PCL学习:点云分割-超体素聚类
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/ironstark/p/5013968.html
1.超体聚类
超体(supervoxel)是一种集合,集合的元素是“体”。与体素滤波器中的体类似,其本质是一个个的小方块。与之前提到的所有分割手段不同,超体聚类的目的并不是分割出某种特定物体,其对点云实施过分割(over segmentation),将场景点云化成很多小块,并研究每个小块之间的关系。这种将更小单元合并的分割思路已经出现了有些年份了,在图像分割中,像素聚类形成超像素,以超像素关系来理解图像已经广为研究。本质上这种方法是对局部的一种总结,纹理,材质,颜色类似的部分会被自动的分割成一块,有利于后续识别工作。比如对人的识别,如果能将头发,面部,四肢,躯干分开,则能更好的对各种姿态,性别的人进行识别。
点云和图像不一样,其不存在像素邻接关系。所以,超体聚类之前,必须以八叉树对点云进行划分,获得不同点团之间的邻接关系。与图像相似点云的邻接关系也有很多,如面邻接,线邻接,点邻接。其具体解释如下图:
基于超体聚类的点云分割,使用点邻接(蓝色)作为相邻判据。
2.超体聚类的实现步骤
举个简单的例子来体会下超体聚类,其过程和结晶类似。但不是水结晶成冰,而是盐溶液过饱和状态下的多晶核结晶。所有的晶核(seed)同时开始生长,最终填满整个空间,使物质具有晶体结构。 超体聚类实际上是一种特殊的区域生长算法,和无限制的生长不同,超体聚类首先需要规律的布置区域生长“晶核”。晶核在空间中实际上是均匀分布的,并指定晶核距离(Rseed)。再指定粒子距离(Rvoxel)。再指定最小晶粒(MOV),过小的晶粒需要融入最近的大晶粒。关系如图所示:
有了晶粒和结晶范围之后,我们只需要控制结晶过程,就能将整个空间划分开了。结晶过程的本质就是不断吸纳类似的粒子(八分空间)。类似是一个比较模糊的概念,关于类似的定义有以下公式:
公式中的Dc表示颜色上的差异,Dn表示法线上的差异,Ds代表点距离上的差异。w_*表示一系列权重。用于控制结晶形状。在晶核周围寻找一圈,D最小的体素被认为是下一个“被发展的党员”。需要注意的是,结晶过程并不是长完一个晶核再长下一个,二是所有的晶核同时开始生长(虽然计算机计算时必然有先后,但从层次上来说是同时的)。其生长顺序如下图所示:
接下来所有晶核继续公平竞争,发展第二个“党员”,以此循环,最终所有晶体应该几乎同时完成生长。整个点云也被晶格所分割开来。并且保证了一个晶包里的粒子都是类似的。
3. 测试示例
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
// Types
typedef pcl::PointXYZRGBA PointT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud PointCloudT;
typedef pcl::PointNormal PointNT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud PointNCloudT;
typedef pcl::PointXYZL PointLT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud PointLCloudT;
void addSupervoxelConnectionsToViewer (PointT &supervoxel_center,
PointCloudT &adjacent_supervoxel_centers,
std::string supervoxel_name,
boost::shared_ptr & viewer);
int
main(int argc, char ** argv)
{
if (argc < 2)
{
pcl::console::print_error("Syntax is: %s \n "
"--NT Dsables the single cloud transform \n"
"-v \n-s \n"
"-c \n-z \n"
"-n \n", argv[0]);
return (1);
}
PointCloudT::Ptr cloud = boost::make_shared ();
pcl::console::print_highlight("Loading point cloud...\n");
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile(argv[1], *cloud))
{
pcl::console::print_error("Error loading cloud file!\n");
return (1);
}
cout << "point size of input: " << cloud->size() << endl;
bool disable_transform = pcl::console::find_switch(argc, argv, "--NT");//禁止单视角转换
float voxel_resolution = 0.008f;
bool voxel_res_specified = pcl::console::find_switch(argc, argv, "-v");//设置体素尺寸大小,该值决定底层八叉树的叶子尺寸
if (voxel_res_specified)
pcl::console::parse(argc, argv, "-v", voxel_resolution);
float seed_resolution = 0.1f;
bool seed_res_specified = pcl::console::find_switch(argc, argv, "-s");//设置种子大小,该设置决定超级体素的大小
if (seed_res_specified)
pcl::console::parse(argc, argv, "-s", seed_resolution);
float color_importance = 0.2f;
if (pcl::console::find_switch(argc, argv, "-c"))//设置颜色在距离测量公式中的权重
pcl::console::parse(argc, argv, "-c", color_importance);
float spatial_importance = 0.4f;
if (pcl::console::find_switch(argc, argv, "-z"))//设置空间距离在距离测量公式中的权重,此值越大超级体素越规则
pcl::console::parse(argc, argv, "-z", spatial_importance);
float normal_importance = 1.0f;
if (pcl::console::find_switch(argc, argv, "-n"))//设置法向量的权重,即表面法向量影响体素分割结果的比重
pcl::console::parse(argc, argv, "-n", normal_importance);
// //
// This is how to use supervoxels
// //
pcl::SupervoxelClustering super(voxel_resolution, seed_resolution);
if (disable_transform)
super.setUseSingleCameraTransform(false);
super.setInputCloud(cloud); //设置输入点云
super.setColorImportance(color_importance); //设置颜色空间距离权重
super.setSpatialImportance(spatial_importance); //设置物理位置空间距离权重
super.setNormalImportance(normal_importance); //设置法向量权重
std::map ::Ptr > supervoxel_clusters;
//该单映射容器以标签为键值存储所有超体素
pcl::console::print_highlight("Extracting supervoxels!\n");
super.extract(supervoxel_clusters);
pcl::console::print_info("Found %d supervoxels\n", supervoxel_clusters.size());
boost::shared_ptr viewer(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("点云库PCL学习教程第二版-超体素分割"));
viewer->setBackgroundColor(1, 1, 1);
