前言
由于刚写项目不久,在写 web 后台接口时,经常会对前端传入的参数进行一些规则校验,如果入参较少还好,一旦需要校验的参数比较多,那么使用 if 校验会带来大量的重复性工作,并且代码看起来会非常冗余,所以我首先想到能否通过一些手段改进这点,让 Controller 层减少参数校验的冗余代码,提升代码的可阅读性。
经过阅读他人的代码,发现使用 annotation 注解是一个比较方便的手段,SpringBoot 自带的 @RequestParam 注解只会校验请求中该参数是否存在,但是该参数是否符合一些规格比如不为 null 且不为空就无法进行判断的,所以我们可以尝试一下增强请求参数中的注解。
准备工作
有了前面的思路,我们先搭一个架子出来。
- SpringBoot 2.3.5.REALEASE
- JDK 1.8
pom.xml 文件如下:
4.0.0 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-parent 2.3.5.RELEASE cn.bestzuo springboot-annotation 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT springboot-annotation Demo project for Spring Boot 1.8 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-web org.projectlombok lombok true org.aspectj aspectjweaver 1.8.5 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-test test org.junit.vintage junit-vintage-engine org.springframework.boot spring-boot-maven-plugin
其中 aspectjweaver 用于引入 AOP 的相关的注解,如 @Aspect、@Pointcut 等.
使用自定义注解实现统一非空校验
总体思路:自定义一个注解,对必填的参数加上该注解,然后定义一个切面,校验该参数是否为空,如果为空则抛出自定义的异常,该异常被自定义的异常处理器捕获,然后返回相应的错误信息。
1.自定义注解
创建一个名为 ParamCheck 的注解,代码如下:
package cn.bestzuo.springbootannotation.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* 参数不能为空注解,作用于方法参数上
*
* @author zuoxiang
* @since 2020-11-11
*/
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ParamCheck {
/**
* 是否非空,默认不能为空
*/
boolean notNull() default true;
}
其中 @Target 注解中的 ElementType.PARAMETER 表示该注解的作用范围,我们查看源码可以看到,注解的作用范围定义比较广泛,可以作用于方法、参数、构造方法、本地变量、枚举等等。
public enum ElementType {
/** Class, interface (including annotation type), or enum declaration */
TYPE,
/** Field declaration (includes enum constants) */
FIELD,
/** Method declaration */
METHOD,
/** Formal parameter declaration */
PARAMETER,
/** Constructor declaration */
CONSTRUCTOR,
/** Local variable declaration */
LOCAL_VARIABLE,
/** Annotation type declaration */
ANNOTATION_TYPE,
/** Package declaration */
PACKAGE,
/**
* Type parameter declaration
*
* @since 1.8
*/
TYPE_PARAMETER,
/**
* Use of a type
*
* @since 1.8
*/
TYPE_USE
}
当然,我们定义的注解可以扩展,不仅仅去校验参数是否为空,比如我们可以增加字符串长度的校验。
2.自定义异常类
我们在这里自定义异常的原因,是为了配合自定义注解使用,一旦校验出不符合我们自定义注解规格的参数,可以直接抛出自定义异常返回。代码如下:
package cn.bestzuo.springbootannotation.exception;
public class ParamIsNullException extends RuntimeException {
private final String parameterName;
private final String parameterType;
public ParamIsNullException(String parameterName, String parameterType) {
super("");
this.parameterName = parameterName;
this.parameterType = parameterType;
}
/**
* 重写了该方法
*
* @return 异常消息通知
*/
@Override
public String getMessage() {
return "Required " + this.parameterType + " parameter \'" + this.parameterName + "\' must be not null !";
}
public final String getParameterName() {
return this.parameterName;
}
public final String getParameterType() {
return this.parameterType;
}
}
该异常继承 RuntimeException,并定义了两个成员属性、重写了 getMessage() 方法
之所以自定义该异常,而不用现有的 org.springframework.web.bind.MissingServletRequestParameterException 类,是因为 MissingServletRequestParameterException为Checked 异常,在动态代理过程中,很容易引发 java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException 异常。
3.自定义 AOP
代码如下:
package cn.bestzuo.springbootannotation.aop;
import cn.bestzuo.springbootannotation.annotation.ParamCheck;
import cn.bestzuo.springbootannotation.exception.ParamIsNullException;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Component
@Aspect
public class ParamCheckAop {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ParamCheckAop.class);
/**
* 定义有一个切入点,范围为 controller 包下的类
*/
@Pointcut("execution(public * cn.bestzuo.controller..*.*(..))")
