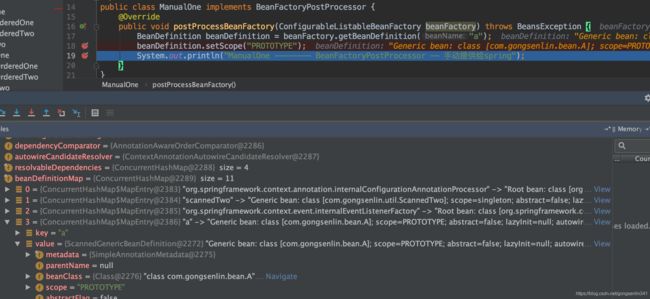
BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口是针对bean容器的,它的实现类可以在当前BeanFactory初始化后,bean实例化之前修改bean的定义属性,达到影响之后实例化bean的效果。Spring允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor在容器实例化任何其它bean之前读取配置元数据,对其进行修改。简单的说就是操作这时候BeanDefinitionMap中的bd 修改它的属性,例如修改scope,如图所示。
1.2 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
这个接口的作用就是往spring容器中注册bean,在Spring和Mybatis进行整合的时候,我们通常会在application.xml中配置一个Bean,也就是MapperScannerConfigurer(该类实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口,所以支持动态注册mapper为Bean组件,并注入到spring容器中)。
并且可以有多个这个接口的实现类,根据需要实现PriorityOrdered接口或Ordered接口来达到bean注册的顺序。
2.准备工作
为了调试这一部分的源码,和分析每一步的具体实现结果。需要准备以下的几个类。
两个手动提供给Spring的类 分别实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口
/**
* @author gongsenlin
* @version 1.0
* @date 2020-09-06 10:47
* 实现 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口 手动提供给Spring的类
*/
public class ManualOne implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("ManualOne -------- BeanFactoryPostProcessor -- 手动提供给spring");
}
}
/**
* @author gongsenlin
* @version 1.0
* @date 2020-09-06 11:03
* 实现 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口 手动提供给Spring的类
*/
public class ManualTwo implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("ManualTwo---BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的实现方法 --- 手动提供给spring");
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("ManualTwo---BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现方法 --- 手动提供给spring");
}
}
两个加了Spring注解的类 分别实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口
/**
* @author gongsenlin
* @version 1.0
* @date 2020-09-06 09:41
* 实现 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口 并且由Spring扫描的类
*/
@Component
public class ScannedOne implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("ScannedTwo---BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现方法");
}
}
/**
* @author gongsenlin
* @version 1.0
* @date 2020-09-06 09:40
* 实现 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口 并且由Spring扫描的类
*/
@Component
public class ScannedTwo implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("ScannedOne---BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的实现方法");
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("ScannedOne---BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现方法");
}
}
下面的4个类就是上面的4个类的基础上多实现了Ordered接口
/**
* @author gongsenlin
* @version 1.0
* @date 2020-09-06 12:08
* 实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口以及Ordered接口 并且由Spring扫描的类
*/
public class ScannedOrderedOne implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor, Ordered {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("ScannedOrderedOne---BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现方法");
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}
/**
* @author gongsenlin
* @version 1.0
* @date 2020-09-06 10:14
* 实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口以及Ordered接口 并且由Spring扫描的类
*/
@Component
public class ScannedOrderedTwo implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor , Ordered {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("ScannedOrderedTwo---BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的实现方法 --- Ordered");
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("ScannedOrderedTwo---BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现方法 --- Ordered");
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}
/**
* @author gongsenlin
* @version 1.0
* @date 2020-09-06 09:41
* 实现 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口 并且由Spring扫描的类
*/
@Component
public class ScannedOne implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("ScannedOne---BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现方法");
}
}
/**
* @author gongsenlin
* @version 1.0
* @date 2020-09-06 09:40
* 实现 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口 并且由Spring扫描的类
*/
@Component
public class ScannedTwo implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("ScannedTwo---BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的实现方法");
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("ScannedTwo---BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现方法");
}
}
3.源码调试
开启spring容器的初始化
/**
* @author gongsenlin
* @version 1.0
* @date 2020-09-04 11:06
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
ac.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new ManualOne());//手动交给spring管理
ac.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new ManualTwo());
ac.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new ManualOrderedOne());
ac.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new ManualOrderedTwo());
ac.register(AppConfig.class);
ac.refresh();
}
}
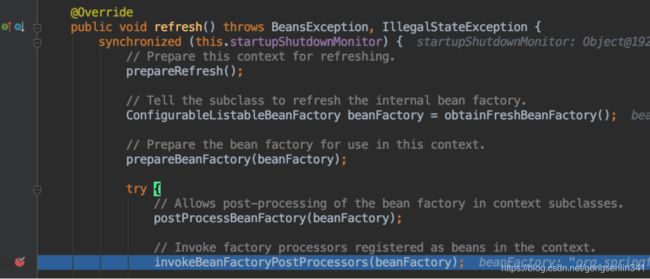
在AbstractApplicationContext的refresh()中invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法处打一个断点
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
重点是两个方法getBeanFactoryPostProcessors() 以及invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List beanFactoryPostProcessors)
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
3.1.getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()
代码执行的逻辑很简单 如下
public List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> getBeanFactoryPostProcessors() {
return this.beanFactoryPostProcessors;
}
那么beanFactoryPostProcessors这个集合里面存放的是什么呢?