PointCloudT::Ptr voxel_centroid_cloud = super.getVoxelCentroidCloud();//voxel_centroid_cloud包含根据八叉树结构得到的体素质心
cout << "voxel centroids: " << voxel_centroid_cloud->size() << endl;
if (0)
{//对于体素中心的可视化和保存,基本就是对原始数据的空间均匀下采样
viewer->addPointCloud(voxel_centroid_cloud, "voxel centroids");
pcl::io::savePCDFile("voxel_centroids.pcd", *voxel_centroid_cloud);
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 4, "voxel centroids");
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_OPACITY, 0.5, "voxel centroids");
}
PointLCloudT::Ptr labeled_voxel_cloud = super.getLabeledVoxelCloud();//labeled_voxel_cloud包含标签的点云数据,属于同一体素的点具有相同标签
if (1)
{//超体素分割结果显示与保存
pcl::io::savePCDFile("labeled_voxels.pcd", *labeled_voxel_cloud);
viewer->addPointCloud(labeled_voxel_cloud, "labeled voxels");
cout << "labeled voxels: " << labeled_voxel_cloud->size() << endl;
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 3, "labeled voxels");
// viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_OPACITY,0.8, "labeled voxels");
}
PointNCloudT::Ptr sv_normal_cloud = super.makeSupervoxelNormalCloud(supervoxel_clusters);//sv_normal_cloud包含超体素法向量的点云数据
//
if (0)//超体素对应的法线特征可视化
viewer->addPointCloudNormals(sv_normal_cloud, 1, 0.05f, "supervoxel_normals");
pcl::console::print_highlight("Getting supervoxel adjacency\n");
std::multimap supervoxel_adjacency;
super.getSupervoxelAdjacency(supervoxel_adjacency);
cout << "size of supervoxel_adjacency: " << supervoxel_adjacency.size() << endl;
//遍历多重映射容器构造邻接图
std::multimap::iterator label_itr = supervoxel_adjacency.begin();
for (; label_itr != supervoxel_adjacency.end(); )
{
//获取标签值
uint32_t supervoxel_label = label_itr->first;
//根据标签索引到该超体素
pcl::Supervoxel::Ptr supervoxel = supervoxel_clusters.at(supervoxel_label);
//遍历该超体素相邻超体素并以其相邻超体素中心为点集构造点云,用于后续可视化,这里的相邻超体素在多重映射容器中具有相同的键值
PointCloudT adjacent_supervoxel_centers;
std::multimap::iterator adjacent_itr = supervoxel_adjacency.equal_range(supervoxel_label).first;
for (; adjacent_itr != supervoxel_adjacency.equal_range(supervoxel_label).second; ++adjacent_itr)
{
pcl::Supervoxel::Ptr neighbor_supervoxel = supervoxel_clusters.at(adjacent_itr->second);
adjacent_supervoxel_centers.push_back(neighbor_supervoxel->centroid_);
}
//
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "supervoxel_" << supervoxel_label;
//cout<centroid_, adjacent_supervoxel_centers, ss.str(), viewer);
//使迭代器指向下一个标签。
label_itr = supervoxel_adjacency.upper_bound(supervoxel_label);
}
while (!viewer->wasStopped())
{
viewer->spinOnce();
}
return (0);
}
void
addSupervoxelConnectionsToViewer(PointT &supervoxel_center,
PointCloudT &adjacent_supervoxel_centers,
std::string supervoxel_name,
boost::shared_ptr & viewer)
{
int i = 0;
//Iterate through all adjacent points, and add a center point to adjacent point pair
PointCloudT::iterator adjacent_itr = adjacent_supervoxel_centers.begin();
for (; adjacent_itr != adjacent_supervoxel_centers.end(); ++adjacent_itr)
{
std::stringstream ss;
ss << supervoxel_name << i;
viewer->addLine(supervoxel_center, *adjacent_itr, ss.str());
viewer->setShapeRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_LINE_WIDTH, 3, ss.str());
viewer->setShapeRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR, 0, 255, 0, ss.str());
ss << supervoxel_name << i;
viewer->addSphere(supervoxel_center, 0.008, 0, 0, 255, ss.str());
viewer->setShapeRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_SHADING, pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_SHADING_GOURAUD, ss.str());
//viewer->setShapeRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_OPACITY,0.9,ss.str());
i++;
}
}
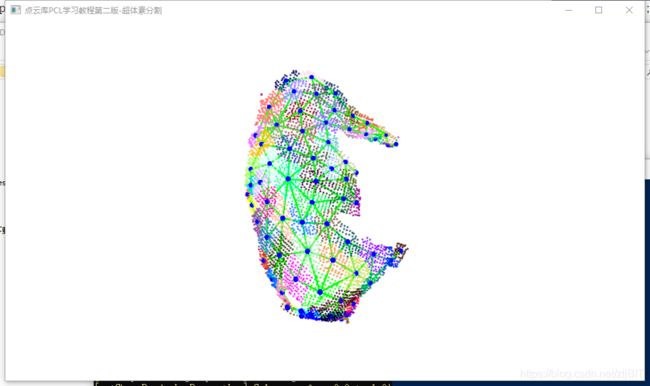
执行命令:
.\supervoxel_clustering.exe ..\..\Source\pig.pcd
打印信息:
> Loading point cloud...
point size of input: 4315
> Extracting supervoxels!
Found 71 supervoxels
voxel centroids: 3746
labeled voxels: 3743
> Getting supervoxel adjacency
size of supervoxel_adjacency: 288可视化: