MPEG音频编码分析
目录
-
- 基本流程
- 设计框架
-
- 变量设置
- 音频读入
- 多相滤波器结合窗函数和滤波
- 计算比例因子
- 心理声学模型
- 比特分配
- 量化与装帧
- 实验要求
-
- 输出音频的采样率和目标码率
- 对于某个数据帧,输出该帧所分配的比特数,该帧的比例因子,该帧的比特分配结果
基本流程
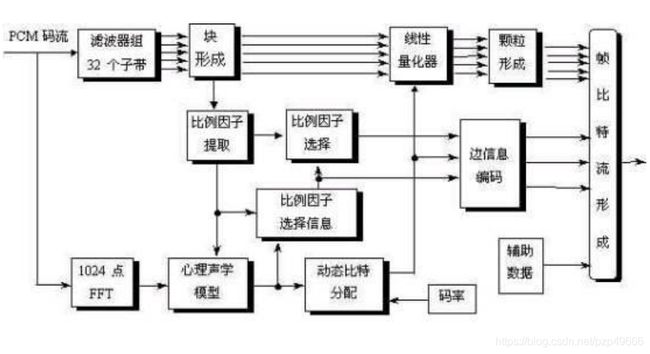
重点关注代码中如何实现双线流程的结合,多项滤波器之后提取比例因子给下面的心理声学模型线。比特分配后利用比特数完成上面流程的线性量化。
设计框架
变量设置
typedef double SBS[2][3][SCALE_BLOCK][SBLIMIT];
SBS *sb_sample;//子带样本12*32*3*2(立体声)
typedef double JSBS[3][SCALE_BLOCK][SBLIMIT];
JSBS *j_sample;
typedef double IN[2][HAN_SIZE];//2*512,FFT
IN *win_que;
typedef unsigned int SUB[2][3][SCALE_BLOCK][SBLIMIT];
SUB *subband;//子带
frame_info frame;//帧信息
frame_header header;//帧头部
char original_file_name[MAX_NAME_SIZE];//原文件名
char encoded_file_name[MAX_NAME_SIZE];
short **win_buf;
static short buffer[2][1152];
static unsigned int bit_alloc[2][SBLIMIT], scfsi[2][SBLIMIT];//比特分配,比例因子选择信息
static unsigned int scalar[2][3][SBLIMIT], j_scale[3][SBLIMIT];//比例因子,
static double smr[2][SBLIMIT], lgmin[2][SBLIMIT], max_sc[2][SBLIMIT];//信号掩蔽比,最小掩噪比,最大信噪比
// FLOAT snr32[32];
short sam[2][1344]; /* was [1056]; */
int model, nch, error_protection;
static unsigned int crc;
int sb, ch, adb;
unsigned long frameBits, sentBits = 0;
unsigned long num_samples;
int lg_frame;
int i;
/* Used to keep the SNR values for the fast/quick psy models */
static FLOAT smrdef[2][32];//快速算法中存放SNR
音频读入
get_audio
unsigned long
get_audio (FILE * musicin, short buffer[2][1152], unsigned long num_samples,
int nch, frame_header *header)//读取音频并返回读取长度
{
int j;
short insamp[2304];
unsigned long samples_read;
if (nch == 2) {
/* stereo判断是立体声 */
samples_read =
read_samples (musicin, insamp, num_samples, (unsigned long) 2304);
if (glopts.channelswap == TRUE) {
//为false则切换通道
for (j = 0; j < 1152; j++) {
buffer[1][j] = insamp[2 * j];
buffer[0][j] = insamp[2 * j + 1];
}
} else {
for (j = 0; j < 1152; j++) {
buffer[0][j] = insamp[2 * j];
buffer[1][j] = insamp[2 * j + 1];
}
}
} else if (glopts.downmix == TRUE) {
//低音混合
samples_read =
read_samples (musicin, insamp, num_samples, (unsigned long) 2304);
for (j = 0; j < 1152; j++) {
buffer[0][j] = 0.5 * (insamp[2 * j] + insamp[2 * j + 1]);
}
} else {
/* 单声道 */
samples_read =
read_samples (musicin, insamp, num_samples, (unsigned long) 1152);
for (j = 0; j < 1152; j++) {
buffer[0][j] = insamp[j];
/* buffer[1][j] = 0; don't bother zeroing this buffer. MFC Nov 99 */
}
}
return (samples_read);
}
read_samples
unsigned long
read_samples (FILE * musicin, short sample_buffer[2304],
unsigned long num_samples, unsigned long frame_size)//读取音频文件到buffer里
{
unsigned long samples_read;
static unsigned long samples_to_read;
static char init = TRUE;