存放的是当前应用上下文中已经注册的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor。默认情况下是空的。
回到我们自己编写的Test类
ac.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new ManualOne());//手动交给spring管理
这一行代码就是将自己实现的后置处理器 添加到beanFactoryPostProcessors这个集合中。可以看下addBeanFactoryPostProcessor方法执行的逻辑 也很简单 如下
@Override
public void addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor) {
Assert.notNull(postProcessor, "BeanFactoryPostProcessor must not be null");
this.beanFactoryPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
就是往beanFactoryPostProcessors这个集合中添加后置处理器。
3.2.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List beanFactoryPostProcessors)
这个方法主要执行两种类型的后置处理器
第一种是BeanFactoryPostProcessor
第二种是上面接口的子接口BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
3.2.1 先来介绍一下这个方法中出现的集合。
- processedBeans 存放所有需要执行的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,目的是为了避免重复的去执行已经执行过的逻辑
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
- regularPostProcessors 存放程序员手动添加的类型为BeanFactoryPostProcessor的bean。
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
- registryProcessors 存放 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 类型的bean。也可以说是已经执行了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor逻辑的类,因为是在执行了这个接口的逻辑之后添加到这个集合中的。目的是这些类还没有执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的逻辑。之后就不需要再去寻找,而是通过记忆集的方式,先缓存下来这些类。
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
- currentRegistryProcessors 当前找出来的需要被执行的bean,执行完毕后会清空这个集合。
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
- priorityOrderedPostProcessors 存放了由Spring扫描的并且实现了priorityOrdered接口和BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的bean。
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
- orderedPostProcessors 存放了由Spring扫描的并且实现了Ordered接口和BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的bean。
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
- nonOrderedPostProcessors 存放了由Spring扫描的并且实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的bean。
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
3.2.2 源码调试分析
介绍完了上述的集合的作用 开始debug调试源码来分析一下 这个方法的具体的执行流程。
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry)
首先是一个if判断,判断beanFactory是否为BeanDefinitionRegistry,beanFactory为DefaultListableBeanFactory,而DefaultListableBeanFactory实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,因此这边为true。 正常来说这里的逻辑就是true
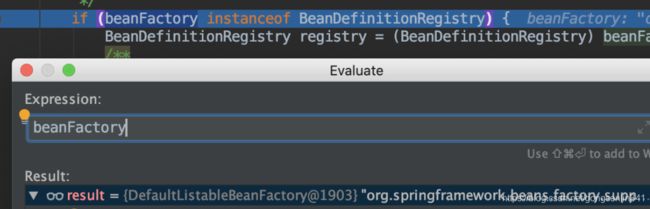
除非程序员对spring进行了很深度的扩展,自己实现了整个工厂的顶级接口AliasRegistry去设计一个工厂,这个判断才会跳过。这里先不考虑这种清空。99%的情况下,都为true
3.2.2.1 处理手动添加的 实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的类
接下来第一个for循环
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
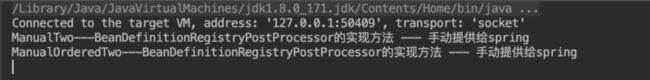
再说一遍 beanFactoryPostProcessors默认是空的,仅当程序员手动添加BeanFactoryPostProcessor才有值。而我们的测试代码手动添加了4个BeanFactoryPostProcessor。所以这时会遍历这个集合。
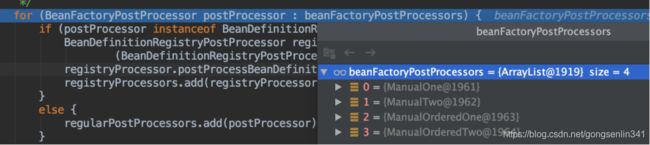
for循环里面会判断遍历到的当前的后置处理器是否是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的类。如果是的话就会去执行这个后置处理器的逻辑。执行完毕后会将这个后置处理器添加到registryProcessors集合中,记忆集缓存。
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);//执行后置处理器的逻辑
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
如果不是的话会添加到regularPostProcessors集合中。说明他是一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的类
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
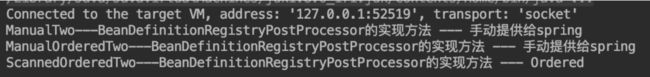
看看代码调试的结果,控制台输入如下:
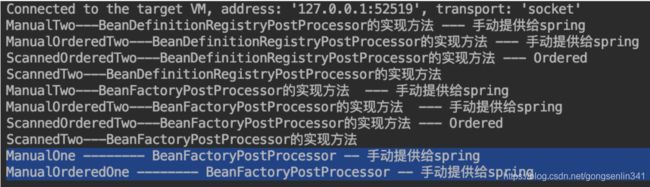
