翻译 | 《JavaScript Everywhere》第24章 移动应用程序认证
写在最前面
大家好呀,我是毛小悠,是一位前端开发工程师。正在翻译一本英文技术书籍。
为了提高大家的阅读体验,对语句的结构和内容略有调整。如果发现本文中有存在瑕疵的地方,或者你有任何意见或者建议,可以在评论区留言,或者加我的微信:code_maomao,欢迎相互沟通交流学习。
(σ゚∀゚)σ..:*☆哎哟不错哦
第24章 移动应用程序认证
如果你曾经与亲戚同住过,或者在度假的旅馆里或租了带家具的公寓,那么你就会体验到被不属于你的事物包围着是什么样的感受。
在这些类型的环境中可能很难感到安定,不想将某些东西放到适当的位置或弄乱它们。当我处于这些情况下时,无论房东多么友善或包容,这种所有权的缺乏使我处于烦躁的边缘状态。我能说什么,我只是不舒服,除非我可以不用杯垫放玻璃杯。
由于无法自定义或读取特定于用户的数据,我们的应用可能会给用户带来同样的不适感。他们的笔记与其他所有人的笔记混在一起,而不是使应用程序真正属于自己。在本章中,我们将向我们的应用程序添加身份验证。为此,我们将介绍一个身份验证路由流,使用Expo的SecureStore存储令牌数据,在React Native中创建文本表单以及执行身份验证GraphQL请求。
认证路由流程
让我们从创建身份验证流程开始。当用户首次访问我们的应用程序时,我们将为他们显示登录界面。当用户登录时,我们会将令牌存储在设备上,从而允许他们绕过将来应用程序使用时的登录界面。我们还将添加一个设置界面,用户可以在其中单击按钮以退出应用程序,并从其设备中删除令牌。
为此,我们将添加几个新界面:
authloading.js
这将是一个插页式界面,用户将不会与之互动。
打开应用程序后,我们将使用界面检查令牌是否存在,并将用户导航到登录界面或应用程序内容。
signin.js
这是用户可以登录其帐户的界面。
成功登录后,我们将令牌存储在设备上。
settings.js
在设置界面中,用户将能够单击按钮并注销该应用程序。
一旦注销,它们将被路由回登录界面。
使用现有帐户
在本章的后面,我们将添加通过该应用程序创建帐户的功能。如果还没有,直接通过你的API实例的GraphQL Playground或Web应用程序界面创建一个帐户将很有用。
为了存储和使用令牌,我们将使用Expo的SecureStore库。
我发现SecureStore是在设备上本地加密和存储数据的直接方法。对于iOS设备,SecureStore使用内置的钥匙串服务,而在Android上,它使用操作系统的“共享首选项”,并使用Keystore加密数据。
所有这些都是在后台进行的,这使我们能够简单地存储和检索数据。
首先,我们将创建登录界面。目前,我们的登录界面将包含一个Button组件,当按下该按钮时,它将存储令牌。让我们在src/screens/signin.js中创建一个新的界面组件,导入依赖项:
import React from 'react';
import { View, Button, Text } from 'react-native';
import * as SecureStore from 'expo-secure-store';
const SignIn = props => {
return (
);
}
SignIn.navigationOptions = {
title: 'Sign In'
};
export default SignIn;接下来,让我们在src/screens/authloading.js中创建我们的身份验证加载组件,该组件现在仅显示一个加载指示器:
import React, { useEffect } from 'react';
import * as SecureStore from 'expo-secure-store';
import Loading from '../components/Loading';
const AuthLoading = props => {
return 最后,我们可以在src/screens/settings.js中创建设置界面:
import React from 'react';
import { View, Button } from 'react-native';
import * as SecureStore from 'expo-secure-store';
const Settings = props => {
return (
);
};
Settings.navigationOptions = {
title: 'Settings'
};
export default Settings;编写完这些组件后,我们将更新路由以处理经过身份验证和未经身份验证的状态。在src/screens/index.js中,将新界面添加到我们的import语句列表中,如下所示:
import AuthLoading from './authloading';
import SignIn from './signin';
import Settings from './settings';我们还需要更新我们的react-navigation依赖项,以包括createSwitchNavigator,这使我们可以一次显示一个界面并在它们之间切换。
当用户导航并且不提供向后导航选项时,SwitchNavigator会将路由重置为默认状态。
import { createAppContainer, createSwitchNavigator } from 'react-navigation';我们可以为我们的身份验证和设置界面创建一个新的StackNavigator。
这将使我们能够在将来或需要时添加子导航界面:
const AuthStack = createStackNavigator({
SignIn: SignIn
});
const SettingsStack = createStackNavigator({
Settings: Settings
});然后,我们将设置界面添加到底部的TabNavigator。
选项卡的其余导航设置将保持不变:
const TabNavigator = createBottomTabNavigator({
FeedScreen: {
// ...
