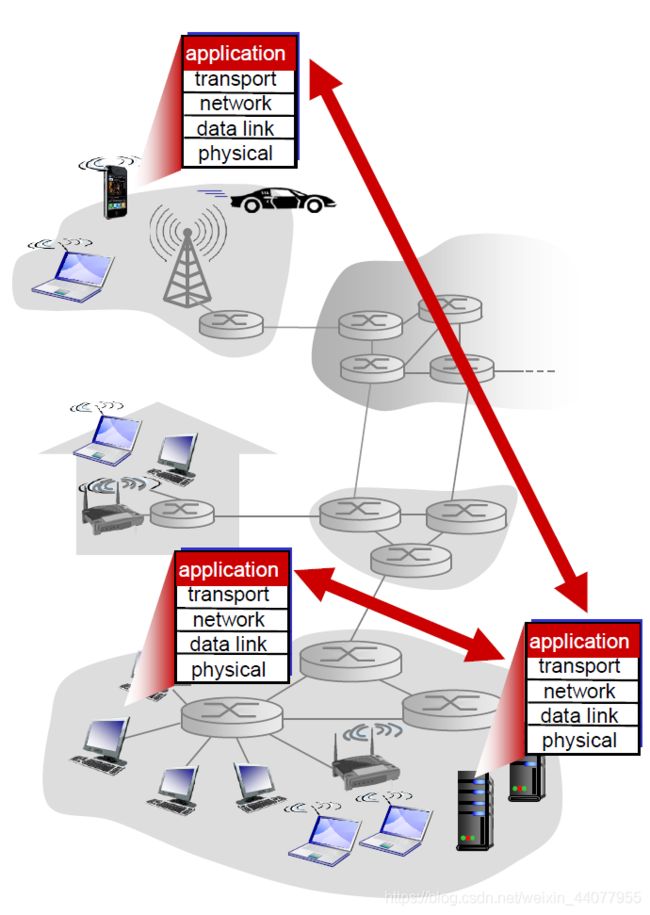
计算机网络-应用层笔记
计算机网络-应用层笔记
忧伤的小马:博客主页:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45504981
github传送门:https://github.com/rzy0901
文章目录
-
- 2.1 principles of network applications
- 2.2 Web and HTTP
- 2.3 electronic mail: SMTP,POP3,IMAP
- 2.4 DNS
- 2.5 P2P applications
- 2.6 Video streaming and content distribution networks (CDNs)
- 2.7 socket programming with UDP and TCP
- Reference:
2.1 principles of network applications
network apps:
-
Some network apps:
e-mail, web, text messaging, remote login, P2P file sharing, multi-user network games, streaming stored video(YouTube, Hulu, Netflix), voice over IP (e.g. Skype), real-time video conferencing, social networking, search.
-
- run on (different) end systems;
- communicate over network;
-
client-server:
- server: always on host, permanently ip, data centers for scaling.
- client: 可以断开,dynamic ip;
-
P2P:
- no always on server;
- arbitrary end systems;
- peers are intermittently connected and change IP addresses(断续连接,改变ip; )
- self-scalability.
Process, socket(套接字):
-
Who?: Process send/receive message to/from network.
-
Where?: Process send/receive message to/from sockets.
-
Process with same hosts: inter-process communication( defined by OS)
P2P 既有server process 又有 client process.
IP and Port number
-
process has identifier (both ip address and port numbers)
-
32-bit ip address.
-
many processes run on same host.
所以需要端口?
-
Example port number:
- HTTP server: 80;
- Mail server: 25;
Internet transfer protocols service
TCP UDP 是传输层协议
-
TCP service:
-
Reliable transport; Flow control; Congestion control; Connection-oriented;
-
Dose not provide timing, minimum throughput guarantee, and security.
-
-
UDP service:
- Unreliable data transfer.
- Does not provide: reliability, flow control, congestion control, timing, throughput guarantee, security, or connection setup.
