Enterprise Library Policy Injection Application Block 之三:PIAB的扩展—创建自定义CallHandler(提供Source Code下载)
本系列的第一部分对PIAB使用场景进行了简单的介绍,作中阐述了通过PI(Policy Injection)的方式实现了Business Logic和Non-Business Infrastructure Logic的分离,从而实现了AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)。在第二部分中详细介绍PIAB的实现机制:通过自定义RealProxy的方式实现了Method Injection。通过这几天接收到的网友的留言,觉得很多人对在具体的项目开发中如何使用PIAB还有很多困惑,对PIAB的价值还不是很了解。为此,在本系列的第三篇文章中,我将以Walk through的方式定义一个Custom CallHandler,并通过两种不同的方式:Attribute和Configuration将其运用到所以得Method上。你可以这里从下载Source Code.
场景描述:本Demo模拟一个简单的场景:订单处理,我们将订单处理之前对订单的验证通过PI的方式提供。我们假设需要进行如何的验证:
- Order Date必须早于当前日期。
- 必须有具体的Product。
- 供应商必须是制定的几家合法供应商(可选)。
- Order的总价必须是所有Product价格之和(可选)。
其中前两个验证规则为必须的,后两个未可选项,可以通过Attribute和Configuration进行相应的配置。
步骤一、创建解决方案和项目
如下图,整个Solution由两个Project组成,一个Class Library和一个Console Application。所有与Custom CallHandler的Class都定义在Artech.CustomCallHandler.ClassLibrary中,而Artech.CustomCallHandler.ConsoleApp重在演示对Custom CallHandler的使用。

在Artech.CustomCallHandler.ClassLibrary中,添加如下3个Dll Reference,你可以在安装Enterprise Library V3 .1的目录中找到。
- Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.Common
- Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.PolicyInjection
- Microsoft.Practices.ObjectBuilder
步骤二、定义辅助类:Order、OrderItem、OrderValidationException
1: namespace Artech.CustomCallHandlers
2: {
3: public class Order
4: {
5: public Order()
6: {
7: this.Items = new List<OrderItem>();
8: }
9: public Guid OrderNo{ get; set; }
10: public DateTime OrderDate{ get; set; }
11: public string Supplier{ get; set; }
12: public IList<OrderItem> Items{ get; set; }
13: public double TotalPrice{ get; set; }
14: }
15: }
1: namespace Artech.CustomCallHandlers
2: {
3: public class OrderItem
4: {
5: public Guid ProductID{ get; set; }
6: public string ProductName{ get; set; }
7: public double UnitPrice{ get; set; }
8: public int Quantity{ get; set; }
9: }
10: }
1: [Serializable]
2: public class OrderValidationException : Exception
3: {
4: public OrderValidationException() { }
5: public OrderValidationException(string message) : base(message) { }
6: public OrderValidationException(string message, Exception inner) : base(message, inner) { }
7: protected OrderValidationException(
8: System.Runtime.Serialization.SerializationInfo info,
9: System.Runtime.Serialization.StreamingContext context)
10: : base(info, context) { }
11: }
步骤三、定义Custom CallHandler: OrderValidationCallHandler
1: namespace Artech.CustomCallHandlers
2: {
3: public class OrderValidationCallHandler : ICallHandler
4: {
5: private static IList<string> _legalSuppliers;
6: public static IList<string> LegalSuppliers
7: {
8: get
9: {
10: if (_legalSuppliers == null)
11: {
12: _legalSuppliers = new List<string>();
13: _legalSuppliers.Add("Company AAA");
14: _legalSuppliers.Add("Company BBB");
15: _legalSuppliers.Add("Company CCC");
16: }
17:
18: return _legalSuppliers;
19: }
20: }
21: public bool ValidateTotalPrice{ get; set; }
22: public bool ValidateSupplier{ get; set; }
