欢迎访问我的GitHub
https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos
内容:所有原创文章分类汇总及配套源码,涉及Java、Docker、Kubernetes、DevOPS等;
欢迎访问我的GitHub
https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos
内容:所有原创文章分类汇总及配套源码,涉及Java、Docker、Kubernetes、DevOPS等;
能独立运行的jar文件
在开发springboot应用时,通过java -jar命令启动应用是常用的方式,今天就来一起了解这个简单操作背后的技术;
开发demo
开发一个springboot应用作为本次研究的对象,对应的版本信息如下:
- JDK:1.8.0_211
- springboot:2.3.1.RELEASE
- maven:3.6.0
接下来开发springboot应用,这个应用非常简单:
springboot应用名为springbootstarterdemo,pom.xml文件内容:
4.0.0 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-parent 2.3.1.RELEASE com.bolingcavalry springbootstarterdemo 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT springbootstarterdemo Demo project for Spring Boot 1.8 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-web org.springframework.boot spring-boot-maven-plugin
只有一个java类,里面有个http接口:
package com.bolingcavalry.springbootstarterdemo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Date;
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class SpringbootstarterdemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootstarterdemoApplication.class, args);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello " + new Date();
}
}
编码完成,在pom.xml所在目录执行命令
mvn clean package -U -DskipTests
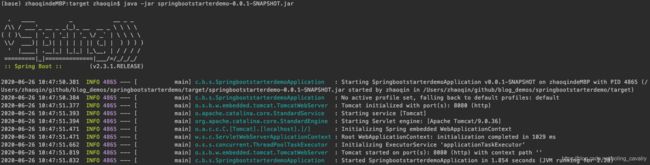
构建成功后,在target目录下得到文件springbootstarterdemo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar就是这个springbootstarterdemo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar,此时执行java -jar springbootstarterdemo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar就能启动应用,如下图:
接下来就用这个springbootstarterdemo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar来分析jar文件能够独立启动的原因;
java -jar做了什么
先要弄清楚java -jar命令做了什么,在oracle官网找到了该命令的描述:
If the -jar option is specified, its argument is the name of the JAR file containing class and resource files for the application. The startup class must be indicated by the Main-Class manifest header in its source code.
再次秀出我蹩脚的英文翻译:
- 使用-jar参数时,后面的参数是的jar文件名(本例中是springbootstarterdemo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar);
- 该jar文件中包含的是class和资源文件;
- 在manifest文件中有Main-Class的定义;
- Main-Class的源码中指定了整个应用的启动类;(in its source code)
小结一下:
java -jar会去找jar中的manifest文件,在那里面找到真正的启动类;
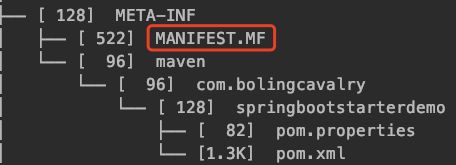
探查springbootstarterdemo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jarspringbootstarterdemo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar是前面的springboot工程的构建结果,是个压缩包,用常见的压缩工具就能解压,我这里的环境是MacBook Pro,用unzip即可解压;解压后有很多内容,我们先关注manifest相关的,下图红框中就是manifest文件:
打开上图红框中的文件,内容如下:
Spring-Boot-Classpath-Index: BOOT-INF/classpath.idx Implementation-Title: springbootstarterdemo Implementation-Version: 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT Start-Class: com.bolingcavalry.springbootstarterdemo.Springbootstarter demoApplication Spring-Boot-Classes: BOOT-INF/classes/ Spring-Boot-Lib: BOOT-INF/lib/ Build-Jdk-Spec: 1.8 Spring-Boot-Version: 2.3.1.RELEASE Created-By: Maven Jar Plugin 3.2.0 Implementation-Vendor: Pivotal Software, Inc. Main-Class: org.springframework.boot.loader.JarLauncher
4.在上述内容可见Main-Class的值org.springframework.boot.loader.JarLauncher,这个和前面的java官方文档对应上了,正是这个JarLauncher类的代码中指定了真正的启动类;
疑惑出现
1.在MANIFEST.MF文件中有这么一行内容:
Start-Class: com.bolingcavalry.springbootstarterdemo.Springbootstarter demoApplication
2.前面的java官方文档中,只提到过Main-Class ,并没有提到Start-Class;
3.Start-Class的值是SpringbootstarterdemoApplication,这是我们的java代码中的唯一类,也只真正的应用启动类;
4.所以问题就来了:理论上看,执行java -jar命令时JarLauncher类会被执行,但实际上是SpringbootstarterdemoApplication被执行了,这其中发生了什么呢?