和上述源码的描述结果一致,将实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 的类的逻辑执行了。还可以发现 此时实现了Ordered的类,并没有在没有实现Ordered的类之前进行处理。
3.2.2.2 处理Spring自带的后置处理器ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
第一个for循环结束,继续
下面第一行的作用是从beanDefinitionMap(bdMap)中找到类型为BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的类的BeanName。而此时的bdMap中只有一个Spring内置的类ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 这个类的逻辑也就是完成扫描,将添加了spring注解的类都注册到bdMap中。
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
//遍历
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
//有没有实现PriorityOrdered接口
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));//添加到集合中准备处理
processedBeans.add(ppName);//添加到已经处理过的集合中,避免重复处理
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
/**
* 完成扫描
*/
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
// 清除
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
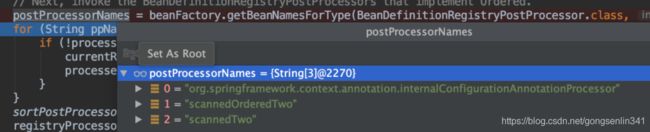
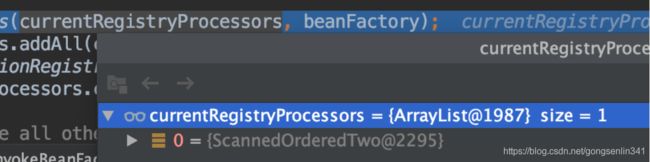
代码调试也可以看出这里只得到了一个beanName 对应的是
![]()
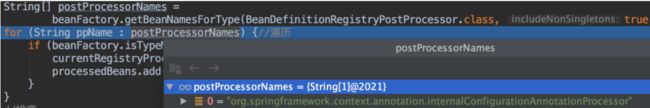
然后就是遍历这个集合。将类型为PriorityOrdered的类添加到currentRegistryProcessors和processedBeans这两个集合中。前面也说过了这两个集合的作用,这里再说一遍加深下印象,currentRegistryProcessors是存放当前准备处理的后置处理器。processedBeans存放的是所有需要被执行的后置处理器
添加完成后,对currentRegistryProcessors集合进去排序,这里的排序不重要 因为就只有一个后置处理器。然后将它添加到registryProcessors中,前面说的记忆集缓存的作用。
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
//遍历
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
//有没有实现PriorityOrdered接口
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));//添加到集合中准备处理
processedBeans.add(ppName);//添加到已经处理过的集合中,避免重复处理
}
}
//排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
接下来就要执行
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
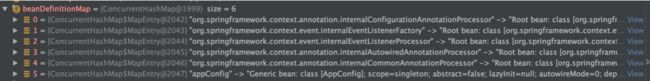
已经知道了ConfigurationClassPostProcessor这个后置处理器是用来扫描并添加到bdmap中的。那么先来看看执行之前bdMap中有哪些
5个Spring提供的 + 一个配置类
执行了上述代码之后,设置了Spring注解的类,被扫描并且添加到bdMap中
处理完了要清空currentRegistryProcessors
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
3.2.2.3 处理spring扫描的并且是实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor和Ordered接口的类
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
//遍历
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
//有没有实现Ordered接口
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));//添加到集合中准备处理
processedBeans.add(ppName);//添加到已经处理过的集合中,避免重复处理
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
第一句和之前出现的一样,找到bdMap中BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的类。
比前面多了两个
然后for循环遍历,将还没处理的后置处理器并且实现了Ordered接口的类 添加到currentRegistryProcessors集合中 准备处理,并添加到processedBeans集合中。
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
//遍历
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
//有没有实现Ordered接口
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));//添加到集合中准备处理
processedBeans.add(ppName);//添加到已经处理过的集合中,避免重复处理
}
}
此时 currentRegistryProcessors 集合中只有一个,spring自带的已经被处理过了,所以不会添加进来,ScannedTwo没有实现Ordered接口。
对currentRegistryProcessors集合排序,然后将这个集合中的后置处理器都添加到registryProcessors记忆集中,等待后续处理。
然后执行currentRegistryProcessors中后置处理器的逻辑
处理完之后清空currentRegistryProcessors
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
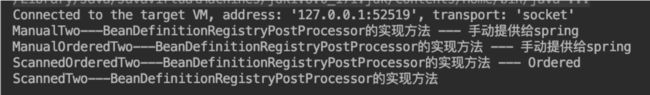
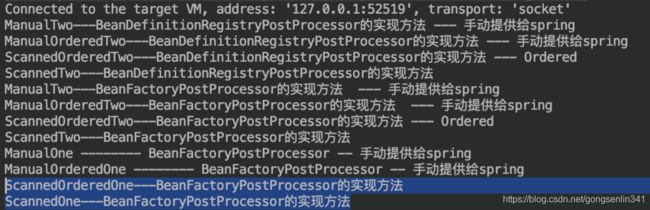
调试源码控制台输出如下:比之前多了一行,也就是执行了currentRegistryProcessors中后置处理器的逻辑
3.2.2.4 处理spring扫描的并且实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口没有实现Ordered接口的类
和上面的逻辑差不多 只是这里处理的是没有实现Ordered接口的类。不再赘述。
但是这里为什么需要一个while循环呢?