23: public IMethodReturn Invoke(IMethodInvocation input, GetNextHandlerDelegate getNext)
24: {
25: if (input.Inputs.Count == 0){return getNext()(input, getNext);}
26: Order order = input.Inputs[0] as Order;
27: if (order == null){return getNext()(input, getNext);}
28: if (order.OrderDate > DateTime.Today)
29: {
30: return input.CreateExceptionMethodReturn(new OrderValidationException("The order date is later than the current date!"));
31: }
32:
33: if (order.Items.Count == 0)
34: {
35: return input.CreateExceptionMethodReturn(new OrderValidationException("There are not any items for the order!"));
36: }
37:
38: if (this.ValidateSupplier)
39: {
40: if (!LegalSuppliers.Contains<string>(order.Supplier))
41: {
42: return input.CreateExceptionMethodReturn(new OrderValidationException("The supplier is inllegal!"));
43: }
44: }
45:
46: if (this.ValidateTotalPrice)
47: {
48: double totalPrice = 0;
49: foreach (OrderItem item in order.Items)
50: {
51: totalPrice += item.Quantity * item.UnitPrice;
52: }
53: if (totalPrice != order.TotalPrice)
54: {
55: return input.CreateExceptionMethodReturn(new OrderValidationException("The sum of the order item is not equal to the order total price!"));
56: }
57: }
58:
59: return getNext()(input, getNext);
60: }
61: }
62: }
OrderValidationCallHandler实现了Interface:Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.PolicyInjection. ICallHandler。ICallHandler仅仅有一个方法成员:
1: namespace Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.PolicyInjection
2: {
3: public interface ICallHandler
4: {
5: IMethodReturn Invoke(IMethodInvocation input, GetNextHandlerDelegate getNext);
6: }
7: }
8:
参数input代表对方法的调用,你可以通过他们获得方法调用的参数、Context、MethodBase和Target Object。上本系列的第二部分已经详细介绍了,运用到某一个Method上的Policy可能包含一个或多个CallHandler,这些Handler在初始化的时候串成一个Pipeline。在一般的情况下在完成某一个Handler的操作之后会调用后一个Handler或者是Target Object(如何改Handler是最后一个Handler)。但是在一些特殊的场合,比如:验证错误;在执行当前Handler的操作时抛出Exception;对于某些特殊的输入有固定的返回值,那么就没有必要再将接力棒向后传递了。在这个时候我们可能直接抛出Exception或者返回一个特设的返回值。这个时候可以调用CreateExceptionMethodReturn和CreateMethodReturn来实现。
1: namespace Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.PolicyInjection
2: {
3: public interface IMethodInvocation
4: {
5: IParameterCollection Arguments { get; }
6: IParameterCollection Inputs { get; }
7: IDictionary InvocationContext { get; }
8: MethodBase MethodBase { get; }
9: object Target { get; }
10: IMethodReturn CreateExceptionMethodReturn(Exception ex);
11: IMethodReturn CreateMethodReturn(object returnValue, params object[] outputs);
12: }
13: }
而第二个参数getNext是一个Delegate,代表对CallHandler Pipeline后面CallHandler或者是Target Object的调用,这也在第二部分有提到。
我们在回到Invoke的具体定义。我们假设我们具体调用的Method的第一个参数必须是我们定义的Order对象:先验证方法的调用是否含有输入参数(如何没有直接调用后面的CallHandler或者Target Object);返回获得第一个输入参数并验证其类型(如果不是Order类型直接调用后面的CallHandler或者Target Object)
1: if (input.Inputs.Count == 0)
2: {
3: return getNext()(input, getNext);
4: }
5: Order order = input.Inputs[0] as Order;
6: if (order == null)
7: {
8: return getNext()(input, getNext);
9: }
然后我们再验证Order对象是否满足我们在上面提出的验证规则,先看看必须的验证规则:对Order Date和Order Item Count的验证。
