引子
性能测试在日常的开发工作中是常规需求,用来摸底服务的性能。
那么如何做性能测试?要么是通过编码的方式完成,写一堆脚本,用完即弃;要么是基于平台,在平台定义的流程中进行。对于后者,通常由于目标场景的复杂性,如部署特定的 workload、观测特定的性能项、网络访问问题等,往往导致性能测试平台要以高成本才能满足不断变化的开发场景的需求。
在云原生的背景下,是否可以更好解决这种问题?
先看两个 yaml 文件:
performance-test.yaml 描述了在 K8s 中的操作流程:
1.创建测试用的 Namespace
2.启动针对 Deployment 创建效率和创建成功率的监控
3.下述动作重复 N 次:① 使用 workload 模板创建 Deployment;② 等待 Deployment 变为 Ready
4.删除测试用的 Namespace
basic-1-pod-deployment.yaml 描述使用的 workload 模板
performance-test.yaml :
apiVersion: aliyun.com/v1alpha1
kind: Beidou
metadata:
name: performance
namespace: beidou
spec:
steps:
- name: "Create Namespace If Not Exits"
operations:
- name: "create namespace"
type: Task
op: CreateNamespace
args:
- name: NS
value: beidou
- name: "Monitor Deployment Creation Efficiency"
operations:
- name: "Begin To Monitor Deployment Creation Efficiency"
type: Task
op: DeploymentCreationEfficiency
args:
- name: NS
value: beidou
- name: "Repeat 1 Times"
type: Task
op: RepeatNTimes
args:
- name: TIMES
value: "1"
- name: ACTION
reference:
id: deployment-operation
- name: "Delete namespace"
operations:
- name: "delete namespace"
type: Task
op: DeleteNamespace
args:
- name: NS
value: beidou
- name: FORCE
value: "false"
references:
- id: deployment-operation
steps:
- name: "Prepare Deployment"
operations:
- name: "Prepare Deployment"
type: Task
op: PrepareBatchDeployments
args:
- name: NS
value: beidou
- name: NODE_TYPE
value: ebm
- name: BATCH_NUM
value: "1"
- name: TEMPLATE
value: "./templates/basic-1-pod-deployment.yaml"
- name: DEPLOYMENT_REPLICAS
value: "1"
- name: DEPLOYMENT_PREFIX
value: "ebm"
- name: "Wait For Deployments To Be Ready"
type: Task
op: WaitForBatchDeploymentsReady
args:
- name: NS
value: beidou
- name: TIMEOUT
value: "3m"
- name: CHECK_INTERVAL
value: "2s"
basic-1-pod-deployment.yaml:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: basic-1-pod
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: basic-1-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: basic-1-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: registry-vpc.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/xxx/nginx:1.17.9
imagePullPolicy: Always
resources:
limits:
cpu: 2
memory: 4Gi
然后通过一个命令行工具执行 performance-test.yaml:
$ beidou server -c ~/.kube/config services/performance-test.yaml1
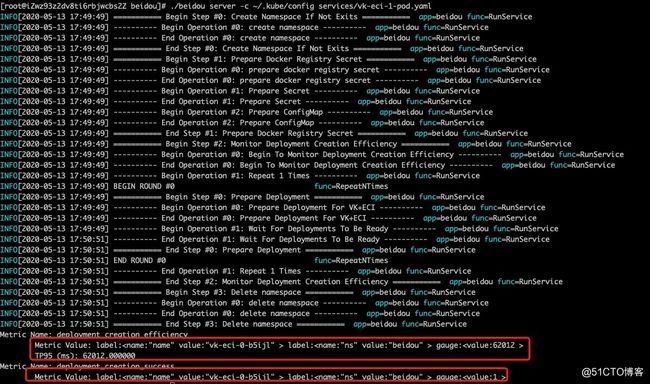
执行效果如下 (每个 Deployment 创建耗时,所有 Deployment 创建耗时的 TP95 值,每个 Deployment 是否创建成功):
这些 metrics 是按照 Prometheus 标准输出,可以被 Prometheus server 收集走,再结合 Grafana 可以可视化展示性能测试数据。
通过在 yaml 中表达想法,编排对 K8s 资源的操作、监控,再也不用为性能测试的实现头疼了
为什么要在 yaml 中编程?
