Spring Security授权过程
文章目录
- 前言
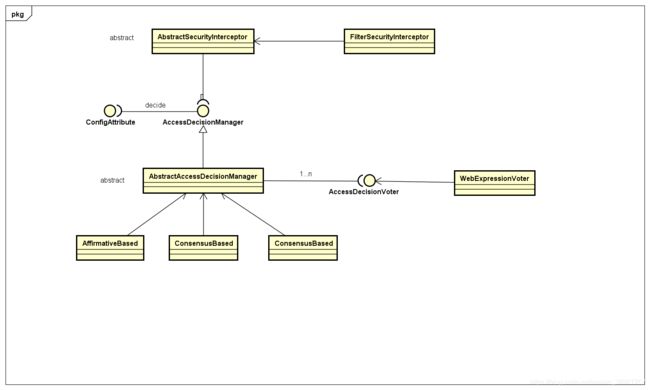
- 类图
- 源码分析
- UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
-
- AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
- UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
- AnonymousAuthenticationFilter
- ExceptionTranslationFilter
- FilterSecurityInterceptor
-
- before invocation: AccessDecisionManager
-
- attributes和object 是什么?
- AccessDecisionManager 是如何授权的?
-
- WebExpressionVoter.vote()
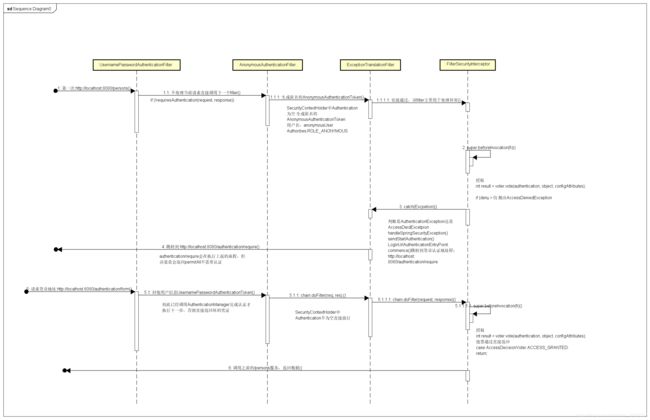
- 时序图
前言
本文是接上一章Spring Security源码分析一:Spring Security认证过程进一步分析Spring Security用户名密码登录授权是如何实现得;
类图
源码分析
如图所示,显示了登录认证过程中的 filters相关的调用流程,作者将几个自认为重要的 filters 标注了出来
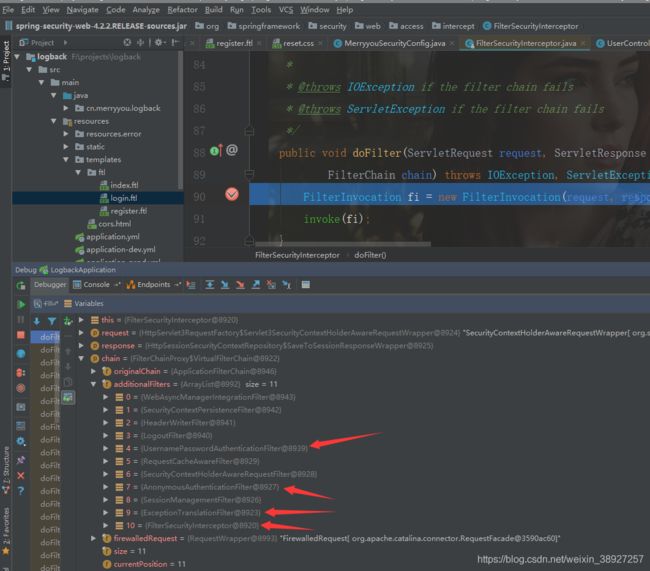
从图中可以看出执行的顺序。来看看几个作者认为比较重要的Filter 的处理逻辑,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter,AnonymousAuthenticationFilter,ExceptionTranslationFilter,FilterSecurityInterceptor以及相关的处理流程如下所述;
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
整个调用流程是,先调用其父类 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter.doFilter() 方法,然后再执行 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.attemptAuthentication() 方法进行验证;
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
#1.判断当前的filter是否可以处理当前请求,不可以的话则交给下一个filter处理
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Request is to process authentication");
}
Authentication authResult;
try {
#2.抽象方法由子类UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter实现
authResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authResult == null) {
// return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn't completed
// authentication
return;
}
#2.认证成功后,处理一些与session相关的方法
sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
logger.error(
"An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.",
failed);
#3.认证失败后的的一些操作
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
catch (AuthenticationException failed) {
// Authentication failed
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
// Authentication success
if (continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
#3. 认证成功后的相关回调方法 主要将当前的认证放到SecurityContextHolder中
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
}
整个程序的执行流程如下:
- 判断
filter是否可以处理当前的请求,如果不可以则放行交给下一个filter - 调用抽象方法
attemptAuthentication进行验证,该方法由子类UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter实现 - 认证成功以后,回调一些与
session相关的方法; - 认证成功以后,认证成功后的相关回调方法;认证成功以后,认证成功后的相关回调方法;
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Authentication success. Updating SecurityContextHolder to contain: "
+ authResult);
}
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