public void checkParam() {
}
@Before("checkParam()")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
}
/**
* 检查参数是否为空
*
* @param pjp 连接点
* @return 对象
* @throws Throwable 异常
*/
@Around("checkParam()")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
MethodSignature signature = ((MethodSignature) pjp.getSignature());
//得到拦截的方法
Method method = signature.getMethod();
//获取方法参数注解,返回二维数组是因为某些参数可能存在多个注解
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
if (parameterAnnotations.length == 0) {
return pjp.proceed();
}
//获取方法参数名
String[] paramNames = signature.getParameterNames();
//获取参数值
Object[] paramValues = pjp.getArgs();
//获取方法参数类型
Class[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < parameterAnnotations.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < parameterAnnotations[i].length; j++) {
//如果该参数前面的注解是ParamCheck的实例,并且notNull()=true,则进行非空校验
if (parameterAnnotations[i][j] != null && parameterAnnotations[i][j] instanceof ParamCheck && ((ParamCheck) parameterAnnotations[i][j]).notNull()) {
paramIsNull(paramNames[i], paramValues[i], parameterTypes[i] == null ? null : parameterTypes[i].getName());
break;
}
}
}
return pjp.proceed();
}
/**
* 在切入点return内容之后切入内容(可以用来对处理返回值做一些加工处理)
*
* @param joinPoint 连接点
*/
@AfterReturning("checkParam()")
public void doAfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
}
/**
* 参数非空校验,如果参数为空,则抛出ParamIsNullException异常
*
* @param paramName 参数名称
* @param value 参数值
* @param parameterType 参数类型
*/
private void paramIsNull(String paramName, Object value, String parameterType) {
if (value == null || "".equals(value.toString().trim())) {
throw new ParamIsNullException(paramName, parameterType);
}
}
}
4.全局异常处理器
该异常处理器捕获在 ParamCheckAop 类中抛出的 ParamIsNullException 异常,并进行处理,代码如下:
import cn.bestzuo.springbootannotation.common.Result;
import cn.bestzuo.springbootannotation.enums.EnumResultCode;
import cn.bestzuo.springbootannotation.utils.ResponseMsgUtil;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MissingServletRequestParameterException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GlobalExceptionHandler.class);
/**
* 参数为空异常处理
*
* @param ex 异常
* @return 返回的异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler({MissingServletRequestParameterException.class, ParamIsNullException.class})
public Result requestMissingServletRequest(Exception ex) {
LOGGER.error("request Exception:", ex);
return ResponseMsgUtil.builderResponse(EnumResultCode.FAIL.getCode(), ex.getMessage(), null);
}
/**
* 特别说明: 可以配置指定的异常处理,这里处理所有
*
* @param request 请求
* @param e 异常体
* @return 返回的异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
public Result errorHandler(HttpServletRequest request, Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("request Exception:", e);
return ResponseMsgUtil.exception();
}
}
5.测试