},
MyNoteScreen: {
// ...
},
FavoriteScreen: {
// ...
},
Settings: {
screen: Settings,
navigationOptions: {
tabBarLabel: 'Settings',
tabBarIcon: ({ tintColor }) => (
现在,我们可以通过定义要切换的界面并设置默认界面AuthLoading来创建SwitchNavigator。然后,我们将现有的导出语句替换为导出SwitchNavigator的语句:
const SwitchNavigator = createSwitchNavigator(
{
AuthLoading: AuthLoading,
Auth: AuthStack,
App: TabNavigator
},
{
initialRouteName: 'AuthLoading'
}
);
export default createAppContainer(SwitchNavigator);总之,我们的src/screens/index.js文件将显示如下:
import React from 'react';
import { Text, View, ScrollView, Button } from 'react-native';
import { createAppContainer, createSwitchNavigator } from 'react-navigation';
import { createBottomTabNavigator } from 'react-navigation-tabs';
import { createStackNavigator } from 'react-navigation-stack';
import { MaterialCommunityIcons } from '@expo/vector-icons';
import Feed from './feed';
import Favorites from './favorites';
import MyNotes from './mynotes';
import Note from './note';
import SignIn from './signin';
import AuthLoading from './authloading';
import Settings from './settings';
const AuthStack = createStackNavigator({
SignIn: SignIn,
});
const FeedStack = createStackNavigator({
Feed: Feed,
Note: Note
});
const MyStack = createStackNavigator({
MyNotes: MyNotes,
Note: Note
});
const FavStack = createStackNavigator({
Favorites: Favorites,
Note: Note
});
const SettingsStack = createStackNavigator({
Settings: Settings
});
const TabNavigator = createBottomTabNavigator({
FeedScreen: {
screen: FeedStack,
navigationOptions: {
tabBarLabel: 'Feed',
tabBarIcon: ({ tintColor }) => (
现在,当我们浏览应用程序时,由于AuthLoading路由是初始界面,因此我们只会看到正在加载界面。让我们对其进行更新,以便在加载界面时检查应用程序的SecureStore中是否存在令牌值。如果令牌存在,我们将引导用户到主应用程序界面。但是,如果不存在令牌,则应将用户路由到登录界面。让我们更新src/screens/authloading.js来执行此检查:
import React, { useEffect } from 'react';
import * as SecureStore from 'expo-secure-store';
import Loading from '../components/Loading';
const AuthLoadingScreen = props => {
const checkLoginState = async () => {
// retrieve the value of the token
const userToken = await SecureStore.getItemAsync('token');
// navigate to the app screen if a token is present
// else navigate to the auth screen
props.navigation.navigate(userToken ? 'App' : 'Auth');
};
// call checkLoginState as soon as the component mounts
useEffect(() => {
checkLoginState();
});
return 进行此更改后,由于没有令牌,因此当我们加载应用程序时,我们现在应该被路由到登录界面。现在,让我们更新登录界面以存储通用令牌,并在用户按下按钮时导航到应用程序(图24-1):
import React from 'react';
import { View, Button, Text } from 'react-native';
import * as SecureStore from 'expo-secure-store';
const SignIn = props => {
// store the token with a key value of `token`
// after the token is stored navigate to the app's main screen
const storeToken = () => {
SecureStore.setItemAsync('token', 'abc').then(
props.navigation.navigate('App')
);
};
return (
);
};
SignIn.navigationOptions = {
title: 'Sign In'
};
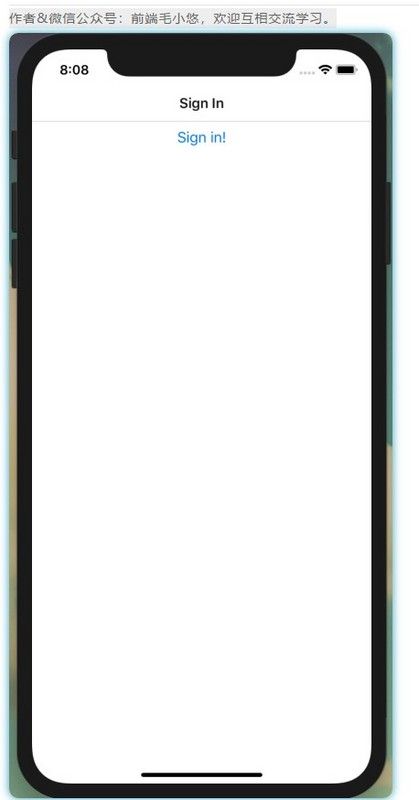
