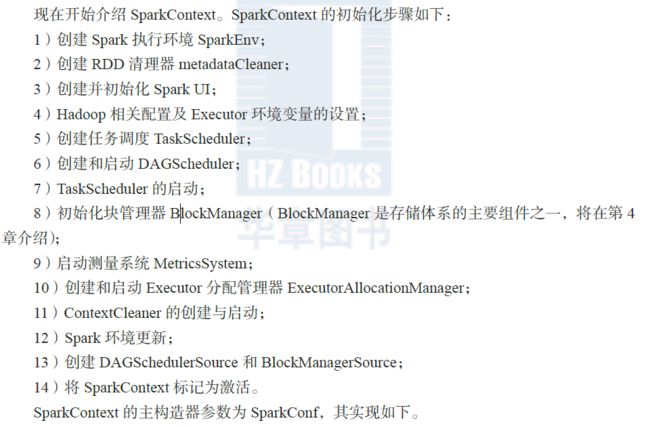
3.1 SparkContext概述
SparkConf负责配置参数,主要通过ConcurrentHaspMap来维护各种Spark的配置属性。
class SparkConf(loadDefaults: Boolean) extends Cloneable with Logging with Serializable {
import SparkConf._
/** Create a SparkConf that loads defaults from system properties and the classpath */
def this() = this(true)
private val settings = new ConcurrentHashMap[String, String]()
@transient private lazy val reader: ConfigReader = {
val _reader = new ConfigReader(new SparkConfigProvider(settings))
_reader.bindEnv(new ConfigProvider {
override def get(key: String): Option[String] = Option(getenv(key))
})
_reader
}
....
读取“spark.”开头的配置文件。
/**
* A config provider that only reads Spark config keys.
*/
private[spark] class SparkConfigProvider(conf: JMap[String, String]) extends ConfigProvider {
override def get(key: String): Option[String] = {
if (key.startsWith("spark.")) {
Option(conf.get(key)).orElse(SparkConf.getDeprecatedConfig(key, conf))
} else {
None
}
}
}
class SparkContext(config: SparkConf) extends Logging {
// The call site where this SparkContext was constructed.
private val creationSite: CallSite = Utils.getCallSite()
// In order to prevent multiple SparkContexts from being active at the same time, mark this
// context as having started construction.
// NOTE: this must be placed at the beginning of the SparkContext constructor.
SparkContext.markPartiallyConstructed(this)
val startTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
private[spark] val stopped: AtomicBoolean = new AtomicBoolean(false)
接下来对于Sparkconfi的赋值,各项配置信息的校验。
try {
_conf = config.clone()
_conf.validateSettings()
if (!_conf.contains("spark.master")) {
throw new SparkException("A master URL must be set in your configuration")
}
if (!_conf.contains("spark.app.name")) {
throw new SparkException("An application name must be set in your configuration")
}
_driverLogger = DriverLogger(_conf)
// log out spark.app.name in the Spark driver logs
logInfo(s"Submitted application: $appName")
3.2 创建执行环境SparkEnv
创建SparkEnv,主要适用createDriverEnv的方法,主要参数有三个sparkconf、isLocal、listenerBus的参数。
Sparkconf是对Spark的复制、isLocal标识是否为单机模式、listenerBus采用监听器模式维护各类事件的处理。
private[spark] def createDriverEnv(
conf: SparkConf,
isLocal: Boolean,
listenerBus: LiveListenerBus,
numCores: Int,
mockOutputCommitCoordinator: Option[OutputCommitCoordinator] = None): SparkEnv = {
assert(conf.contains(DRIVER_HOST_ADDRESS),
s"${DRIVER_HOST_ADDRESS.key} is not set on the driver!")
assert(conf.contains("spark.driver.port"), "spark.driver.port is not set on the driver!")
val bindAddress = conf.get(DRIVER_BIND_ADDRESS)
val advertiseAddress = conf.get(DRIVER_HOST_ADDRESS)
val port = conf.get("spark.driver.port").toInt
val ioEncryptionKey = if (conf.get(IO_ENCRYPTION_ENABLED)) {
Some(CryptoStreamUtils.createKey(conf))
} else {
None
}
create(
conf,
SparkContext.DRIVER_IDENTIFIER,
bindAddress,
advertiseAddress,
Option(port),
isLocal,
numCores,
ioEncryptionKey,
listenerBus = listenerBus,
mockOutputCommitCoordinator = mockOutputCommitCoordinator
)
}
最终调用create方法创建SparkEnv。
/**
* Helper method to create a SparkEnv for a driver or an executor.