// Fire event
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(
authResult, this.getClass()));
}
successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult);
}
- 将当前认证成功的
Authentication放置到SecurityContextHolder中; - 将当前认证成功的
Authentication放置到SecurityContextHolder中; - 调用其它可扩展的
handlers继续处理该认证成功以后的回调事件;(实现AuthenticationSuccessHandler接口即可)
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
#1.判断请求的方法必须为POST请求
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
#2.从request中获取username和password
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
#3.构建UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(两个参数的构造方法setAuthenticated(false))
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
#4. 调用 AuthenticationManager 进行验证(子类ProviderManager遍历所有的AuthenticationProvider认证)
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
- 认证请求的方法必须为
POST - 从
request中获取username和password - 封装
Authenticaiton的实现类UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken,(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken调用两个参数的构造方法setAuthenticated(false)) - 调用
AuthenticationManager的authenticate方法进行验证;可参考ProviderManager部分;
AnonymousAuthenticationFilter
从上图中过滤器的执行顺序图中可以看出AnonymousAuthenticationFilter过滤器是在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter等过滤器之后,如果它前面的过滤器都没有认证成功,Spring Security则为当前的SecurityContextHolder中添加一个Authenticaiton的匿名实现类AnonymousAuthenticationToken;
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
#1.如果前面的过滤器都没认证通过,则SecurityContextHolder中Authentication为空
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
#2.为当前的SecurityContextHolder中添加一个匿名的AnonymousAuthenticationToken
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(
createAuthentication((HttpServletRequest) req));
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Populated SecurityContextHolder with anonymous token: '"
+ SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() + "'");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("SecurityContextHolder not populated with anonymous token, as it already contained: '"
+ SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() + "'");
}
}
chain.doFilter(req, res);
}
#3.创建匿名的AnonymousAuthenticationToken
protected Authentication createAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request) {
AnonymousAuthenticationToken auth = new AnonymousAuthenticationToken(key,
principal, authorities);
auth.setDetails(authenticationDetailsSource.buildDetails(request));
return auth;
}
/**
* Creates a filter with a principal named "anonymousUser" and the single authority
* "ROLE_ANONYMOUS".
