设计模式 保护性暂停/解耦等待/生产者消费者
文章目录
- 设计模式-保护性暂停
-
- 保护性暂停
- Thread.join()
- 设计模式-解耦等待
- 生产者消费者
设计模式-保护性暂停
保护性暂停
实现原理:
因为线程各类数据都在栈中,而对象数据都在堆中所以可以实现两个线程在同一个对象代码块里面操作(临界区)。一个设置,一个拿取出。在setThread还未将数据写入时,getThread进行wait操作直到setThread进行notifuall操作时getThread才能拿到对象运行。
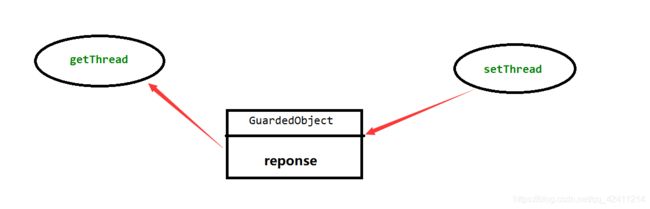
class GuardedObject{
private Object reponse;//中间对象
//得到对象
public Object get(long timeout){
synchronized (this){
//经过时间
long passtime=0;
//开始时间
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//剩余等待时间, 为防止“虚假唤醒”,这一轮循环应该等待的时间
long timeleft=timeout-passtime;
while (reponse==null){
timeleft=timeout-passtime;
if (timeleft<=0){
System.out.println("超时");
break;
}
try {
this.wait(timeleft);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
passtime=System.currentTimeMillis()-beginTime;
}
}
return reponse;
}
//生成对象
public void setReponse(Object object){
synchronized (this){
this.reponse=object;
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GuardedObject guardedObject=new GuardedObject();
new Thread(()->{
Object getobj = guardedObject.get(2);
System.out.println("结果是"+getobj);
},"getThread").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
guardedObject.setReponse("nihao");
},"setThread").start();
}
}
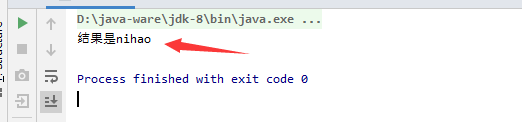
首先我们这里用带参数的wait,是因为我们这里不想一直去等待唤醒,当等待一定时间还未唤醒时,就放弃等待。其次为何我们不直接wait参数是我们直接传的时间,这是因为wait参数如果是传入的固定值那么每轮等待是固定时间,看下面的代码,我们能看到当一只没等到唤醒,那么还是换一只在while循环中,无法退出,所以和没有加参数没啥区别。我们希望的是在我们指定时间里当线程没有等到唤醒,那么就不在等待。
public Object get(long timeout){
synchronized (this){
while (reponse==null){
try {
this.wait(timeout);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return reponse;
}
用到剩余等待时间,而不是直接用timeout还有一个原因。
//剩余等待时间, 为防止“虚假唤醒”
long timeleft=timeout-passtime;
这里我们需要注意这行代码,为了防止虚假唤醒,所以不在this.wait(timeleft);等待时间里面直接填timeout时间防止多等。
什么是虚假唤醒
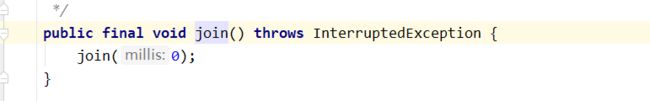
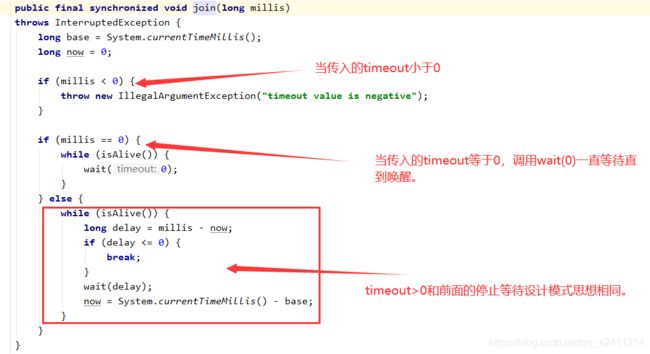
Thread.join()
join方法实现原理大致和上面的设计模式 保护性暂停相同。
设计模式-解耦等待
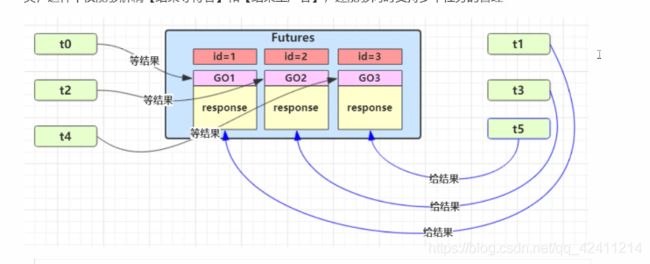
基于上面的保护性暂停,设计每个邮递员只能给一个人送信,Futures是MailBox楼下面的综合邮箱,人通过ID找自己的信箱。就是一个生产者对应一个消费者模式。
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i <3; i++) {
new People().start();
}
Thread.sleep(3);
for (Integer ID:MailBox.getIDs()) {
//无法进入这个循环
new PostMan(ID,"nihao").start();
System.out.println("送信");
}
}
}
class People extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
GuardedObject guardedObject=MailBox.generateGuObject();
System.out.println("等待到信");
Object getmail = guardedObject.get(5000);
}
}
class PostMan extends Thread{
private int ID;
private Object mail;
public PostMan(int ID, Object mail) {
this.ID = ID;
this.mail = mail;
}
@Override