*/
private def create(
conf: SparkConf,
executorId: String,
bindAddress: String,
advertiseAddress: String,
port: Option[Int],
isLocal: Boolean,
numUsableCores: Int,
ioEncryptionKey: Option[Array[Byte]],
listenerBus: LiveListenerBus = null,
mockOutputCommitCoordinator: Option[OutputCommitCoordinator] = None): SparkEnv = {
val isDriver = executorId == SparkContext.DRIVER_IDENTIFIER
// Listener bus is only used on the driver
if (isDriver) {
assert(listenerBus != null, "Attempted to create driver SparkEnv with null listener bus!")
}
val authSecretFileConf = if (isDriver) AUTH_SECRET_FILE_DRIVER else AUTH_SECRET_FILE_EXECUTOR
//第一步创建:安全管理器SecurityManager
val securityManager = new SecurityManager(conf, ioEncryptionKey, authSecretFileConf)
if (isDriver) {
securityManager.initializeAuth()
}
ioEncryptionKey.foreach { _ =>
if (!securityManager.isEncryptionEnabled()) {
logWarning("I/O encryption enabled without RPC encryption: keys will be visible on the " +
"wire.")
}
}
val systemName = if (isDriver) driverSystemName else executorSystemName
val rpcEnv = RpcEnv.create(systemName, bindAddress, advertiseAddress, port.getOrElse(-1), conf,
securityManager, numUsableCores, !isDriver)
// Figure out which port RpcEnv actually bound to in case the original port is 0 or occupied.
if (isDriver) {
conf.set("spark.driver.port", rpcEnv.address.port.toString)
}
// Create an instance of the class with the given name, possibly initializing it with our conf
def instantiateClass[T](className: String): T = {
val cls = Utils.classForName(className)
// Look for a constructor taking a SparkConf and a boolean isDriver, then one taking just
// SparkConf, then one taking no arguments
try {
cls.getConstructor(classOf[SparkConf], java.lang.Boolean.TYPE)
.newInstance(conf, java.lang.Boolean.valueOf(isDriver))
.asInstanceOf[T]
} catch {
case _: NoSuchMethodException =>
try {
cls.getConstructor(classOf[SparkConf]).newInstance(conf).asInstanceOf[T]
} catch {
case _: NoSuchMethodException =>
cls.getConstructor().newInstance().asInstanceOf[T]
}
}
}
第二步:创建基于Akka的分布式消息系统ActorSystem
第三步:创建Map任务输出跟踪器mapOutputTracker
第四步:实例化ShuffleManager
第五步:创建shuffleMemoryManager
第六步:创建块传输服务BlockTransferService
第七步:创建BlockManagerMaster
第八步:创建块管理器BlockManager
第九步:创建广播管理器Broadcastmanager
第十步:创建缓存管理器CacheManager
第十一步:创建HTTP文件服务器HttpFileServer
第十二步:创建测量系统MetricsSystem
第十三步:创建SparkEnv
3.2.1 安全管理器SecurityManager
主要对权限、账号进行设置。
def initializeAuth(): Unit = {
import SparkMasterRegex._
if (!sparkConf.get(NETWORK_AUTH_ENABLED)) {
return
}
// TODO: this really should be abstracted somewhere else.
val master = sparkConf.get(SparkLauncher.SPARK_MASTER, "")
val storeInUgi = master match {
case "yarn" | "local" | LOCAL_N_REGEX(_) | LOCAL_N_FAILURES_REGEX(_, _) =>
true
case k8sRegex() =>
// Don't propagate the secret through the user's credentials in kubernetes. That conflicts
// with the way k8s handles propagation of delegation tokens.
false
case _ =>
require(sparkConf.contains(SPARK_AUTH_SECRET_CONF),
s"A secret key must be specified via the $SPARK_AUTH_SECRET_CONF config.")
return
}
if (sparkConf.get(AUTH_SECRET_FILE_DRIVER).isDefined !=
sparkConf.get(AUTH_SECRET_FILE_EXECUTOR).isDefined) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid secret configuration: Secret files must be specified for both the driver and the" +
" executors, not only one or the other.")
}
secretKey = secretKeyFromFile().getOrElse(Utils.createSecret(sparkConf))
if (storeInUgi) {
val creds = new Credentials()
creds.addSecretKey(SECRET_LOOKUP_KEY, secretKey.getBytes(UTF_8))
UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser().addCredentials(creds)
}
}
3.2.2 基于Akka的分布式消息系统ActorSystem
Scala 认为Java线程通过共享数据以及通过锁来维护数据的一致性是糟糕的做法。
锁容易引起争用,降低并发程序的性能,甚至引入死锁的问题。
3.2.3 map任务输出跟踪器mapOutputTracker
用于跟踪map阶段任务的输出状态,此状态便于reduce阶段任务获取地址以及中间的输出中间结果。
3.2.4 实例化ShuffleManager
ShuffleManager负责管理本地以及远程的block数据的shuffle操作。
为什么需要Shuffle操作?
