java并发原理实战(14)--自己实现简易web服务器
简易web服务器
- 0.web服务器知识储备
- 1.简易web服务器-版本1
- 2.简易web服务器版本2-多线程版
- 3.1简易web服务器版本3-访问图片资源
- 3.2简易web服务器版本3-访问外链地址测试
- 4.简易web服务器-版本4-连接池版
0.web服务器知识储备
web服务器知识储备,了解网络编程,其实就是java的socket。如果实现网络请求,也就是服务端能够接收客户端的请求,然后服务端再对客户端进行响应。响应的话需要按照http的请求格式,浏览器才能识别显示。
http的格式推荐文章
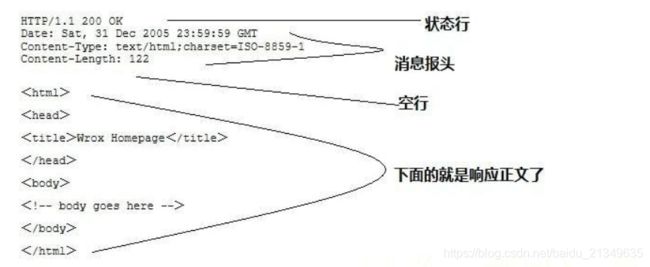
HTTP的请求包括:请求行(request line)、请求头部(header)、空行 和 请求数据 四个部分组成。
Http请求消息结构
抓包的request结构如下:
GET /mix/76.html?name=kelvin&password=123456 HTTP/1.1
Host: www.fishbay.cn
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_11_5) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/56.0.2924.87 Safari/537.36
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,/;q=0.8
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, sdch
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,en;q=0.6
1.请求行
GET为请求类型,/mix/76.html?name=kelvin&password=123456为要访问的资源,HTTP/1.1是协议版本
2.请求头部
从第二行起为请求头部,Host指出请求的目的地(主机域名);User-Agent是客户端的信息,它是检测浏览器类型的重要信息,由浏览器定义,并且在每个请求中自动发送。
3.空行
请求头后面必须有一个空行
4.请求数据
请求的数据也叫请求体,可以添加任意的其它数据。这个例子的请求体为空
Response
一般情况下,服务器收到客户端的请求后,就会有一个HTTP的响应消息,HTTP响应也由4部分组成,分别是:状态行、响应头、空行 和 响应体。
1.简易web服务器-版本1
之前的javaweb项目中,一般把项目放在tomcat的webapps目录或者直接放在ROOT根目录下,我们在浏览器输入服务器的地址和tomcat的端口号等信息就可以访问到服务器上的资源了。
现在我们要实现类似tomcat的web服务器功能:
假设我们本地就是服务器,现在就实现在浏览器输入个地址,访问到本地的某个盘符的资源的功能:
- 首先
在e盘建个webroot目录,我们的资源都放在这个目录下。
在这个文件下写个index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>index.html</title>
</head>
<body>
hello world
</body>
</html>
- 写web服务端代码:
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Date;
public class HttpServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//启动服务器,监听8888端口
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888);
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
//不停的接收客户端请求
Socket client = server.accept();
//获取输入流
InputStream ins = client.getInputStream();
OutputStream out = client.getOutputStream();
// int len = 0;
// byte[] b = new byte[1024];
// while ((len = ins.read(b)) != -1) {
// System.out.println(new String(b, 0, len));
// }
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(client.getInputStream()));
String line = reader.readLine();
System.out.println(line);
//给用户(客户端)响应
FileInputStream i = new FileInputStream("e:\\webroot\\index.html");
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(out);
BufferedReader fr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(i, "UTF-8"));
String c = null;
pw.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
pw.println("Content-Type: text/html;charset=utf-8");
pw.println("Content-Length: " + i.available());
pw.println("Server: hello");
pw.println("Date: " + new Date());
pw.println("");
pw.flush();
while ((c = fr.readLine()) != null) {
pw.println(c);
}
pw.flush();
fr.close();
pw.close();
reader.close();
client.close();
}
server.close();
}
}
关键的代码:需要按照http格式响应,客户端才能识别。
pw.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
pw.println("Content-Type: text/html;charset=utf-8");
pw.println("Content-Length: " + i.available());
pw.println("Server: hello");