if (init) {
samples_to_read = num_samples;
init = FALSE;//确定读取长度
}
if (samples_to_read >= frame_size)
samples_read = frame_size;//最多读取不超过2304
else
samples_read = samples_to_read;
if ((samples_read =
fread (sample_buffer, sizeof (short), (int) samples_read,
musicin)) == 0)
fprintf (stderr, "Hit end of audio data\n");//读完
/*
Samples are big-endian. If this is a little-endian machine
we must swap
*/
if (NativeByteOrder == order_unknown) {
NativeByteOrder = DetermineByteOrder ();
if (NativeByteOrder == order_unknown) {
fprintf (stderr, "byte order not determined\n");
exit (1);
}
}
if (NativeByteOrder != order_littleEndian || (glopts.byteswap == TRUE))
SwapBytesInWords (sample_buffer, samples_read);
if (num_samples != MAX_U_32_NUM)
samples_to_read -= samples_read;
if (samples_read < frame_size && samples_read > 0) {
/* fill out frame with zeros */
for (; samples_read < frame_size; sample_buffer[samples_read++] = 0);
samples_to_read = 0;
samples_read = frame_size;
}
return (samples_read);
}
available_bits函数:计算出可用比特数
多相滤波器结合窗函数和滤波
WindowFilterSubband函数:对buffer里数据分解进行子带滤波
for( gr = 0; gr < 3; gr++ )
for ( bl = 0; bl < 12; bl++ )
for ( ch = 0; ch < nch; ch++ )
WindowFilterSubband( &buffer[ch][gr * 12 * 32 + 32 * bl], ch,
&(*sb_sample)[ch][gr][bl][0] );//
计算比例因子
scale_factor_calc函数:使用二分法查找比例因子
pick_scale:每个字带3个样本选择三个比例因子
如果是立体声,则使用combine_LR函数结合左右声道后,查找比例因子
transmission_pattern函数:决定发送几个比例因子,并根据此填写比例因子选择信息
心理声学模型
根据model选择心理声学模型并计算SMR
以模型0为例
void psycho_0(double SMR[2][SBLIMIT], int nch, unsigned int scalar[2][3][SBLIMIT], FLOAT sfreq)//通过子带内最低ATH值和比例因子结合的方法,以简单方式计算出SMR
{
int ch, sb, gr;
int minscaleindex[2][SBLIMIT]; /* scale越小尺度因子越大 Smaller scale indexes mean bigger scalefactors */
static FLOAT ath_min[SBLIMIT];
int i;
static int init=0;
if (!init) {
FLOAT freqperline = sfreq/1024.0;
for (sb=0;sb<SBLIMIT;sb++) {
ath_min[sb] = 1000; /* set it huge */
}
/* 找到每个子带中最小的ATH */
for (i=0;i<512;i++) {
FLOAT thisfreq = i * freqperline;
FLOAT ath_val = ATH_dB(thisfreq, 0);
if (ath_val < ath_min[i>>4])
ath_min[i>>4] = ath_val;
}
init++;
}
/* 找到最小的比例因子index for each ch/sb */
for (ch=0;ch<nch;ch++)
for (sb=0;sb<SBLIMIT;sb++)
minscaleindex[ch][sb] = scalar[ch][0][sb];
for (ch=0;ch<nch;ch++)
for (gr=1;gr<3;gr++)
for (sb=0;sb<SBLIMIT;sb++)
if (minscaleindex[ch][sb] > scalar[ch][gr][sb])
minscaleindex[ch][sb] = scalar[ch][gr][sb];
/* Oh yeah. Fudge the hell out of the SMR calculations
by combining the scalefactor table index and the min ATH in that subband
There are probably more elegant/correct ways of combining these values,
but who cares? It works pretty well