export default SignIn;图24-1。单击该按钮将存储令牌并将用户路由到应用程序
现在,当用户按下按钮时,将通过SecureStore存储令牌。使用登录功能后,让我们为用户添加退出应用程序的功能。为此,我们将在设置界面上添加一个按钮,当按下该按钮时,将从SecureStore中删除令牌(图24-2)。在src/screens/settings.js中:
import React from 'react';
import { View, Button } from 'react-native';
import * as SecureStore from 'expo-secure-store';
const Settings = props => {
// delete the token then navigate to the auth screen
const signOut = () => {
SecureStore.deleteItemAsync('token').then(
props.navigation.navigate('Auth')
);
};
return (
);
};
Settings.navigationOptions = {
title: 'Settings'
};
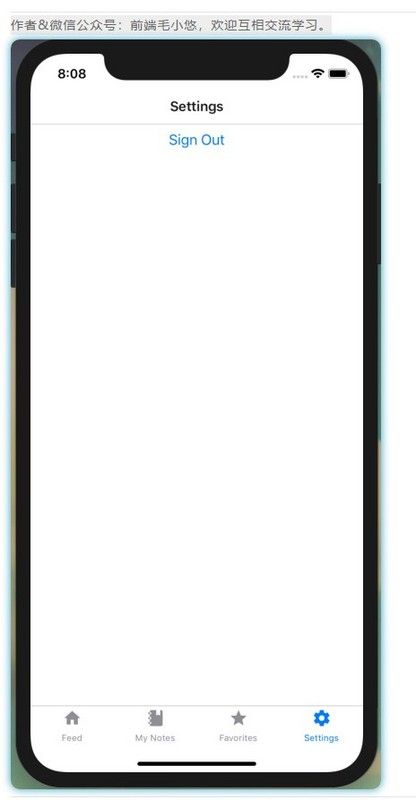
export default Settings;图24-2。单击该按钮将从设备中删除令牌,并使用户返回登录界面
完成这些步骤后,我们便拥有了创建应用程序身份验证流程所需的一切。
请确保退出
如果还没有,请在本地应用程序实例中点击“退出”按钮。
我们将在接下来的部分中添加适当的登录功能。
创建登录表单
现在,我们可以单击一个按钮并将令牌存储在用户的设备上,但我们还不允许用户通过输入自己的信息来登录帐户。让我们通过创建一个表单来纠正此问题,用户可以在其中输入他们的电子邮件地址和密码。为此,我们将使用React Native的TextInput组件在src/components/UserForm.js中使用表单创建一个新组件:
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { View, Text, TextInput, Button, TouchableOpacity } from 'react-native';
import styled from 'styled-components/native';
const UserForm = props => {
return (
Email Password );
}
export default UserForm;现在,我们可以在身份验证界面上显示此表单。为此,更新src/screens/signin.js以导入和使用组件,如下所示:
import React from 'react';
import { View, Button, Text } from 'react-native';
import * as SecureStore from 'expo-secure-store';
import UserForm from '../components/UserForm';
const SignIn = props => {
const storeToken = () => {
SecureStore.setItemAsync('token', 'abc').then(
props.navigation.navigate('App')
);
};
return (
);
}
export default SignIn;这样,我们将在身份验证界面上看到一个基本表单,但是它缺少任何样式或功能。我们可以继续在src/components/UserForm.js文件中实现表单。我们将使用React的useState挂钩,用于读取和设置表单元素的值:
const UserForm = props => {
// form element state
const [email, setEmail] = useState();
const [password, setPassword] = useState();
return (
Email
setEmail(text)} value={email} />
Password
setPassword(text)} value={password} />
);
}现在,我们可以在表单元素中添加一些其他属性,在使用电子邮件地址或密码时为用户提供预期的功能。有关TextInput API的完整文档,请参见
React本地文档。按下按钮时,我们还会调用一个函数,尽管该功能会受到限制。
const UserForm = props => {
// form element state
const [email, setEmail] = useState();
const [password, setPassword] = useState();
const handleSubmit = () => {
// this function is called when the user presses the form button
};
return (
Email
setEmail(text)}
value={email}
textContentType="emailAddress"
autoCompleteType="email"
autoFocus={true}
autoCapitalize="none"
/>
Password
setPassword(text)}
value={password}
textContentType="password"
secureTextEntry={true}
/>
);
}我们的表单具有所有必要的组件,但是样式还有很多不足之处。让我们使用样式化组件库为表单提供更合适的外观:
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { View, Text, TextInput, Button, TouchableOpacity } from 'react-native';
import styled from 'styled-components/native';
const FormView = styled.View` padding: 10px; `;
const StyledInput = styled.TextInput` border: 1px solid gray;
font-size: 18px;
padding: 8px;