性能测试、回归测试等对于服务质量保障有很大帮助,需要做,但常规的实现方法在初期需要投入较多的时间和精力,新增变更后维护成本比较高。
通常这个过程是以代码的方式实现原子操作,如创建 Deployment、检测 Pod 配置等,然后再组合原子操作来满足需求,如 创建 Deployment -> 等待 Deployment ready -> 检测 Pod 配置等。
有没有办法在实现的过程中既可以尽量低成本实现,又可以复用已有的经验?
可以将原子操作封装为原语,如 CreateDeployment、CheckPod,再通过 yaml 的结构表达流程,那么就可以通过 yaml 而非代码的方式描述想法,又可以复用他人已经写好的 yaml 文件来解决某类场景的需求。
即在 yaml 中编程,减少重复性代码工作,通过 声明式 的方式描述逻辑,并以 yaml 文件来满足场景级别的复用。
业界有很多种类型的 声明式操作 服务,如运维领域中的 Ansible、SaltStack,Kubernetes 中的Argo Workflow、clusterloader2。它们的思想整体比较类似,将高频使用的操作封装为原语,使用者通过原语来表述操作逻辑。
通过声明式的方法,将面向 K8s 的操作抽象成 yaml 中的关键词,在 yaml 中提供串行、并行等控制逻辑,那么就可以通过 yaml 文件完整描述想要进行的工作。
这种思想和 Argo Workflow 比较像,但粒度比 Argo 更细,关注在操作函数上:
下面简单描述该服务的设计和实现。
设计和实现
1. 服务形态
使用者在 yaml 中,通过 声明式 的方式描述操作逻辑;
以 all-in-one 的二进制工具或 Operator 的方式交付;
服务内置常见原语的实现,以关键字的方式在 yaml 中提供;
支持配置原生 K8s 资源。
2. 设计
该方案的核心在于配置管理的设计,将操作流程配置化,自上而下有如下概念:
Service:Modules 或 Tasks 的编排;
Module:一种任务场景,是操作单元的集合(其中包含 templates/ 目录,表征模板文件的集合,可用来配置 K8s 原生资源);
Task:操作单元,使用 plugin 及参数执行操作;
Plugin:操作指令,类似开发语言中的函数。
抽象目标场景中的通用操作,这些通用操作即为可在 yaml 中使用的原语,对应上述 Plugin:
K8s 相关
CreateNamespace
DeleteNamespace
PrepareSecret
PrepareConfigMap
PrepareBatchDeployments
WaitForBatchDeploymentsReady
etc.
观测性相关
DeploymentCreationEfficiency
PodCreationEfficiency
etc.
检测项相关
CheckPodAnnotations
CheckPodObjectInfo
CheckPodInnerStates
etc.
控制语句相关
RepeatNTimes
etc.
上述 4 个概念的关系如下:
示例可参见文章开头的 yaml 文件,对应形式二。
3. 核心实现
CRD 设计:
package v1alpha1
import (
corev1 "k8s.io/api/core/v1"
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
)
// BeidouType is the type related to Beidou execution.
type BeidouType string
const (
// BeidouTask represents the Task execution type.
BeidouTask BeidouType = "Task"
)
// +genclient
// +k8s:deepcopy-gen:interfaces=k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime.Object
// Beidou represents a crd used to describe serices.
type Beidou struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=metadata"`
Spec BeidouSpec `json:"spec,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=spec"`
Status BeidouStatus `json:"status,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=status"`
}
// BeidouSpec is the spec of a Beidou.
type BeidouSpec struct {
Steps []BeidouStep `json:"steps" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=steps"`
References []BeidouReference `json:"references" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=references"`
}
// BeidouStep is the spec of step.
type BeidouStep struct {
Name string `json:"name" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=name"`
Operations []BeidouOperation `json:"operations" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=operations"`
}
// BeidouOperation is the spec of operation.
type BeidouOperation struct {
Name string `json:"name" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=name"`
Type BeidouType `json:"type" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=type"`
Op string `json:"op" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=op"`
Args []BeidouArg `json:"args" protobuf:"bytes,4,opt,name=args"`
}
// BeidouArg is the spec of arg.
type BeidouArg struct {
Name string `json:"name" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=name"`
Value string `json:"value,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=value"`
Reference BeidouOperationReference `json:"reference,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=reference"`
Tolerations []corev1.Toleration `json:"tolerations,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,4,opt,name=tolerations"`
Checking []string `json:"checking,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,5,opt,name=checking"`
}
// BeidouOperationReference is the spec of operation reference.
type BeidouOperationReference struct {
ID string `json:"id" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=id"`
}
// BeidouReference is the spec of reference.