1: if (order.OrderDate > DateTime.Today)
2: {
3: return input.CreateExceptionMethodReturn(new OrderValidationException("The order date is later than the current date!"));
4: }
5: if(order.Items.Count == 0)
6: {
7: return input.CreateExceptionMethodReturn(new OrderValidationException("There are not any items for the order!"));
8: }
以及对可选的规则的验证:Total Price和Supplier。是否需要对其进行验证由两个Property来决定: ValidateSupplier和ValidateTotalPrice。
1: if (this.ValidateSupplier)
2: {
3: if (!LegalSuppliers.Contains<string>(order.Supplier))
4: {
5: return input.CreateExceptionMethodReturn(new OrderValidationException("The supplier is inlegal!"));
6: }
7: }
8:
9: if(this.ValidateTotalPrice)
10: {
11: double totalPrice = 0;
12: foreach (OrderItem item in order.Items)
13: {
14: totalPrice += item.Quantity * item.UnitPrice;
15: }
16: if (totalPrice != order.TotalPrice)
17: {
18: return input.CreateExceptionMethodReturn(new OrderValidationException("The sum of product unit price * quantity is not equal to the order total price!"));
19: }
20: }
最后将接力棒向后传递:
1: return getNext()(input, getNext);
到此为止,我们的OrderValidationCallHandler就定义完毕。但这仅仅完成了一半而已。因为我们最终需要通过Attribute或者Configuration的方式将我们的CallHandler运用到具体的Method上。我们先来看看使用Attribute的清况。我们需要在定一个Custom Attribute: OrderValidationCallHandlerAttribute.
1: namespace Artech.CustomCallHandlers
2: {
3: [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method | AttributeTargets.Class)]
4: public class OrderValidationCallHandlerAttribute : HandlerAttribute
5: {
6: public bool ValidateTotalPrice{ get; set; }
7: public bool ValidateSupplier{ get; set; }
8:
9: public override ICallHandler CreateHandler()
10: {
11: return new OrderValidationCallHandler() { ValidateSupplier = this.ValidateSupplier, ValidateTotalPrice = this.ValidateTotalPrice };
12: }
13: }
14: }
这是一个派生Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.PolicyInjection. HandlerAttribute自得特殊的Custom Attribute。HandlerAttribute是一个Abstract Class,继承自该Class通过其Orverride的CreateHandler来创建所需要的CallHandler,在这里当然是创建我们定义的OrderValidationCallHandler。由于对Total Price和Supplier的验证时可选的,所以我们定义了两个对应的Property来供Developer进行自由地配置,这两个Property用于初始化CallHandler。
步骤四、通过Attribute运用OrderValidationCallHandler
我想到此为止,我们已经迫不及待地想将我们定义的OrderValidationCallHandler应用到我们程序中了。我们就通过一个Console Application来演示如何通过Attibute的方式来运用OrderValidationCallHandler到我们所需的Method 上。现在定义以一个处理Order的Class: OrderProcessor。
1: public class OrderProcessor : MarshalByRefObject
2: {
3: [OrderValidationCallHandlerAttribute]
4: public void ProcessOrder(Order order)
5: {
6: Console.WriteLine("The order has been processed!");
7: }
8: public static Order CreateOrder(DateTime orderDate, string supplier)
9: {
10: Order order = new Order() { OrderNo = Guid.NewGuid(), OrderDate = orderDate, Supplier = supplier, TotalPrice = 10000 };
11: order.Items.Add(new OrderItem() { ProductID = Guid.NewGuid(), UnitPrice = 6000, Quantity = 1, ProductName = "PC" });
12: order.Items.Add(new OrderItem() { ProductID = Guid.NewGuid(), UnitPrice = 5000, Quantity = 2, ProductName = "Print" });
