pandas操作数据库
使用sqlite3
# 从数据库中读取数据。
import sqlite3
# sqlite3连接参数指定的数据库。如果数据库不存在,则会创建该数据库,然后再进行连接。
# 存在则直接进行连接。该方法返回数据库的连接。
con = sqlite3.connect("ttd.db")
# 通过数据库连接对象的execute方法执行sql语句。
con.execute("create table person(id varchar(32) primary key, name varchar(100) )")
# 向数据表中插入数据记录。
# con.execute("insert into person(id, name) values('1', 'bill')")
# con.execute("insert into person(id, name) values('2', 'li')")
# 提交之前的操作
# con.commit()
# 从数据中指定的sql中,读取数据。需要指定一个数据库的连接对象。
pd.read_sql("select id, name from person", con)使用pymysql
# 原理和sqlite3差不太多,只是连接方式不一样而已
import pymysql
con = pymysql.connect('localhost',
'root',
'eve136712',
db='model_save',
charset='utf8',
use_unicode=True)
cursor = con.cursor()
# 通过游标的execute方法执行sql语句。
cursor.execute("create table person(id varchar(32) primary key, name varchar(100) )")pandas读写数据库
- 1.根据库的文档,我们看到to_sql函数支持两类mysql引擎一个是sqlalchemy,另一个是sqlliet3.没错,在你写入库的时候,pymysql是不能用的!!!
- mysqldb也是不能用的,你只能使用sqlalchemy或者sqlliet3!!鉴于sqllift3已经很久没有更新了,这里建议使用sqlalchemy!!
- 2.to_sql函数并不在pd之中,而是在io.sql之中,是sql脚本下的一个类!!!所以to_sql的最好写法就是:
- pd.io.sql.to_sql(df1,tablename,con=conn,if_exists='repalce')
import pandas as pd
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
# 初始化数据库连接,使用pymysql模块
# MySQL的用户:root, 密码:147369, 端口:3306,数据库:test
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@localhost:3306/test')
# 查询语句,选出employee表中的所有数据
sql = ''' select * from employee; '''
# read_sql_query的两个参数: sql语句, 数据库连接
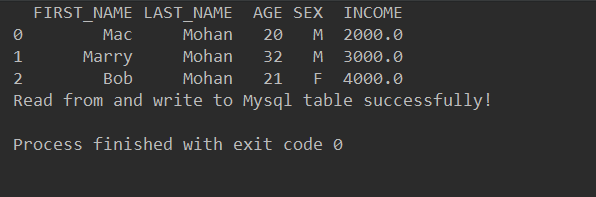
df = pd.read_sql_query(sql, engine)
# 输出employee表的查询结果
print(df)
# 新建pandas中的DataFrame, 只有id,num两列
df = pd.DataFrame({'id': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'name': ['zhangsan', 'lisi', 'wangwu', 'zhuliu']})
# 将新建的DataFrame储存为MySQL中的数据表,储存index列
df.to_sql('mydf', engine, index=True)
print('Read from and write to Mysql table successfully!')pandas将dataframe写入数据库
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 导入必要模块
import pandas as pd
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
# 初始化数据库连接,使用pymysql模块
db_info = {'user': 'root',
'password': '123456',
'host': 'localhost',
'port': 3306,
'database': 'test'
}
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://%(user)s:%(password)s@%(host)s:%(port)d/%(database)s?charset=utf8' % db_info, encoding='utf-8')
# 直接使用下一种形式也可以
# engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@localhost:3306/test')
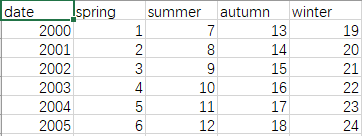
# 读取本地CSV文件
df = pd.read_csv("C:/Users/fuqia/Desktop/example.csv", sep=',')
print(df)
# 将新建的DataFrame储存为MySQL中的数据表,不储存index列(index=False)
# if_exists:
# 1.fail:如果表存在,啥也不做
# 2.replace:如果表存在,删了表,再建立一个新表,把数据插入
# 3.append:如果表存在,把数据插入,如果表不存在创建一个表!!
pd.io.sql.to_sql(df, 'example', con=engine, index=False, if_exists='replace')
# df.to_sql('example', con=engine, if_exists='replace')这种形式也可以
print("Write to MySQL successfully!")补充:engine.execute(sql)可以直接执行sql语句:
1 from sqlalchemy import create_engine
2
3
4 engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@localhost:3306/test')
5 sql = "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS example"
6 engine.execute(sql)如果用pymysql,则必须用cursor
import pymysql
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='123456', db='test')
# engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@localhost:3306/test')
sql = "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test_input"
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute(sql)