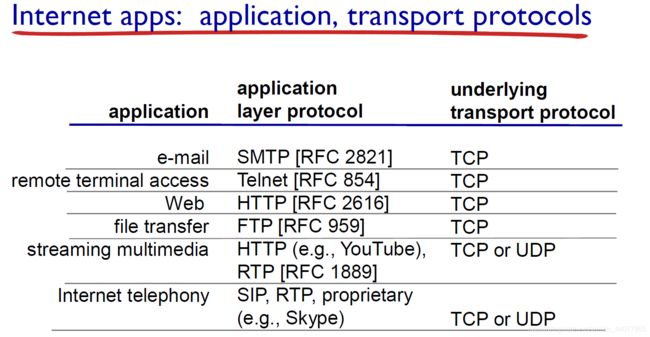
2.2 Web and HTTP
Web
-
Web page consists of objects.
object can be HTML file, JPEG image, Java applet, audio file,…
-
web page consists of base HTML-file which includes several referenced objects.
-
Each object is addressable by a URL.
HTML 基本文件 (bases HTML-file) 通过对象的URL地址引用页面中的对象。
HTTP overview
-
Hypertext transfer protocol
-
Web’s application layer protocol (应用层协议)
-
client/server mode.
-
uses TCP.(步骤从上到下1、2、3)
HTTP messages exchangedHTTP messages exchangedclient initiate TCP connectionserver accepts TCP connection from clientbrowser (HTTP client)Web server (HTTP server)TCP connection closed -
HTTP is stateless .
server maintains no information about past client request.
HTTP connection
-
non-persistent HTTP: (非持续连接HTTP)
At most one object sent over TCP connection.
Connection then closed.
Downloading multiple objects required multiple connections.
一个connection传一个object. 每传完object都会关闭connection.
-
persistent HTTP: (持续连接HTTP)
multiple objects can be sent over single TCP connection between client, server.
一个connection传多个object.
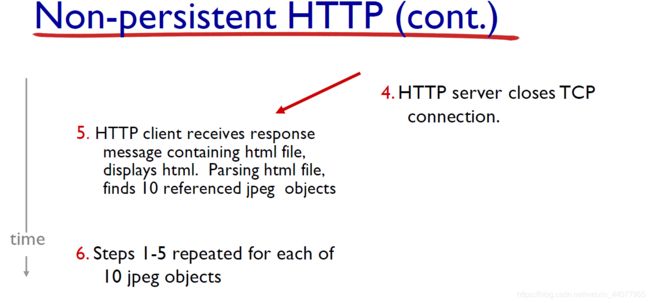
Non-persistent HTTP
第4步,HTTP server 通知TCP断开connection,但是直到TCP确认客户完整收到响应报文为止,它才会实际中断连接。
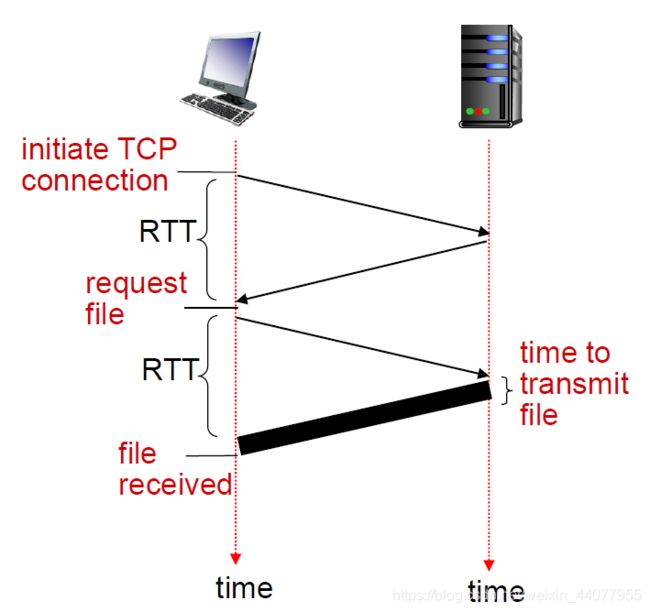
Non-persistent HTTP: response time
-
RTT (definition): time for a small packet to travel from client to server and back.
传输一个packet往返的时间。
-
Non-persistent HTTP: response time = 2*RTT+file transmission time.
Persistent HTTP
server leaves connection open after sending response.
One RTT needed.