*
* @param key the key to identify tokens created by this filter
*/
##.创建一个用户名为anonymousUser 授权为ROLE_ANONYMOUS
public AnonymousAuthenticationFilter(String key) {
this(key, "anonymousUser", AuthorityUtils.createAuthorityList("ROLE_ANONYMOUS"));
}
- 判断
SecurityContextHolder中Authentication为否为空; - 如果空则为当前的
SecurityContextHolder中添加一个匿名的AnonymousAuthenticationToken(用户名为anonymousUser的AnonymousAuthenticationToken)
ExceptionTranslationFilter
ExceptionTranslationFilter异常处理过滤器,该过滤器用来处理在系统认证授权过程中抛出的异常(也就是下一个过滤器FilterSecurityInterceptor),主要是 处理 AuthenticationException 和 AccessDeniedException 。
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
logger.debug("Chain processed normally");
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Try to extract a SpringSecurityException from the stacktrace
#.判断是不是AuthenticationException
Throwable[] causeChain = throwableAnalyzer.determineCauseChain(ex);
RuntimeException ase = (AuthenticationException) throwableAnalyzer
.getFirstThrowableOfType(AuthenticationException.class, causeChain);
if (ase == null) {
#. 判断是不是AccessDeniedException
ase = (AccessDeniedException) throwableAnalyzer.getFirstThrowableOfType(
AccessDeniedException.class, causeChain);
}
if (ase != null) {
handleSpringSecurityException(request, response, chain, ase);
}
else {
// Rethrow ServletExceptions and RuntimeExceptions as-is
if (ex instanceof ServletException) {
throw (ServletException) ex;
}
else if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
// Wrap other Exceptions. This shouldn't actually happen
// as we've already covered all the possibilities for doFilter
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
FilterSecurityInterceptor
此过滤器为认证授权过滤器链中最后一个过滤器,该过滤器之后就是请求真正的/persons 服务
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
FilterInvocation fi = new FilterInvocation(request, response, chain);
invoke(fi);
}
public void invoke(FilterInvocation fi) throws IOException, ServletException {
if ((fi.getRequest() != null)
&& (fi.getRequest().getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null)
&& observeOncePerRequest) {
// filter already applied to this request and user wants us to observe
// once-per-request handling, so don't re-do security checking
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
}
else {
// first time this request being called, so perform security checking
if (fi.getRequest() != null) {
fi.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
}
#1. before invocation重要
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(fi);
try {
#2. 可以理解开始请求真正的 /persons 服务
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
}
finally {
super.finallyInvocation(token);
}
#3. after Invocation
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
}
before invocation重要- 请求真正的
/persons服务 after Invocation
三个部分中,最重要的是 #1,该过程中会调用 AccessDecisionManager来验证当前已认证成功的用户是否有权限访问该资源;
before invocation: AccessDecisionManager
protected InterceptorStatusToken beforeInvocation(Object object) {
...
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource()
.getAttributes(object);
...
Authentication authenticated = authenticateIfRequired();
// Attempt authorization
try {
#1.重点
this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);