Spark作为并行计算框架, 同一个作业会被划分成多个任务在多个节点上执行。
reduce的输入可能存在于多个节点上,因此需要通过洗牌将所有的reduce的输入汇总起来。
这个过程就是shuffle。
3.2.5 shuffle线程内存管理器ShuffleMemoryManager
ShuffleMemoryManager负责管理Shuffle线程占有内存的分配和释放。
3.2.6 块传输服务BlockTransferService
BlockTransferService默认为NettyBlockTransferService(可以配置属性Spark.shuffle.blockTransferService使用NioBlockTransferService)
它使用Netty提供的异步事件驱动的网络应用架构,提供Web服务以及客户端,获取远程节点上的Block的集合。
3.2.7 BlockManagerMaster介绍
BlockManagerMaster负责对Block的管理和协调,具体操作依赖于BlockManagerMasterActor。
3.2.8 创建块管理器BlockManager
BlockManager负责对Block的管理。
3.2.9 创建广播管理器BroadcastManager
BroadcastManager用于配置信息和序列化后的RDD、JOB、以及ShuffleDependency等信息在本地存储。
为了容灾,也会复制到其他节点上。创建BroadcastManager的代码实现如下:
private[spark] class BroadcastManager(
val isDriver: Boolean,
conf: SparkConf,
securityManager: SecurityManager)
BroadcastManager必须在初始化方案被调用之后才能生效。
private def initialize() {
synchronized {
if (!initialized) {
broadcastFactory = new TorrentBroadcastFactory
broadcastFactory.initialize(isDriver, conf, securityManager)
initialized = true
}
}
}
3.2.10 创建缓存管理器CacheManager
CacheManager用于缓存RDD某个分区计算后的中间结果。
3.2.11 HTTP文件服务器HttpFileServer
HttpFIleServer主要提供对jar及其他文件的http访问,访问jar包包括用户上传的jar包。
3.2.12 创建测量系统MetricsSystem
MetricsSystem是Spark的测量系统
3.2.13 创建SparkEnv
当所有的基础组件准备好后,最终使用下边的代码创建执行环境SparkEnv。
3.3 创建metadataCleaner
SparkContext为了保持对所有的持久化的RDD的追踪,使用类型为TimeStampedWeakValueHashMap的persistentRdds缓存。
metadataCleaner的功能是清除过期的持久化RDD。
MetadataCleaner的实现可以看出其实质是一个用TimerTask实现的定时器,不断调用cleanupFunc这样的参数函数。构造metadataCleaner时的函数参数是cleanup,
用于清理persistentRdds中的过期内容。
3.4 SparkUI详解
异步事件监听。
DAGScheduler是主要的产生各类SparkListenerEvent的源头,它将各类中SparkListenerEvent发送到listenerBus的事件队列中,listenerBus通过
定时器将SparkListenerEvent事件匹配到具体的SparkListener,改变SparkListener中的传统监控数据,最终有SparkUI的界面展示。
各类监听器JobProgressListener、EnvironmentListener、StorageListener、ExecutorListener集成体系。
3.5 hadoop相关配置以及Executor环境变量
3.6 创建任务调度器TaskScheduler
3.7 创建和启动DAGScheduler
DAGScheduler主要在于任务正式交给TaskSchedulerImpl交给之前做一些准备工作,包括创建Job,将DAG中的RDD划分为不同的Stage,提交Stage,等等。
3.8 TaskScheduler启动
3.9 启动测量系统MetricsSystem
3.10 创建和启动ExecutorAllocationManager
ExecutorAllocationManager用于已经分配的Executor进行管理。
3.11 ContextCleaner的创建和启动
ContextCleaner用于那些清理超出应用范围的Rdd、shuffleDependency和Broadcast对象。
3.12 Spark环境更新
3.13 创建DAGSchedulerSource和BlockManagerSource
3.14 将SparkCOntext标记为激活
3.15小结
回顾本章,Scala与Akka的基于Actor的并发编程模型给人的印象深刻。
listenerBus对于监听器的模式的经典应用看起来并不复杂,希望读者朋友能都应用到自己的产品中去。
使用Netty所提供的异步网络架构构建的Block传输服务,基于Jetty构建的内嵌Web服务(HTTP文件服务器和SparkUI)。
基于codahale提供的第三方测量仓库创建的测量系统。
Executor中的心跳实现等内容。