pw.println("Date: " + new Date());
pw.println("");
pw.flush();
- 运行代码,这样我们就在服务端开放了8888端口,客户端请求去就可以了
- 在浏览器输入 http://localhost:8888/ 查看能否访问到index.html
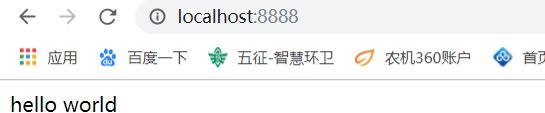
结果: 我们访问到了本地的index.html资源。
但是这里有个问题,只能请求一次,所以我们要进行优化,变成多线程版本。
2.简易web服务器版本2-多线程版
这里我们修改服务器端的代码
- 抽出一个单独响应客户端的线程类
mport java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Date;
public class ServerThread implements Runnable {
private Socket client;
private InputStream ins;
private OutputStream out;
private PrintWriter pw;
private BufferedReader br;
private void init() {
try {
ins = client.getInputStream();
out = client.getOutputStream();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public ServerThread(Socket client) {
this.client = client;
init();
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
go();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void go() throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(ins));
String line = reader.readLine();
System.out.println(line);
//给用户响应
FileInputStream i = new FileInputStream("e:\\webroot\\index.html");
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(out);
BufferedReader fr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(i, "UTF-8"));
String c = null;
pw.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
pw.println("Content-Type: text/html;charset=utf-8");
pw.println("Content-Length: " + i.available());
pw.println("Server: hello");
pw.println("Date: " + new Date());
pw.println("");
pw.flush();
while ((c = fr.readLine()) != null) {
pw.println(c);
}
pw.flush();
fr.close();
pw.close();
reader.close();
client.close();
}
}
- 服务端的主类
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class HttpServer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//启动服务器,监听8888端口
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888);
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
//不停的接收客户端请求
Socket client = server.accept();
new Thread(new ServerThread(client)).start();
}
server.close();
}
}
这样多线程版已完成,测试
打开多个浏览器窗口,都可以访问到index.html的资源:

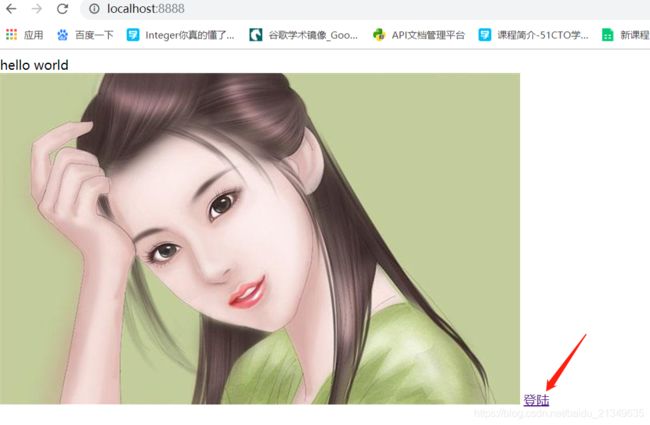
3.1简易web服务器版本3-访问图片资源
上面的index.html资源中,只有文字,如果我们修改下
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>index.htmltitle>
head>
<body>
hello world
<br>
<img src="1.jpg">
body>
html>

1.jpg图片如下:

现在修改代码,能够访问到图片,这样我们不能通过
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(out);
while ((c = fr.readLine()) != null) {
pw.println(c);
}
这段代码了,因为,这个只能读取文本,我们只能使用inputstream来读取二进制。同时,响应的时候content-type的响应头也不能固定为text/html了,要根据请求的资源动态修改,比如jpg的图片,后缀就应该是image/jpeg。
我们可以定义个缓存map进行动态赋值。
private static Map<String, String> contentMap = new HashMap<>();
static {
contentMap.put("html", "text/html;charset=utf-8");
contentMap.put("jpg", "image/jpeg");
}
浏览器访问的时候,可以看到打印的line为:
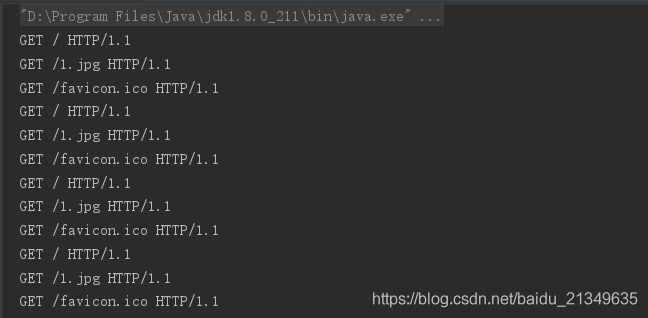
这其实就是http请求格式的第一行:

我们用空格分割,索引为1的就是资源,我们可以得到资源的后缀,给content-type动态赋值,如果直接就是\。我们可以手动改成index.html:
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(ins));
String line = reader.readLine().split(" ")[1].replace("/","\\");
