0、引言
不知道大家有没有留意过,目前主流的网站,如果请求出错了,一般都会有友好提示页,比如 Bilibili ,访问一个不存在的页面,返回提示页:
这样的页面显然比返回一堆错误代码,甚至堆栈信息要友好多了。
本文将使用 SpringBoot 2.3.3 + Thymeleaf 来演示如何在请求出错的情况下返回友好提示页面。
1、搭建项目
作为演示项目,我们只需要 Web 和 Thymleaf 组件即可,pom 中依赖如下:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.junit.vintage
junit-vintage-engine
搭建完项目,写个简单的 HelloWorldController,环境就算是搭建好了
@Controller
public class HelloWorldController {
@GetMapping("hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
}2.定制错误页面
请求已定义的 /hello 接口自然是没什么问题,但此时如果请求一个不存在的 URL 呢?比如/hi ,由于并没有定义此接口,SpringBoot 将返回一个默认的错误页面: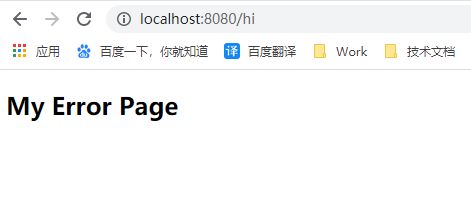
简单解释一下这个页面的来历:
当 SpringBoot 启动的时候,有一个配置类: ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration 里面会配置一些错误处理,其中就包括请求出错时的默认页面。
相关代码如下:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "server.error.whitelabel", name = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
@Conditional(ErrorTemplateMissingCondition.class)
protected static class WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration {
private final StaticView defaultErrorView = new StaticView();
@Bean(name = "error")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "error")
public View defaultErrorView() {
return this.defaultErrorView;
}
// 省略无关代码
}
}可以看到,属性server.error.whitelabel.enabled控制着这个类是否自动装配,而它的默认值是true
可以直接在 yml 中将他禁用掉:
server:
error:
whitelabel:
enabled: false此时再访问 未定义的/hi接口,将会收到 Tomcat 返回的默认页面 ,提示 HTTP Status 404 – Not Found.
这是因为我们禁用了默认的错误页面,并且没指定新的错误页面, Thymleaf 不知道该渲染什么页面了,从后端的报错信息中也能看到此提示:
Caused by: org.thymeleaf.exceptions.
TemplateInputException: Error resolving template [error],
template might not exist or might not be accessible by any of the configured Template ResolversThymeleaf 没找到 error 模板,于是报错了,可以在 templates目录下,新建一个error.html模板,再次请求未定义的/hi接口,就会得到自定义的错误页面:
到目前为止,一个简单的全局错误页面就搞定了。
不过这个方法虽然简单,其局限性也是显而易见的,一切都是写死的,它没法在出错时执行业务逻辑。
3.自定义 ErrorController
想要在出错时根据错误类型进行特殊处理,就需要自定义一个 ErrorController来实现了。
这里展示如何根据不同的错误类型返回不同的页面:
@Controller
public class CustomErrorController implements ErrorController {
@RequestMapping("/error")
public String handleError(HttpServletRequest request) {
Object status = request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_STATUS_CODE);
if (status != null) {
Integer statusCode = Integer.valueOf(status.toString());
if (statusCode == HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.value()) {
return "my404";
} else if (statusCode == HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value()) {
return "my401";
} else if (statusCode == HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value()) {
return "my500";
}
// 这里后期可以扩展其他错误页面
}
return "my404";
}只需要实现handlerError方法,即可处理相应的业务逻辑,如果有需要的话,也可以在里面组装 model 数据。
解释一下为什么有 @RequestMapping("/error"),因为默认的错误处理路径就是 /error,在ErrorProperties.java中定义如下:
public class ErrorProperties {
/**
- Path of the error controller.
*/
@Value("${error.path:/error}")
private String path = "/error";
// 省略...
}
我们完全可以根据需要去修改这个路径,只需要在 yml 里配置一下,并保持 yml 的设置和 ErrorController实现类的@RequestMapping值一致即可
server:
error:
# 使用默认的 /error
path: /error
whitelabel:
enabled: false至此,一个可编写业务代码的自定义错误页面就编写完成了。
4.总结
本文采用两种不同的方式,介绍了自定义错误页面的实现:
- 默认 error 模板
- 自定义 ErrorController
文中相关代码已上传至课代表的 github
如果本文对你有帮助,欢迎收藏、分享、在看三连
关注 Java课代表,获取最新 Java 干货![]()