}
catch (AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) {
publishEvent(new AuthorizationFailureEvent(object, attributes, authenticated,accessDeniedException));
throw accessDeniedException;
}
...
}
authenticated就是当前认证的Authentication,那么object和attributes又是什么呢?
attributes和object 是什么?
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource()
.getAttributes(object);
调试
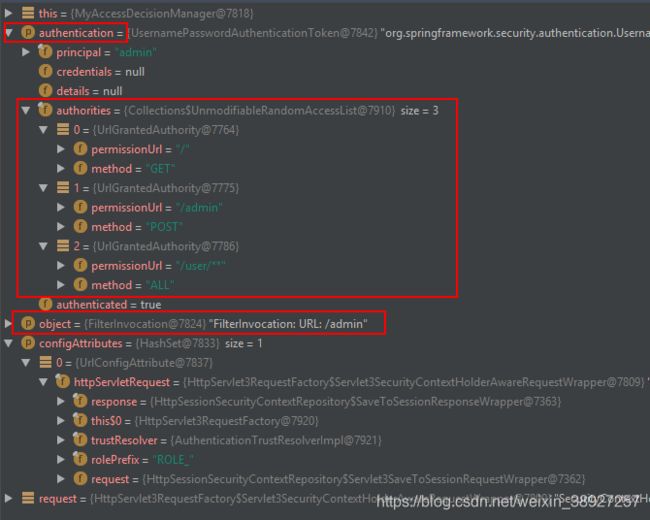
我们发现object为当前请求的 url:/persons, 那么getAttributes方法就是使用当前的访问资源路径去匹配我们自己定义的匹配规则。
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin()//使用表单登录,不再使用默认httpBasic方式
.loginPage(SecurityConstants.DEFAULT_UNAUTHENTICATION_URL)//如果请求的URL需要认证则跳转的URL
.loginProcessingUrl(SecurityConstants.DEFAULT_SIGN_IN_PROCESSING_URL_FORM)//处理表单中自定义的登录URL
.and()
.authorizeRequests().antMatchers(SecurityConstants.DEFAULT_UNAUTHENTICATION_URL,
SecurityConstants.DEFAULT_SIGN_IN_PROCESSING_URL_FORM,
SecurityConstants.DEFAULT_REGISTER_URL,
"/**/*.js",
"/**/*.css",
"/**/*.jpg",
"/**/*.png",
"/**/*.woff2")
.permitAll()//以上的请求都不需要认证
.anyRequest()//剩下的请求
.authenticated()//都需要认证
.and()
.csrf().disable()//关闭csrd拦截
;
}
0-7返回permitALL 即不需要认证 ,8 对应anyRequest返回authenticated 即当前请求需要认证;
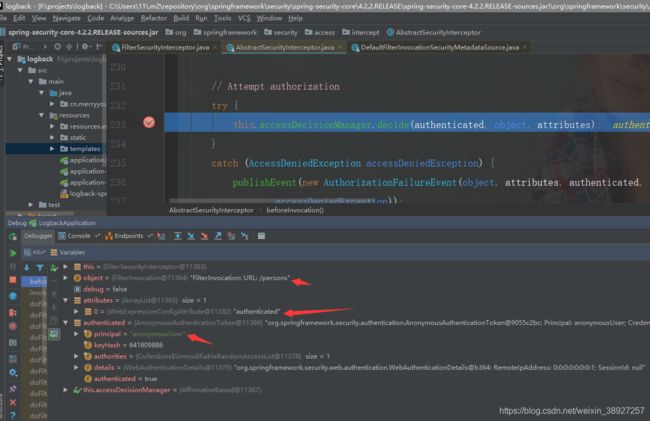
可以看到当前的authenticated为匿名AnonymousAuthentication用户名为anonymousUser
AccessDecisionManager 是如何授权的?
Spring Security默认使用AffirmativeBased实现 AccessDecisionManager的decide 方法来实现授权
public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes) throws AccessDeniedException {
int deny = 0;
#1.调用AccessDecisionVoter 进行vote(投票)
for (AccessDecisionVoter voter : getDecisionVoters()) {
int result = voter.vote(authentication, object, configAttributes);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Voter: " + voter + ", returned: " + result);
}
switch (result) {
#1.1只要有voter投票为ACCESS_GRANTED,则通过 直接返回
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_GRANTED://1
return;
@#1.2只要有voter投票为ACCESS_DENIED,则记录一下
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_DENIED://-1
deny++;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
if (deny > 0) {
#2.如果有两个及以上AccessDecisionVoter(姑且称之为投票者吧)都投ACCESS_DENIED,则直接就不通过了
throw new AccessDeniedException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractAccessDecisionManager.accessDenied", "Access is denied"));
}
// To get this far, every AccessDecisionVoter abstained
checkAllowIfAllAbstainDecisions();
}
- 调用
AccessDecisionVoter进行vote(投票) - 只要有投通过
(ACCESS_GRANTED)票,则直接判为通过。 - 如果没有投通过则
deny++,最后判断if(deny>0 抛出AccessDeniedException(未授权)
WebExpressionVoter.vote()
public int vote(Authentication authentication, FilterInvocation fi,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes) {
assert authentication != null;
assert fi != null;
assert attributes != null;
WebExpressionConfigAttribute weca = findConfigAttribute(attributes);
if (weca == null) {
return ACCESS_ABSTAIN;
}
EvaluationContext ctx = expressionHandler.createEvaluationContext(authentication,
fi);
ctx = weca.postProcess(ctx, fi);
return ExpressionUtils.evaluateAsBoolean(weca.getAuthorizeExpression(), ctx) ? ACCESS_GRANTED
: ACCESS_DENIED;
}
到此位置authentication当前用户信息,fl当前访问的资源路径及attributes当前资源路径的决策(即是否需要认证)。剩下就是判断当前用户的角色Authentication.authorites是否权限访问决策访问当前资源fi。