答:当通过bdMap 拿到后置处理器。而这个后置处理器是实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口,这个后置处理器可以去执行和Spring提供的ConfigurationClassPostProcessor一样的功能,去扫描指定的包下的bean。如果此时扫描到的bean恰好也是一个后置处理器。那么此时就需要while循环,在下一次循环的时候去拿到这个bean的实例并执行逻辑。
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);//bd中找到实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的类的beanName
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
//判断是否有没有处理过
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));//添加到集合中准备处理
processedBeans.add(ppName);//添加到已经处理过的集合中,避免重复处理
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
上述逻辑处理完 控制台输出结果如下:多了最后一行。
可以看出由Spring扫描的类,实现了Ordered接口的会先于没有实现Ordered接口的执行。
3.2.2.5 处理实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的类 的父接口BeanFactoryPostProcessor的逻辑
之前在处理实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的类的过程中,已经将这些都记忆了下来 保存在了registryProcessors中。所以这里就不需要在进行遍历的寻找。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
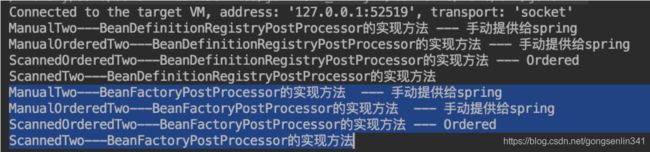
执行完之后,控制台输出的结果如下:
多了这4行,也就是上述的那些执行过BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor逻辑的后置处理器再执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor逻辑。因为BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子接口,所以也属于BeanFactoryPostProcessor
3.2.2.6 处理程序手动添加的并且实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类
regularPostProcessors这个集合里面的内容,在第一个for循环的时候就已经添加了,存放的是程序员手动添加的实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
执行完之后,控制台输出的结果如下。
3.2.2.7 处理Spring扫描的并且实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类
第一行和上面出现的类似,得到实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类的beanName
然后开辟了三个集合。
分别是存放实现了PriorityOrdered接口的后置处理器、存放实现了Ordered接口的后置处理器的BeanName、存放没有实现这两个接口的后置处理器的BeanName。
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
可能有的人会有疑问,为什么上面的代码仅仅将实现了PriorityOrdered接口的后置处理器进行实例化添加到集合中,而其他的后置处理器仅仅保存了beanName。
因为实现了PriorityOrdered接口的后置处理器 在处理逻辑的时候。可以去修改bdMap中的比它优先级低的beanDefinition,也就是可以去修改这些后置处理器。所以需要依次按照顺序去实例化后置处理器并执行逻辑。
下面的逻辑很简单,也就是先执行实现了PriorityOrdered接口的后置处理器,然后实例化并执行实现了Ordered接口的后置处理器,最后再实例化并执行没有实现这两个接口的后置处理器。
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
控制台的输出结果如下
4.总结
后置处理器的执行顺序
- 程序员手动添加的 并且是实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的接口的后置处理器。详情参考3.2.2.1
- spring自带的后置处理器,也就是ConfigurationClassPostProcessor。详情参考3.2.2.2
- Spring扫描的并且实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口和Ordered接口的后置处理器。详情参考3.2.2.3
- Spring扫描的并且实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口但没有实现Ordered接口的后置处理器。详情参考3.2.2.4
- 处理上述后置处理器中的父接口BeanFactoryPostProcessor的逻辑。详情参考3.2.2.5
- 程序员手动添加的并且实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的后置处理器。详情参考3.2.2.6
- Spring扫描的,并且实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的后置处理器。按照实现了Priority接口、Ordered接口和没有实现这两个接口的顺序执行。详情参考3.2.2.7