13: return order;
14: }
15: }
CreateOrder用于创建Order对象。而我们将我们的OrderValidationCallHandlerAttribute运用到ProcessOrder Method上。现在我们就可以在Main方法上调用这个方法了:
1: class Program
2: {
3: static void Main(string[] args)
4: {
5: OrderProcessor orderProcessor = PolicyInjection.Create<OrderProcessor>();
6: Order order;
7: try
8: {
9: order = OrderProcessor.CreateOrder(DateTime.Today.AddDays(1), " Company AAA");
10: Console.WriteLine("Proceed to process an order with an invalid order date!");
11: orderProcessor.ProcessOrder(order);
12: }
13: catch (OrderValidationException ex)
14: {
15: Console.WriteLine("Error: {0}", ex.Message);
16: }
17: try
18: {
19: order = OrderProcessor.CreateOrder(DateTime.Today.AddDays(-1), " Company DDD");
20: Console.WriteLine("Proceed to process an order with an illegal supplier!");
21: orderProcessor.ProcessOrder(order);
22: }
23:
24: catch (OrderValidationException ex)
25: {
26: Console.WriteLine("Error: {0}", ex.Message);
27: }
28:
29: try
30: {
31: order = OrderProcessor.CreateOrder(DateTime.Today.AddDays(-1), " Company AAA");
32: Console.WriteLine("Proceed to process an order with incorrect total price!");
33: orderProcessor.ProcessOrder(order);
34: }
35: catch (OrderValidationException ex)
36: {
37: Console.WriteLine("Error: {0}", ex.Message);
38:
39: }
40: }
41: }
下面试输出结果:
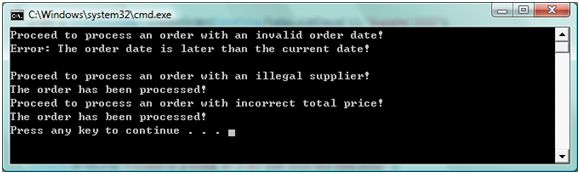
我们看出,Order Date 的验证正常执行,而对于Total Price和Supplier的验证却没有起作用。因为这两个是可选的(默认为不进行验证),我们可以通过修改运用在ProcessOrder Method的OrderValidationCallHandlerAttribute来进行有效的配置。比如:
1: [OrderValidationCallHandlerAttribute(ValidateSupplier = true, ValidateTotalPrice = true)]
2: public void ProcessOrder(Order order)
3: {
4: Console.WriteLine("The order has been processed!");
5: }
这样将会出现如下的结果:
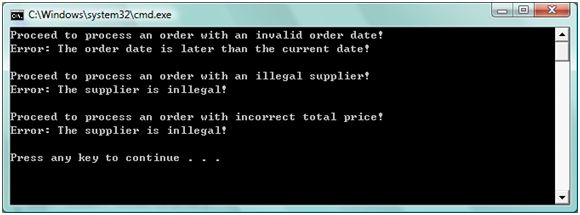
步骤五、 定义HandlerData和CallHandlerAssembler
在上面我们实现了通过Attribute的方式使用CallHandler的方式,我们现在来看看另一种运用CallHandler的方式:Configuration。为此我们需要定义两个额外的Class: HandlerData和CallHandlerAssembler。前者用于定义Configuration相关的Property,而后者则通过Configuration创建并初始化相应的CallHandler。
下面是HandlerData的定义:
1: namespace Artech.CustomCallHandlers
2: {
3: [Assembler(typeof(OrderValidationCallHandlerAssembler))]
4: public class OrderValidationCallHandlerData : CallHandlerData
5: {
6: [ConfigurationProperty("validateSupplier", DefaultValue = false)]
7: public bool ValidateSupplier
8: {
9: get{return (bool)base["validateSupplier"];}
10: set{base["validateSupplier"] = value;}
11: }
12:
13: [ConfigurationProperty("validateTotalPrice", DefaultValue = false)]
14: public bool ValidateTotalPrice
15: {
16: get{return (bool)base["validateTotalPrice"];}
17: set{base["validateTotalPrice"] = value;}
18: }
19: }
20: }
这和ConfigurationProperty相同,唯一的区别是在Class上运用了一个Assembler Attribute,并制定了一个CallHandlerAssembler type:OrderValidationCallHandlerAssembler。OrderValidationCallHandlerAssembler定义如下:
1: namespace Artech.CustomCallHandlers
2: {
3: public class OrderValidationCallHandlerAssembler : IAssembler<ICallHandler, CallHandlerData>
4: {
