LinkedHashMap
文章目录
-
-
- LinkedHashMap详解
-
- 基本数据结构
- 遍历顺序按照插入顺序
- 遍历顺序按照访问顺序
- LinkedHashMap实现LRU
-
LinkedHashMap详解
相信大家都知道,HashMap的访问时无序的,如果你想按照插入顺序,访问元素,就必须使用
LinkedHashMap, 下面详细讲述其原理。
基本数据结构
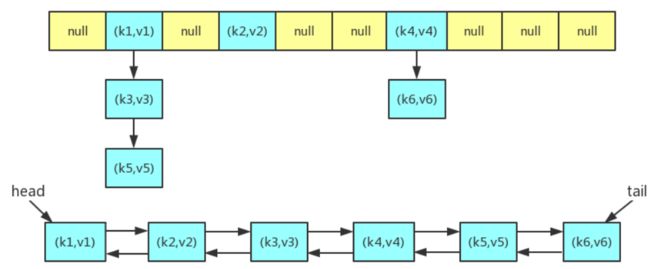
LinkedHashMap 的大致数据结构如下图所示
(链表和哈希表中相同的键值对都是指向同一个对象,区分开来是为了呈现清晰的结构)
其中双向链表,对元素进行排序,保证按照插入的顺序,访问元素
遍历顺序按照插入顺序
LinkedHashMap的链表节点继承了HashMap的节点,而且每个节点都包含了前指针和后指针,所以这里可以看出它是一个双向链表
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
头指针和尾指针
/**
* The head (eldest) of the doubly linked list.
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head;
/**
* The tail (youngest) of the doubly linked list.
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail;
在插入key,value键值对后,如果是新的键值对(不存在重复key),会将此键值对作为双链表的尾节点
调用put方法后,如果是新的键值对,一定会调用newNode方法
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) {
// existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
newNode方法, 将新的键值对,作为双链表尾部节点
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
linkNodeLast(p);
return p;
}
private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last = tail;
tail = p;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
}
遍历顺序按照访问顺序
final boolean accessOrder;
LinkedHashMap,默认是按照插入顺序,来遍历元素。但是同时也支持按照访问顺序(get方法),来遍历元素
遍历顺序按照访问顺序,只需要设置accessOrder =true
按照访问顺序遍历,举个具体的例子
插入,key为1、2、3、4、5的键值对
执行一次get(2)的操作
遍历输出的结果为 1 3 4 5 2
如果设置accessOrder为true, LinkedMap在get元素后,会将元素移动至双链表的尾节点
执行get方法后,会执行afterNodeAcess方法
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return null;
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
afterNodeAccess方法。将元素移动至双链表尾节点
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) {
// move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}
需要注意的时,put时,发生值覆盖情况,也会支持afterNodeAccess方法
LinkedHashMap实现LRU
实现LRU要保证几点
- 插入时,新元素在双链表尾部,如果size超过数量,需要删除双链表头部元素(重写removeEldestEntry方法)
- 插入时,发生key值重复,即值覆盖情况,需要将相应元素移动至双链表尾部(accessOrder设置为true)
- 访问时,需要将相应的元素移动至队列尾部(accessOrder设置为true)
- 删除时,哈希表和双链表均需要删除相应元素(满足)
Leetcode真题https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lru-cache-lcci/submissions
import java.util.*;
class ZYMap<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap<K,V> {
private int cacheSize;
public ZYMap(int cacheSize) {
super(16,0.75f,true);
this.cacheSize = cacheSize;
}
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) {
return this.size() > cacheSize;
}
}
class LRUCache {
ZYMap map;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
map = new ZYMap<Integer, Integer>(capacity);
}
public int get(int key) {
if(map.get(key) == null) return -1;
else return (int)map.get(key);
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
map.put(key,value);
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/