AutoResetEvent和ManualResetEvent的使用与区别
其主要区别:是否自动将同步状态设置为非终止状态,以阻塞线程。在有循环WaitOne的情况下才可看出其区别。
区别就是:AutoResetEvent执行完WaitOne()后会自动执行Reset()方法阻塞线程,而ManualResetEvent需要手动执行Reset()方法才能阻塞线程。
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Collections;
namespace ThreadPoolTest
{
class Program
{
static void Main( string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine( " aaaaaaaaaa ");
EventWaitHandle eventX = new AutoResetEvent( false);// new ManualResetEvent( false);
for ( int n = 0; n < 10; n++)
{
AA aa = new AA( 5);
aa.eventX = eventX;
for ( int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem( new WaitCallback(aa.fun));
eventX.WaitOne(Timeout.Infinite, true);
}
Console.WriteLine( " bbbbbbbbbb ");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
public class AA
{
public EventWaitHandle eventX;
public static int iCount = 0;
public static int iMaxCount = 0;
public AA( int MaxCount)
{
iMaxCount = MaxCount;
}
public void fun( object o)
{
Console.WriteLine( " 11111111 ");
Interlocked.Increment( ref iCount);
Console.WriteLine( " iCount: " + iCount);
if (iCount == iMaxCount)
{
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine( " Setting eventX ");
eventX.Set();
}
}
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
AutoResetEvent 允许线程通过发信号互相通信。通常,此通信涉及线程需要独占访问的资源。
线程通过调用 AutoResetEvent 上的 WaitOne 来等待信号。如果 AutoResetEvent 处于非终止状态,则该线程阻塞,并等待当前控制资源的线程
通过调用 Set 发出资源可用的信号。
调用 Set 向 AutoResetEvent 发信号以释放等待线程。AutoResetEvent 将保持终止状态,直到一个正在等待的线程被释放,然后自动返回非终止状态。如果没有任何线程在等待,则状态将无限期地保持为终止状态。
可以通过将一个布尔值传递给构造函数来控制 AutoResetEvent 的初始状态,如果初始状态为终止状态,则为 true;否则为 false。
通俗的来讲只有等myResetEven.Set()成功运行后,myResetEven.WaitOne()才能够获得运行机会;Set是发信号,WaitOne是等待信号,只有发了信号,
等待的才会执行。如果不发的话,WaitOne后面的程序就永远不会执行。下面我们来举一个例子:我去书店买书,当我选中一本书后我会去收费处付钱,
付好钱后再去仓库取书。这个顺序不能颠倒,我作为主线程,收费处和仓库做两个辅助线程,代码如下:
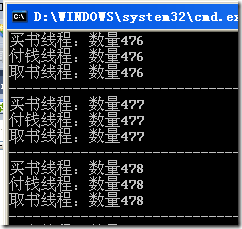
using System; using System.Linq; using System.Activities; using System.Activities.Statements; using System.Threading; namespace CaryAREDemo { class Me { const int numIterations = 550; static AutoResetEvent myResetEvent = new AutoResetEvent(false); static AutoResetEvent ChangeEvent = new AutoResetEvent(false); //static ManualResetEvent myResetEvent = new ManualResetEvent(false); //static ManualResetEvent ChangeEvent = new ManualResetEvent(false); static int number; //这是关键资源 static void Main() { Thread payMoneyThread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(PayMoneyProc)); payMoneyThread.Name = "付钱线程"; Thread getBookThread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(GetBookProc)); getBookThread.Name = "取书线程"; payMoneyThread.Start(); getBookThread.Start(); for (int i = 1; i <= numIterations; i++) { Console.WriteLine("买书线程:数量{0}", i); number = i; //Signal that a value has been written. myResetEvent.Set(); ChangeEvent.Set(); Thread.Sleep(0); } payMoneyThread.Abort(); getBookThread.Abort(); } static void PayMoneyProc() { while (true) { myResetEvent.WaitOne(); //myResetEvent.Reset(); Console.WriteLine("{0}:数量{1}", Thread.CurrentThread.Name, number); } } static void GetBookProc() { while (true) { ChangeEvent.WaitOne(); // ChangeEvent.Reset(); Console.WriteLine("{0}:数量{1}", Thread.CurrentThread.Name, number); Console.WriteLine("------------------------------------------"); Thread.Sleep(0); } } } } 运行结果如下:
AutoResetEvent与ManualResetEvent的区别
他们的用法\声明都很类似,Set方法将信号置为发送状态 Reset方法将信号置为不发送状态WaitOne等待信号的发送。其实,从名字就可以看出一个手动,
一个自动,这个手动和自动实际指的是在Reset方法的处理上,如下面例子:
public AutoResetEvent autoevent=new AutoResetEvent(true);
public ManualResetEvent manualevent=new ManualResetEvent(true);
默认信号都处于发送状态,
autoevent.WaitOne();
manualevent.WaitOne();
如果 某个线程调用上面该方法,则当信号处于发送状态时,该线程会得到信号,得以继续执行。差别就在调用后,autoevent.WaitOne()每次只允许一个线程
进入,当某个线程得到信号(也就是有其他线程调用了autoevent.Set()方法后)后,autoevent会自动又将信号置为不发送状态,则其他调用WaitOne的线程只
有继续等待.也就是说,autoevent一次只唤醒一个线程。而manualevent则可以唤醒多个线程,因为当某个线程调用了set方法后,其他调用waitone的线程
获得信号得以继续执行,而manualevent不会自动将信号置为不发送.也就是说,除非手工调用了manualevent.Reset().方法,则manualevent将一直保持有信号状态,manualevent也就可以同时唤醒多个线程继续执行。如果上面的程序换成ManualResetEvent的话,就需要在waitone后面做下reset。