public void run() {
GuardedObject guardedObject = MailBox.getguaObject(ID);
guardedObject.setReponse(mail);
System.out.println("邮递员放入了邮件");
}
}
//小区综合邮箱
class MailBox{
private static Map<Integer,Object> mapbox=new Hashtable<>();
private static int ID=1;
private static synchronized int generateID(){
return ID++;
}
public static GuardedObject getguaObject(int ID){
return (GuardedObject) mapbox.get(ID);
}
public static GuardedObject generateGuObject(){
//因为Hashtable是线程安全的,所以不用synchronized ()
GuardedObject guardedObject=new GuardedObject(generateID());
mapbox.put(guardedObject.getID(),guardedObject);
return guardedObject;
}
public static Set<Integer> getIDs(){
return mapbox.keySet();
}
}
class GuardedObject {
private Object reponse;//中间对象
private int ID;
public GuardedObject(int ID) {
this.ID = ID;
}
//得到对象
public Object get(long timeout) {
synchronized (this) {
//经过时间
long passtime = 0;
//开始时间
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//剩余等待时间, 为防止“虚假唤醒”,这一轮循环应该等待的时间
long timeleft = timeout - passtime;
while (reponse == null) {
timeleft = timeout - passtime;
if (timeleft <= 0) {
System.out.println("超时");
break;
}
try {
this.wait(timeleft);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
passtime = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginTime;
}
}
return reponse;
}
//生成对象
public void setReponse(Object object){
synchronized (this){
this.reponse=object;
this.notifyAll();
}
}
public int getID() {
return ID;
}
}
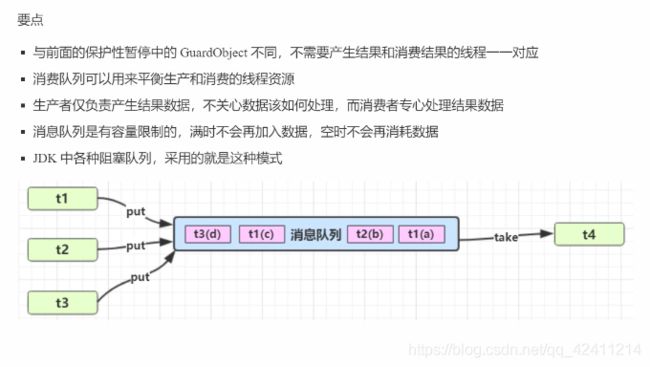
生产者消费者
class MessageQueue{
private static LinkedList<MessageEntry> linkedList=new LinkedList<>();//存放消息队列
private int capcity;
public MessageQueue(int capcity) {
this.capcity = capcity;
}
private MessageEntry take(){
//拿队列首部的messageEntry
synchronized (linkedList){
while (linkedList.isEmpty()){
//队列为空
try {
linkedList.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
MessageEntry messageEntry=linkedList.removeFirst();//不为空则放回队列首,并删除
linkedList.notifyAll();//挪走一个之后队列不满,唤醒满队列情况的wait
return messageEntry;
}
}
private void put(MessageEntry messageEntry){
//将messageEntry放入队列尾部
synchronized (linkedList){
//给消息队列加锁
while(capcity>=5){
//当消息队列满则wait不能让继续放了
try {
linkedList.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
linkedList.addLast(messageEntry);
linkedList.notifyAll();//当没有满且有消息则唤醒消息队列
}
}
}
class MessageEntry{
private int ID;
private Object value;
public MessageEntry(int ID, Object value) {
this.ID = ID;
this.value = value;
}
public int getID() {
return ID;
}
public Object getValue() {
return value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MessageEntry{" +
"ID=" + ID +
", value=" + value +
'}';
}
}