MFC Mar 03 */
for (ch=0;ch<nch;ch++)
for (sb=0;sb<SBLIMIT;sb++)
SMR[ch][sb] = 2.0 * (30.0 - minscaleindex[ch][sb]) - ath_min[sb];
}
比特分配
根据心理声学模型和码率限制进行比特分配
main_bit_allocation (smr, scfsi, bit_alloc, &adb, &frame, &glopts);
“动态比特分配”:根据信号掩蔽比(SMR)确定子
带的量化级数(比特数,对总数据率进行比特分配。
原则:(1)SMR(dB) = SNRmax(dB) – MNRmin(dB)
(2)使各子带的量化信噪比SNR>最小信掩蔽比SMR,
将允许数据率分配给音频帧,再分给子带。音频帧的总
的供使用的数据率扣除用于传送比例因子、比例因子选
择信息、动态比特分配(BAL)、数据帧头与必要的差错
检测和考虑附加数据后,分配给音频取样值。
量化与装帧
encode_bit_alloc (bit_alloc, &frame, &bs);//比特分配编码
encode_scale (bit_alloc, scfsi, scalar, &frame, &bs);//比例因子编码
subband_quantization (scalar, *sb_sample, j_scale, *j_sample, bit_alloc,
*subband, &frame);//子带量化
sample_encoding (*subband, bit_alloc, &frame, &bs);//量化后编码
实验要求
输出音频的采样率和目标码率
if (frameNum == random_frame_number)
{
fprintf(trace_file, "采样率为:%.1fkhz \r\n", s_freq[header.version][header.sampling_frequency]);
fprintf(trace_file, "目标码率为:%dMbps \r\n", bitrate[header.version][header.bitrate_index]);
fprintf(trace_file, "可获得比特数为:%dbits\r\n", adb);
}
这一步在滤波前即可输出,此时音频读入后这些参数都已经算出
输出结果:
采样率为:48.0khz
目标码率为:192Mbps
可获得比特数为:4608bits
对于某个数据帧,输出该帧所分配的比特数,该帧的比例因子,该帧的比特分配结果
这一步在比特分配后可以输出
if (frameNum == random_frame_number)
{
fprintf(trace_file, "选择的数据帧为:%d \r\n", frameNum);
for (int k = 0; k < nch; k++)
{
fprintf(trace_file, "声道[%d] \r\n", k + 1);
for (int j = 0; j < frame.sblimit; j++)//子带总数
{
fprintf(trace_file, "子带[%d]: ", j + 1);
for (int m = 0; m < 3; m++)//每个子带有3个比例因子
{
fprintf(trace_file, "%d\t", scalar[k][m][j]);
}
fprintf(trace_file, "\r\n");
}
}
}
输出结果:代码中提示多余bit自动补0
声道[1]
子带[1]: 14 14 19
子带[2]: 27 27 27
子带[3]: 27 27 27
子带[4]: 31 31 31
子带[5]: 33 33 33
子带[6]: 34 34 34
子带[7]: 37 37 37
子带[8]: 37 37 37
子带[9]: 37 37 37
子带[10]: 39 39 39
子带[11]: 37 39 39
子带[12]: 39 41 41
子带[13]: 42 42 42
子带[14]: 41 41 41
子带[15]: 42 42 42
子带[16]: 42 42 42
子带[17]: 42 45 45
子带[18]: 44 44 44
子带[19]: 43 43 43
子带[20]: 44 44 44
子带[21]: 46 46 46
子带[22]: 46 46 46
子带[23]: 45 46 46
子带[24]: 46 46 46
子带[25]: 44 44 44
子带[26]: 47 47 47
子带[27]: 45 45 45
子带[28]: 0 0 0
子带[29]: 0 0 0
子带[30]: 0 0 0
子带[31]: 0 0 0
子带[32]: 0 0 0
声道[2]
子带[1]: 14 14 19
子带[2]: 26 26 26
子带[3]: 27 27 27
子带[4]: 30 30 30
子带[5]: 33 33 33
子带[6]: 34 34 34
子带[7]: 37 37 37
子带[8]: 37 37 37
子带[9]: 37 37 37
子带[10]: 39 39 39
子带[11]: 37 39 39
子带[12]: 39 39 39
子带[13]: 41 41 41
子带[14]: 41 41 41
子带[15]: 42 42 42
子带[16]: 43 43 43
子带[17]: 44 44 44
子带[18]: 45 45 45
子带[19]: 42 44 44
子带[20]: 44 44 44
子带[21]: 45 45 45
子带[22]: 46 46 46
子带[23]: 46 46 44
子带[24]: 45 45 45
子带[25]: 44 44 44
子带[26]: 43 43 43
子带[27]: 47 43 46
子带[28]: 0 0 0
子带[29]: 0 0 0
子带[30]: 0 0 0
子带[31]: 0 0 0
子带[32]: 0 0 0