5: public ICallHandler Assemble(IBuilderContext context, CallHandlerData objectConfiguration, IConfigurationSource configurationSource, ConfigurationReflectionCache reflectionCache)
6: {
7: OrderValidationCallHandlerData handlerData = objectConfiguration as OrderValidationCallHandlerData;
8: return new OrderValidationCallHandler() { ValidateSupplier = handlerData.ValidateSupplier, ValidateTotalPrice = handlerData.ValidateTotalPrice };
9: }
10: }
11: }
OrderValidationCallHandlerAssembler派生自IAssembler<ICallHandler, CallHandlerData>,实现了Assemble方法。该方法用于收集的Configuration来创建所需的CallHandler。
到此为止,任务尚未结束,我们还需要将我们定义的CallHandler和HandlerData之间建立一个Mapping关系。这主要通过在CallHandler Class上运用ConfigurationElementType Attribute来实现。为此我们将此Attribute加在OrderValidationCallHandler上面:
1: namespace Artech.CustomCallHandlers
2: {
3: [ConfigurationElementType(typeof(OrderValidationCallHandlerData))]
4: public class OrderValidationCallHandler:ICallHandler
5: {
6: //...
7: }
8: }
Step VI 通过Configuration来使用CallHandler
现在我们就可以采用Configuration的方式来讲我们定义的OrderValidationCallHandler运用到我们所需的Method上。我们先去掉OrderProcessor. ProcessOrder上的OrderValidationCallHandlerAttribute。然后添加一个Application Configuration 文件,并进行如下配置:
1: <configuration>
2: <configSections>
3: <sectionname="policyInjection"type="Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.PolicyInjection.Configuration.PolicyInjectionSettings, Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.PolicyInjection, Version=3.1.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a" />
4: </configSections>
5: <policyInjection>
6: <policies>
7: <addname="Policy">
8: <matchingRules>
9: <addtype="Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.PolicyInjection.MatchingRules.MemberNameMatchingRule, Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.PolicyInjection, Version=3.1.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a" name="Member Name Matching Rule">
10: <matches>
11: <addmatch="ProcessOrder"ignoreCase="false" />
12: </matches>
13: </add>
14: </matchingRules>
15: <handlers>
16: <addtype="Artech.CustomCallHandlers.OrderValidationCallHandler, Artech.CustomCallHandlers"name="OrderValidationCallHandler"validateSupplier="true"validateTotalPrice="true"/>
17: </handlers>
18: </add>
19: </policies>
20: </policyInjection>
21: </configuration>
在policyInjection Configuration Section中添加了一个Policy(Policy=Matching Rule + Call Handler), 对于Matching Rule,我们采用的是基于Method Name的Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.PolicyInjection.MatchingRules.MemberNameMatchingRule。而我们定义的OrderValidationCallHandler则加在<handlers> element下,两个属性validateSupplier和validateTotalPrice直接置于其中。
我们再次运行我们的程序,我们的输出结果和上面的没有任何区别:

EnterLib PIAB系列:
Enterprise Library Policy Injection Application Block 之一: PIAB Overview
Enterprise Library Policy Injection Application Block 之二: PIAB设计和实现原理
Enterprise Library Policy Injection Application Block 之三: PIAB的扩展—创建自定义CallHandler(提供Source Code下载)
Enterprise Library Policy Injection Application Block 之四:如何控制CallHandler的执行顺序