猜测
动手之前先猜一下,个人觉得原因应该如下:
- java -jar命令会启动JarLauncher;
- Start-Class是给JarLauncher用的;
- JarLauncher根据Start-Class找到了SpringbootstarterdemoApplication,然后执行它;
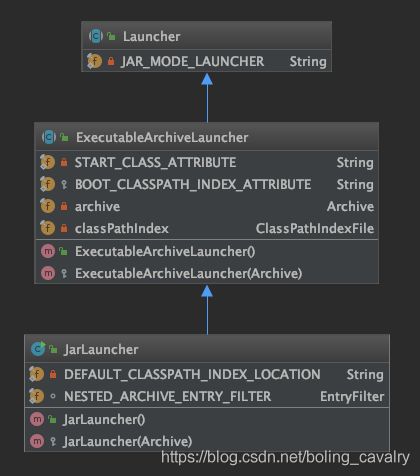
分析JarLauncher先下载SpringBoot源码,我下载的是2.3.1版本,地址:https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/releases/tag/v2.3.1.RELEASEJarLauncher所在的工程是spring-boot-loader,先弄明白JarLauncher的继承关系,如下图,可见JarLauncher继承自ExecutableArchiveLauncher,而ExecutableArchiveLauncher的父类Launcher位于最顶层,是个抽象类:
3. java -jar执行的是JarLauncher的main方法,如下,会实例化一个JarLauncher对象,然后执行其launch方法,并且将所有入参都带入:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new JarLauncher().launch(args);
}
4.上面的launch方法在父类Launcher中:
protected void launch(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 将jar解压后运行的方式叫做exploded mode
// 如果是exploded mode,就不能支持通过URL加载jar
// 如果不是exploded mode,就可以通过URL加载jar
if (!isExploded()) {
// 如果允许通过URL加载jar,就在此注册对应的处理类
JarFile.registerUrlProtocolHandler();
}
// 创建classLoader
ClassLoader classLoader = createClassLoader(getClassPathArchivesIterator());
// jarmode是创建docker镜像时用到的参数,使用该参数是为了生成带有多个layer信息的镜像
// 这里暂时不关注jarmode
String jarMode = System.getProperty("jarmode");
//如果没有jarmode参数,launchClass的值就来自getMainClass()返回
String launchClass = (jarMode != null && !jarMode.isEmpty()) ? JAR_MODE_LAUNCHER : getMainClass();
launch(args, launchClass, classLoader);
}
5.可见要重点关注的是getMainClass()方法,在看这个方法之前,我们先去关注一个重要的成员变量archive,是JarLauncher的父类ExecutableArchiveLauncher的archive,如下可见,该变量又来自方法createArchive:
public ExecutableArchiveLauncher() {
try {
this.archive = createArchive();
this.classPathIndex = getClassPathIndex(this.archive);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}
6.方法来自Launcher.createArchive,如下所示,可见成员变量archive实际上是个JarFileArchive对象:
protected final Archive createArchive() throws Exception {
ProtectionDomain protectionDomain = getClass().getProtectionDomain();
CodeSource codeSource = protectionDomain.getCodeSource();
URI location = (codeSource != null) ? codeSource.getLocation().toURI() : null;
String path = (location != null) ? location.getSchemeSpecificPart() : null;
if (path == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to determine code source archive");
}
File root = new File(path);
if (!root.exists()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to determine code source archive from " + root);
}
return (root.isDirectory() ? new ExplodedArchive(root) : new JarFileArchive(root));
}
7.现在回到getMainClass()方法,可见this.archive.getManifest方法返回的是META-INF/MANIFEST.MF文件的内容,然后getValue(START_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)方法实际上就是从META-INF/MANIFEST.MF中取得了Start-Class的属性:
@Override
protected String getMainClass() throws Exception {
// 对应的是JarFileArchive.getManifest方法,
// 进去后发现对应的就是JarFile.getManifest方法,
// JarFile.getManifest对应的就是META-INF/MANIFEST.MF文件的内容
Manifest manifest = this.archive.getManifest();
String mainClass = null;
if (manifest != null) {
// 对应的是META-INF/MANIFEST.MF文件中的Start-Class的属性
mainClass = manifest.getMainAttributes().getValue(START_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE);
}
if (mainClass == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No 'Start-Class' manifest entry specified in " + this);
}
return mainClass;
}
8.从上述分析可知:getMainClass()方法返回的是META-INF/MANIFEST.MF中取得了Start-Class的属性com.bolingcavalry.springbootstarterdemo.SpringbootstarterdemoApplication,再次回到launch方法中,可见最终运行的代码是launch(args, launchClass, classLoader),它的launchClass参数就是com.bolingcavalry.springbootstarterdemo.SpringbootstarterdemoApplication:
protected void launch(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (!isExploded()) {
JarFile.registerUrlProtocolHandler();
}
ClassLoader classLoader = createClassLoader(getClassPathArchivesIterator());
String jarMode = System.getProperty("jarmode");
// 这里的launchClass等于"com.bolingcavalry.springbootstarterdemo.SpringbootstarterdemoApplication"
String launchClass = (jarMode != null && !jarMode.isEmpty()) ? JAR_MODE_LAUNCHER : getMainClass();
// 这里就是启动SpringbootstarterdemoApplication的地方
launch(args, launchClass, classLoader);
}
9.展开launch(args, launchClass, classLoader),最终查到了MainMethodRunner类:
public class MainMethodRunner {
private final String mainClassName;
private final String[] args;
/**
* Create a new {@link MainMethodRunner} instance.