margin-bottom: 24px; `;
const FormLabel = styled.Text` font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold; `;
const UserForm = props => {
const [email, setEmail] = useState();
const [password, setPassword] = useState();
const handleSubmit = () => {
// this function is called when the user presses the form button
};
return (
Email
setEmail(text)}
value={email}
textContentType="emailAddress"
autoCompleteType="email"
autoFocus={true}
autoCapitalize="none"
/>
Password
setPassword(text)}
value={password}
textContentType="password"
secureTextEntry={true}
/>
);
};
export default UserForm;最后,我们的Button组件仅限于默认样式选项,但接受颜色属性值除外。要创建自定义样式的按钮组件,我们可以使用React Native包装器TouchableOpacity(参见图24-3):
const FormButton = styled.TouchableOpacity`
background: #0077cc;
width: 100%;
padding: 8px;
`;
const ButtonText = styled.Text`
text-align: center;
color: #fff;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 18px;
`;
const UserForm = props => {
const [email, setEmail] = useState();
const [password, setPassword] = useState();
const handleSubmit = () => {
// this function is called when the user presses the form button
};
return (
Email
setEmail(text)}
value={email}
textContentType="emailAddress"
autoCompleteType="email"
autoFocus={true}
autoCapitalize="none"
/>
Password
setPassword(text)}
value={password}
textContentType="password"
secureTextEntry={true}
/>
Submit
);
};这样,我们实现了登录表单并应用了自定义样式。现在,让我们实现表单的功能。
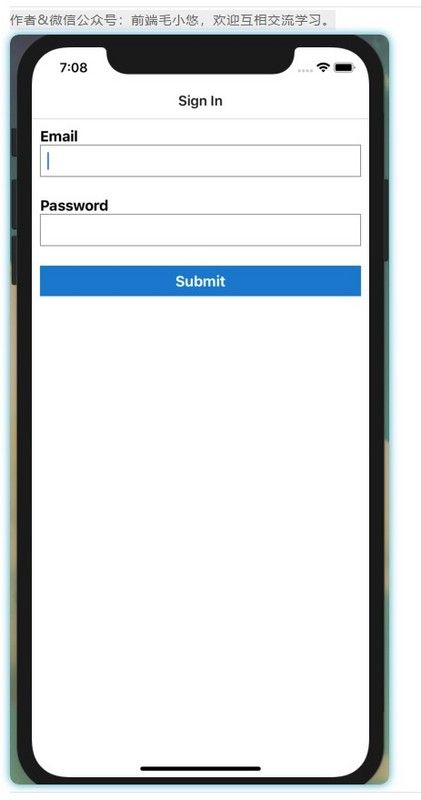
图24-3。我们的登录表单具有自定义样式
使用GraphQL修改进行身份验证
你可能还记得我们在API和Web应用程序章节开发的身份验证流程,但是在继续进行之前,让我们快速回顾一下。我们会将GraphQL请求发送到我们的API,其中包括用户的电子邮件地址和密码。如果数据库中存在电子邮件地址,并且密码正确,我们的API将以JWT进行响应。然后,我们可以像以前一样将令牌存储在用户的设备上,并将其与每个GraphQL请求一起发送。这样一来,我们就可以在每个API请求中识别用户,而无需他们重新输入密码。
放置好表格后,我们可以在src/screens/signin.js中编写GraphQL请求。首先,我们将Apollo库以及我们的Loading组件添加到导入列表中:
import React from 'react';
import { View, Button, Text } from 'react-native';
import * as SecureStore from 'expo-secure-store';
import { useMutation, gql } from '@apollo/client';
import UserForm from '../components/UserForm';
import Loading from '../components/Loading';接下来,我们可以添加我们的GraphQL查询:
const SIGNIN_USER = gql`
mutation signIn($email: String, $password: String!) {
signIn(email: $email, password: $password)
}
`;更新我们的storeToken函数存储作为参数传递的令牌字符串:
const storeToken = token => {
SecureStore.setItemAsync('token', token).then(
props.navigation.navigate('App')
);
};最后,我们将组件更新为GraphQL修改。我们还将把几个属性值传递给UserForm组件,使我们可以共享修改数据,识别正在调用的表单的类型以及利用路由器的导航。
const SignIn = props => {
const storeToken = token => {
SecureStore.setItemAsync('token', token).then(
props.navigation.navigate('App')
);
};
const [signIn, { loading, error }] = useMutation(SIGNIN_USER, {
onCompleted: data => {
storeToken(data.signIn)
}
});
// if loading, return a loading indicator
if (loading) return
{error && Error signing in! }
);
};现在,我们可以在src/components/UserForm.js组件中进行简单的更改,这将使其能够将用户输入的数据传递给请求。在组件内,我们将更新handleSubmit函数,以将表单值传递给我们的请求:
const handleSubmit = () => {
props.action({
variables: {
email: email,
password: password
}
});
};编写好我们的请求并完成表格后,用户现在可以登录该应用程序,该应用程序将存储返回的JSON Web令牌以供将来使用。
认证的GraphQL查询
现在我们的用户可以登录其帐户了,我们将需要使用存储的令牌对每个请求进行身份验证。这将使我们能够请求特定于用户的数据,例如当前用户的笔记列表或用户已标记为“收藏夹”的笔记列表。为此,我们将更新Apollo配置以检查令牌是否存在,如果令牌存在,则在每个API调用中发送该令牌的值。
在src/Main.js中,首先将SecureStore添加到导入列表中,并更新Apollo Client依赖项以包括createHttpLink和setContext:
// import the Apollo libraries
import {
ApolloClient,
ApolloProvider,
createHttpLink,
InMemoryCache
} from '@apollo/client';
import { setContext } from 'apollo-link-context';
// import SecureStore for retrieving the token value
import * as SecureStore from 'expo-secure-store';然后,我们可以更新Apollo客户端配置,以随每个请求发送令牌值:
// configure our API URI & cache
const uri = API_URI;
const cache = new InMemoryCache();
const httpLink = createHttpLink({ uri });
// return the headers to the context
const authLink = setContext(async (_, { headers }) => {
return {
headers: {
...headers,
authorization: (await SecureStore.getItemAsync('token')) || ''
}
};
});
// configure Apollo Client
const client = new ApolloClient({
link: authLink.concat(httpLink),
cache
});通过在每个请求的标头中发送令牌,我们现在可以更新mynotes和“收藏夹”界面以请求用户特定的数据。如果按照网络章节进行操作,这些查询应该看起来非常熟悉。
在src/screens/mynotes.js中:
import React from 'react';
import { Text, View } from 'react-native';
import { useQuery, gql } from '@apollo/client';
import NoteFeed from '../components/NoteFeed';
import Loading from '../components/Loading';
// our GraphQL query
const GET_MY_NOTES = gql`
query me {
me {
id
username
notes {
id
createdAt
content
favoriteCount
author {
username
id
avatar
}
}
}
}
`;
const MyNotes = props => {
const { loading, error, data } = useQuery(GET_MY_NOTES);
// if the data is loading, our app will display a loading message
if (loading) return Error loading notes ;
// if the query is successful and there are notes, return the feed of notes
// else if the query is successful and there aren't notes, display a message
if (data.me.notes.length !== 0) {
return No notes yet ;
}
};
MyNotes.navigationOptions = {
title: 'My Notes'
};
export default MyNotes;在src/screens/favorites.js中:
import React from 'react';
import { Text, View } from 'react-native';
import { useQuery, gql } from '@apollo/client';
import NoteFeed from '../components/NoteFeed';
import Loading from '../components/Loading';
// our GraphQL query
const GET_MY_FAVORITES = gql`
query me {
me {
id
username
favorites {
id
createdAt
content
favoriteCount
author {
username
id
avatar
}
}
}
}
`;
const Favorites = props => {
const { loading, error, data } = useQuery(GET_MY_FAVORITES);
// if the data is loading, our app will display a loading message
if (loading) return Error loading notes ;
// if the query is successful and there are notes, return the feed of notes
// else if the query is successful and there aren't notes, display a message
if (data.me.favorites.length !== 0) {