type BeidouReference struct {
ID string `json:"id" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=id"`
Steps []BeidouStep `json:"steps" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=steps"`
}
// BeidouStatus represents the current state of a Beidou.
type BeidouStatus struct {
Message string `json:"message" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=message"`
}
// +k8s:deepcopy-gen:interfaces=k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime.Object
// BeidouList is a collection of Beidou.
type BeidouList struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
metav1.ListMeta `json:"metadata" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=metadata"`
Items []Beidou `json:"items" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=items"`
}
核心流程:
// ExecSteps executes steps.
func ExecSteps(ctx context.Context, steps []v1alpha1.BeidouStep, references []v1alpha1.BeidouReference) error {
logger, _ := ctx.Value(CtxLogger).(*log.Entry)
var hasMonitored bool
for i, step := range steps {
for j, op := range step.Operations {
switch op.Op {
case "DeploymentCreationEfficiency":
if !hasMonitored {
defer func() {
err := monitor.Output()
if err != nil {
logger.Errorf("Failed to output: %s", err)
}
}()
}
hasMonitored = true
}
err := ExecOperation(ctx, op, references)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to run operation %s: %s", op.Name, err)
}
}
}
return nil
}
// ExecOperation executes operation.
func ExecOperation(ctx context.Context, op v1alpha1.BeidouOperation, references []v1alpha1.BeidouReference) error {
switch op.Type {
case v1alpha1.BeidouTask:
if !tasks.IsRegistered(op.Op) {
return ErrNotRegistered
}
if !tasks.DoesSupportReference(op.Op) {
return ExecTask(ctx, op.Op, op.Args)
}
return ExecTaskWithRefer(ctx, op.Op, op.Args, references)
}
return nil
}
// ExecTask executes a task.
func ExecTask(ctx context.Context, opname string, args []v1alpha1.BeidouArg) error {
switch opname {
case tasks.CreateNamespace:
var ns string
for _, arg := range args {
switch arg.Name {
case "NS":
ns = arg.Value
}
}
return op.CreateNamespace(ctx, ns)
// ...
}
// ...
}
// ExecTaskWithRefer executes a task with reference.
func ExecTaskWithRefer(ctx context.Context, opname string, args []v1alpha1.BeidouArg, references []v1alpha1.BeidouReference) error {
switch opname {
case tasks.RepeatNTimes:
var times int
var steps []v1alpha1.BeidouStep
var err error
for _, arg := range args {
switch arg.Name {
case "TIMES":
times, err = strconv.Atoi(arg.Value)
if err != nil {
return ErrParseArgs
}
case "ACTION":
for _, refer := range references {
if refer.ID == arg.Reference.ID {
steps = refer.Steps
break
}
}
}
}
return RepeatNTimes(ctx, times, steps)
}
return ErrNotImplemented
}
操作原语的实现示例:
// PodAnnotations is an operation used to check whether annotations of Pod are expected.
func PodAnnotations(ctx context.Context, data PodAnnotationsData) error {
kclient, ok := ctx.Value(tasks.KubernetesClient).(kubernetes.Interface)
if !ok {
return tasks.ErrNoKubernetesClient
}
pods, err := kclient.CoreV1().Pods(data.Namespace).List(metav1.ListOptions{})
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to list pods in ns %s: %s", data.Namespace, err)
}
for _, pod := range pods.Items {
if pod.Annotations == nil {
return fmt.Errorf("pod %s in ns %s has no annotations", pod.Name, data.Namespace)
}
for _, annotation := range data.Exists {
if _, exists := pod.Annotations[annotation]; !exists {
return fmt.Errorf("annotation %s does not exist in pod %s in ns %s", annotation, pod.Name, data.Namespace)
}
}
for k, v := range data.Equal {
if pod.Annotations[k] != v {
return fmt.Errorf("value of annotation %s is not %s in pod %s in ns %s", k, v, pod.Name, data.Namespace)
}
}
}
return nil
}
后续
目前阿里云容器服务团队内部已经实现了初版,已用于部分云产品的内部性能测试以及常规的回归测试,很大程度上提升了我们的工作效率。
在 yaml 中编程,是对云原生场景下声明式操作的体现,也是对声明式服务的一种实践。对于常规工作场景中重复编码或重复操作,可考虑类似的方式进行满足。
最后
感谢大家看到这里,文章有不足,欢迎大家指出;如果你觉得写得不错,那就给我一个赞吧。
也欢迎大家关注我的公众号:程序员麦冬,麦冬每天都会分享java相关技术文章或行业资讯,欢迎大家关注和转发文章!