if (line.equals("\\")){
line += "index.html";
}
System.out.println(line);
- 现在全部的修改如下
HttpServer2类代码不变,修改ServerThread
public class ServerThread implements Runnable {
private static final String webroot = "e:\\webroot\\";
private static Map<String, String> contentMap = new HashMap<>();
static {
contentMap.put("html", "text/html;charset=utf-8");
contentMap.put("jpg", "image/jpeg");
}
private Socket client;
private InputStream ins;
private OutputStream out;
private PrintWriter pw;
private BufferedReader br;
private void init() {
try {
ins = client.getInputStream();
out = client.getOutputStream();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public ServerThread(Socket client) {
this.client = client;
init();
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
go();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void go() throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(ins));
String line = reader.readLine().split(" ")[1].replace("/","\\");
if (line.equals("\\")){
line += "index.html";
}
System.out.println(line);
//给用户响应
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(out);
FileInputStream i = new FileInputStream(webroot + line);
// BufferedReader fr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(i, "UTF-8"));
String c = null;
pw.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
String s = line.substring(line.lastIndexOf(".")+1);
System.out.println(s);
pw.println("Content-Type: "+contentMap.get(s));
pw.println("Content-Length: " + i.available());
pw.println("Server: hello");
pw.println("Date: " + new Date());
pw.println("");
pw.flush();
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = i.read(buff)) != -1) {
out.write(buff, 0 , len);
}
pw.flush();
i.close();
pw.close();
reader.close();
client.close();
}
}
3.2简易web服务器版本3-访问外链地址测试
版本3,其实也可以访问到外链地址,我们测试下:
修改index.html
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>index.htmltitle>
head>
<body>
hello world
<br>
<img src="1.jpg">
<a href="login.html">登陆a>
body>
html>
我们在webroot下新建login.html
 login.html
login.html
<html>
<head>
<title>title>
head>
<body>
this is sign in html
这是登陆页面奥
body>
html>
4.简易web服务器-版本4-连接池版
上面的代码有啥问题吗,其实每次都是重新开个线程,比较消耗资源,我们可以使用连接池进行,管理,这样对以后的线程的监控,管理等都可以有效控制。阿里代码规范中,也有说到,凡是创建线程,必须通过,线程池,现在我们进行优化,其实只修改HttpServer2主类即可。
原来的代码:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class HttpServer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//启动服务器,监听8888端口
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888);
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
//不停的接收客户端请求
Socket client = server.accept();
new Thread(new ServerThread(client)).start();
}
server.close();
}
}
修改为:
public class HttpServer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//启动服务器,监听8888端口
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888);
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
//不停的接收客户端请求
Socket client = server.accept();
pool.execute(new ServerThread(client));
}
server.close();
}
}
现在简易的web服务器已经实现了,其实还有需要可以优化的地方。比如httpservet的支持等,tomcat的源码中可以多多去研读。
完