return No notes yet ;
}
};
Favorites.navigationOptions = {
title: 'Favorites'
};
export default Favorites;图24-4。在每个请求的标头中传递令牌可以使我们在应用程序中进行特定于用户的查询
现在,我们将基于存储在用户设备上的令牌值来检索用户特定的数据(图24-4)。
添加注册表格
现在,用户可以登录到现有帐户,但是如果不存在,则无法创建帐户。常见的UI模式是在登录链接下方添加指向注册表单的链接(反之亦然)。让我们添加一个注册界面,以允许用户从我们的应用程序中创建一个新帐户。
首先,让我们在src/screens/signup.js中创建一个新的界面组件。该组件与登录界面几乎相同,但是我们将其称为signUp GraphQL请求,并将formType =“ signUp”属性传递给UserForm组件:
import React from 'react';
import { Text } from 'react-native';
import * as SecureStore from 'expo-secure-store';
import { useMutation, gql } from '@apollo/client';
import UserForm from '../components/UserForm';
import Loading from '../components/Loading';
// signUp GraphQL mutation
const SIGNUP_USER = gql`
mutation signUp($email: String!, $username: String!, $password: String!) {
signUp(email: $email, username: $username, password: $password)
}
`;
const SignUp = props => {
// store the token with a key value of `token`
// after the token is stored navigate to the app's main screen
const storeToken = token => {
SecureStore.setItemAsync('token', token).then(
props.navigation.navigate('App')
);
};
// the signUp mutation hook
const [signUp, { loading, error }] = useMutation(SIGNUP_USER, {
onCompleted: data => {
storeToken(data.signUp);
}
});
// if loading, return a loading indicator
if (loading) return
{error && Error signing in! }
);
};
SignUp.navigationOptions = {
title: 'Register'
};
export default SignUp;创建界面后,我们可以将其添加到路由器。在src/screens/index.js文件中,首先将新组件添加到我们的文件导入列表中:
import SignUp from './signup';接下来,我们将更新AuthStack包括注册界面:
const AuthStack = createStackNavigator({
SignIn: SignIn,
SignUp: SignUp
});这样,我们的组件就可以创建并路由了;但是,我们的UserForm组件并不包含所有必需的字段。除了创建注册表单组件之外,根据类型,使用传递给自定义的表格的UrserForm的formType属性。
在我们的src/components/UserForm.js文件中,在formType等于signUp时,让我们更新表单的用户名字段:
const UserForm = props => {
const [email, setEmail] = useState();
const [password, setPassword] = useState();
const [username, setUsername] = useState();
const handleSubmit = () => {
props.action({
variables: {
email: email,
password: password,
username: username
}
});
};
return (
Email
setEmail(text)}
value={email}
textContentType="emailAddress"
autoCompleteType="email"
autoFocus={true}
autoCapitalize="none"
/>
{props.formType === 'signUp' && (
Username
setUsername(text)}
value={username}
textContentType="username"
autoCapitalize="none"
/>
)}
Password
setPassword(text)}
value={password}
textContentType="password"
secureTextEntry={true}
/>
Submit
);
};接下来,让我们在登录表单的底部添加一个链接,该链接使用户在按下时可以转到登录表单:
return (
{/* existing form component code is here */}
{props.formType !== 'signUp' && ( props.navigation.navigate('SignUp')}> Sign up )}
)然后,我们可以使用样式化的组件来更新链接的外观:
const SignUp = styled.TouchableOpacity`
margin-top: 20px;
`;
const Link = styled.Text`
color: #0077cc;
font-weight: bold;
`;在组件的JSX中:
{props.formType !== 'signUp' && (
props.navigation.navigate('SignUp')}> Need an account? Sign up.