首先定义一个 Controller 进行测试:
@RestController
public class HelloController {
/**
* 测试@RequestParam注解
*
* @param name 测试参数
* @return 包装结果
*/
@GetMapping("/hello1")
public Result hello1(@RequestParam String name) {
return ResponseMsgUtil.builderResponse(EnumResultCode.SUCCESS.getCode(), "请求成功", "Hello," + name);
}
/**
* 测试@ParamCheck注解
*
* @param name 测试参数
* @return 包装结果
*/
@GetMapping("/hello2")
public Result hello2(@ParamCheck String name) {
return ResponseMsgUtil.builderResponse(EnumResultCode.SUCCESS.getCode(), "请求成功", "Hello," + name);
}
/**
* 测试@ParamCheck与@RequestParam一起时
*
* @param name 测试参数
* @return 包装结果
*/
@GetMapping("/hello3")
public Result hello3(@ParamCheck @RequestParam String name) {
return ResponseMsgUtil.builderResponse(EnumResultCode.SUCCESS.getCode(), "请求成功", "Hello," + name);
}
}
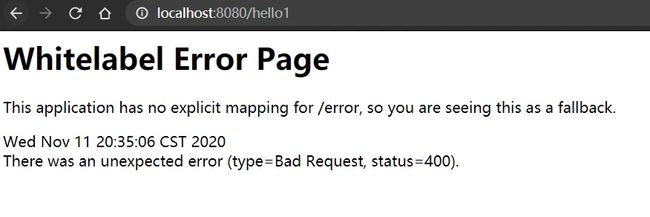
测试访问 http://localhost:8080/hello1,此时只有 @RequestParam 注解,如果不加 name 参数,会请求得到一个异常:
并且控制台会报 MissingServletRequestParameterException: Required String parameter 'name' is not present] 异常
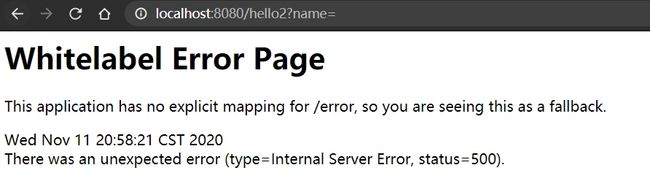
如果访问 http://localhost:8080/hello2?name=,此时使用的是我们自定义的 @ParamCheck 注解,此时没有参数输入,那么也会捕获输入的异常:
如果访问 http://localhost:8080/hello3?name=,此时既有参数存在校验,又有我们自定义的 ParamCheck 不为空校验,所以此时访问不加参数会抛出异常:
控制台抛出我们自定义的异常:
测试总结:
当参数名为空时,分别添加两个注解的接口都会提示参数不能为空
当参数名不为空,值为空时,@RequestParam注解不会报错,但@ParamCheck注解提示参数'name'的值为空
6.总结
- 经过以上的测试也验证了 @RequestParam 只会验证对应的参数是否存在,而不会验证值是否为空
- ParamCheck 还可以进行拓展,比如参数值长度、是否含有非法字符等校验
7.代码附录
上述使用到的代码:
package cn.bestzuo.springbootannotation.common; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; @Getter @Setter public class Result{ private Integer resCode; private String resMsg; private T data; }
package cn.bestzuo.springbootannotation.enums;
/**
* 枚举参数结果
*
* @author zuoxiang
* @since 2020-11-11
*/
public enum EnumResultCode {
SUCCESS(200),
FAIL(400),
UNAUTHORIZED(401),
NOT_FOUND(404),
INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR(500);
private final int code;
EnumResultCode(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
}
package cn.bestzuo.springbootannotation.utils;
import cn.bestzuo.springbootannotation.common.Result;
import cn.bestzuo.springbootannotation.enums.EnumResultCode;
public class ResponseMsgUtil {
/**
* 根据消息码等生成接口返回对象
*
* @param code 结果返回码
* @param msg 结果返回消息
* @param data 数据对象
* @param 泛型
* @return 包装对象
*/
public static Result builderResponse(int code, String msg, T data) {
Result res = new Result<>();
res.setResCode(code);
res.setResMsg(msg);
res.setData(data);
return res;
}
/**
* 请求异常返回结果
*
* @param 泛型
* @return 包装对象
*/
public static Result exception() {
return builderResponse(EnumResultCode.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.getCode(), "服务异常", null);
}
}
以上就是SpringBoot中自定义注解实现参数非空校验的示例的详细内容,更多关于SpringBoot 参数非空校验的资料请关注脚本之家其它相关文章!