* @param mainClass the main class
* @param args incoming arguments
*/
public MainMethodRunner(String mainClass, String[] args) {
// mainClassName被赋值为"com.bolingcavalry.springbootstarterdemo.SpringbootstarterdemoApplication"
this.mainClassName = mainClass;
this.args = (args != null) ? args.clone() : null;
}
public void run() throws Exception {
// 得到SpringbootstarterdemoApplication的Class对象
Class mainClass = Class.forName(this.mainClassName, false, Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader());
// 得到SpringbootstarterdemoApplication的main方法对象
Method mainMethod = mainClass.getDeclaredMethod("main", String[].class);
mainMethod.setAccessible(true);
// 通过反射执行main方法
mainMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { this.args });
}
}
终于,真相大白了;
小结
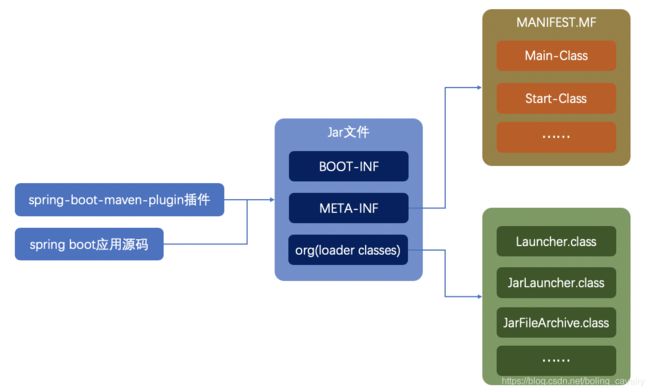
最后尽可能简短做个小结,先看jar是如何产生的,如下图,maven插件生成的jar文件中,有常见的class、jar,也有符合java规范的MANIFEST.MF文件,并且,还在MANIFEST.MF文件中额外生成了名为Start-Class的配置,这里面是我们编写的应用启动类SpringbootstarterdemoApplication:
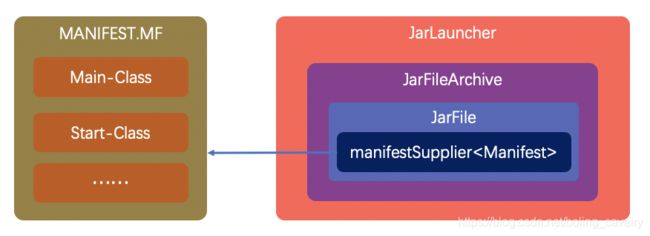
启动类是JarLauncher,它是如何与MANIFEST.MF文件关联的呢?从下图可以看出,最终是通过JarFile类的成员变量manifestSupplier关联上的:
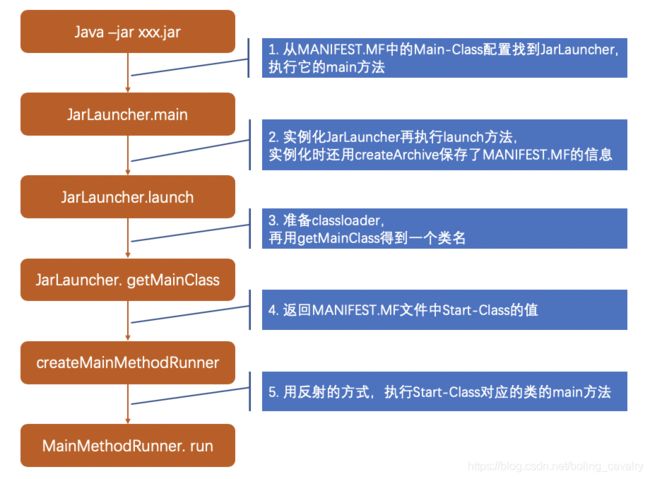
再来看看关键代码的执行情况,如下图:
至此,SpringBoot的jar独立运行的基本原理已经清楚,探究的过程中,除了熟悉关键代码流程,还对jar中的文件有了更多了解,如果您正在学习SpringBoot,希望本文能给您一些参考;
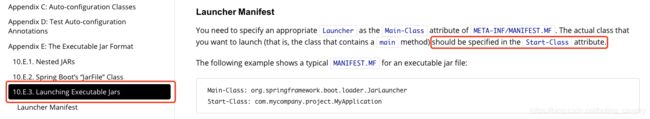
官方文档最后附上SpringBoot官方文档,可以看到Start-Class描述信息:
上述文档明确提到:Start-Class定义的是实际的启动类,此时的您应该对一切都了然于胸,产生本该如此的感慨;
到此这篇关于springboot的jar为何能独立运行的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot的jar为何能独立运行内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!