)}现在,我们的src/components/UserForm.js文件将如下所示:
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { View, Text, TextInput, Button, TouchableOpacity } from 'react-native';
import styled from 'styled-components/native';
const FormView = styled.View`
padding: 10px;
`;
const StyledInput = styled.TextInput`
border: 1px solid gray;
font-size: 18px;
padding: 8px;
margin-bottom: 24px;
`;
const FormLabel = styled.Text`
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold;
`;
const FormButton = styled.TouchableOpacity`
background: #0077cc;
width: 100%;
padding: 8px;
`;
const ButtonText = styled.Text`
text-align: center;
color: #fff;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 18px;
`;
const SignUp = styled.TouchableOpacity`
margin-top: 20px;
`;
const Link = styled.Text`
color: #0077cc;
font-weight: bold;
`;
const UserForm = props => {
const [email, setEmail] = useState();
const [password, setPassword] = useState();
const [username, setUsername] = useState();
const handleSubmit = () => {
props.action({
variables: {
email: email,
password: password,
username: username
}
});
};
return (
Email
setEmail(text)}
value={email}
textContentType="emailAddress"
autoCompleteType="email"
autoFocus={true}
autoCapitalize="none"
/>
{props.formType === 'signUp' && (
Username
setUsername(text)}
value={username}
textContentType="username"
autoCapitalize="none"
/>
)}
Password
setPassword(text)}
value={password}
textContentType="password"
secureTextEntry={true}
/>
Submit
{props.formType !== 'signUp' && (
props.navigation.navigate('SignUp')}>
Need an account? Sign up.
)}
);
};
export default UserForm;进行了这些更改后,用户可以使用我们的应用程序登录并注册帐户(图24-5)。
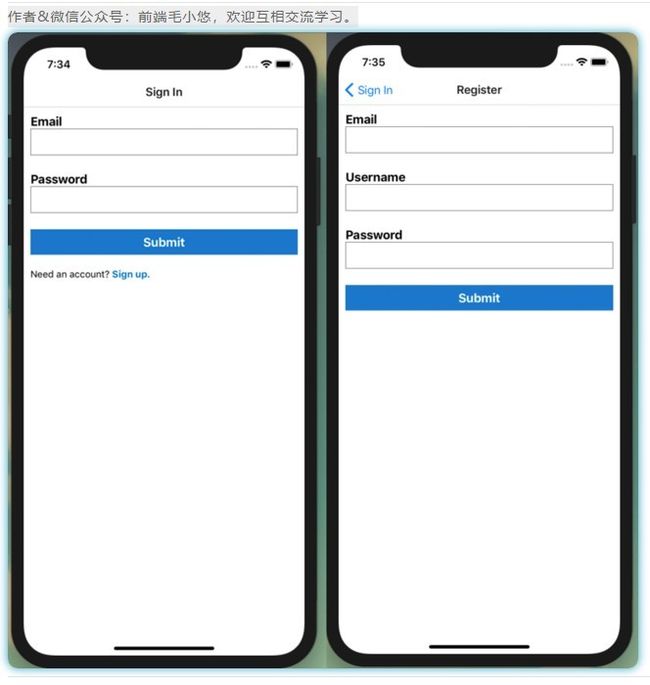
图24-5用户现在可以注册帐户并在身份验证界面之间导航
结论
在本章中,我们研究了如何将身份验证引入应用程序。通过结合React Native的表单元素、React Navigation的路由功能、Expo的SecureStore库和GraphQL请求,我们可以创建一个用户友好的身份验证流程。对这种身份验证有扎实的了解,这也使我们能够探索其他React Native身份验证方法,例如Expo的AppAuth或GoogleSignIn。在下一章中,我们将研究如何发布和分发React Native应用程序。
如果有理解不到位的地方,欢迎大家纠错。如果觉得还可以,麻烦您点赞收藏或者分享一下,希望可以帮到更多人。