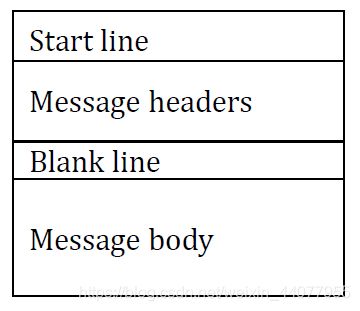
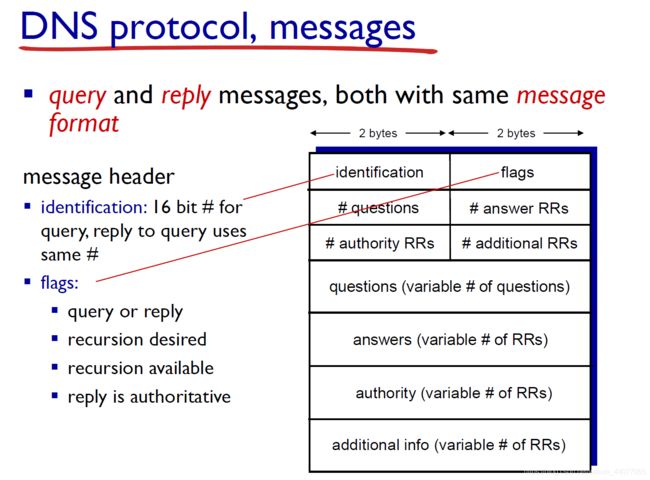
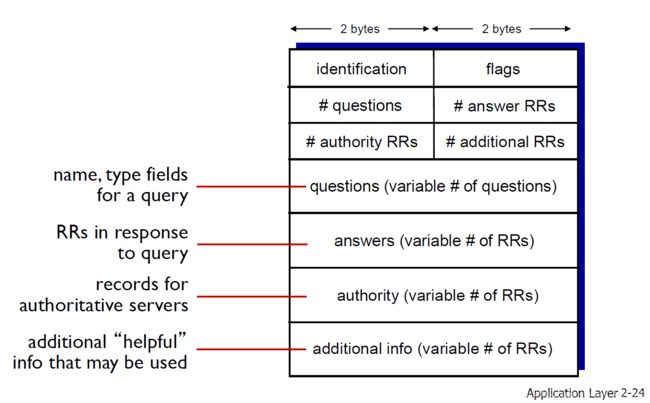
HTTP message
HTTP request message
-
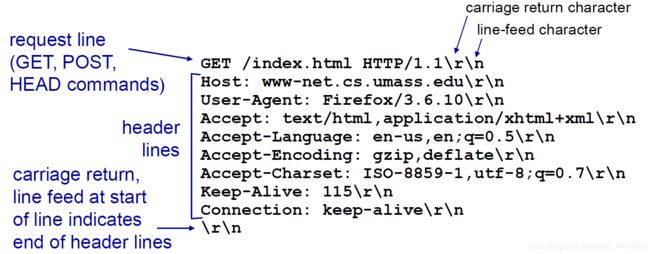
CR: carriage return;(回车) LF: line feed(换行) 其实就是\r\rn
request line coding = ASCII (human-readable format)
request line = method + url + http version
Uploading form input: POST method, URL method.
Method types:
-
HTTP/1.0:
GET. POST, HEAD
-
HTTP/1.1:
GET,POST,HEAD.
PUT, DELETE.(上传或删除指定URL文件)
-
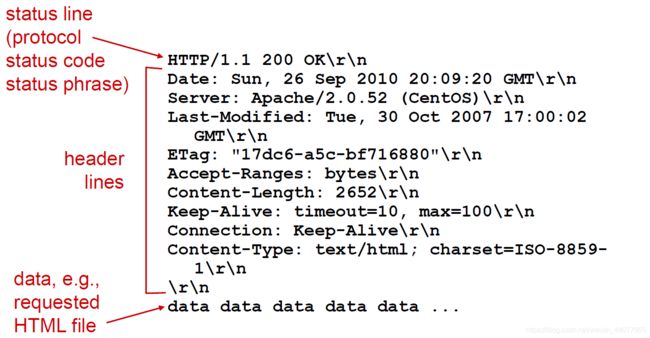
HTTP response messages
User-server state: Cookies
-
Four components for “cookie”: (对应下图蓝色圆柱)
- cookie header line in HTTP response message.
- cookie header line in next HTTP request message.
- cookie file kept on user’s host, managed by user’s browser.
- back-end database at Web site.
第一次request没有cookie, 创建ID:1678,返回response message (cookie header line: Set cookie:1678)
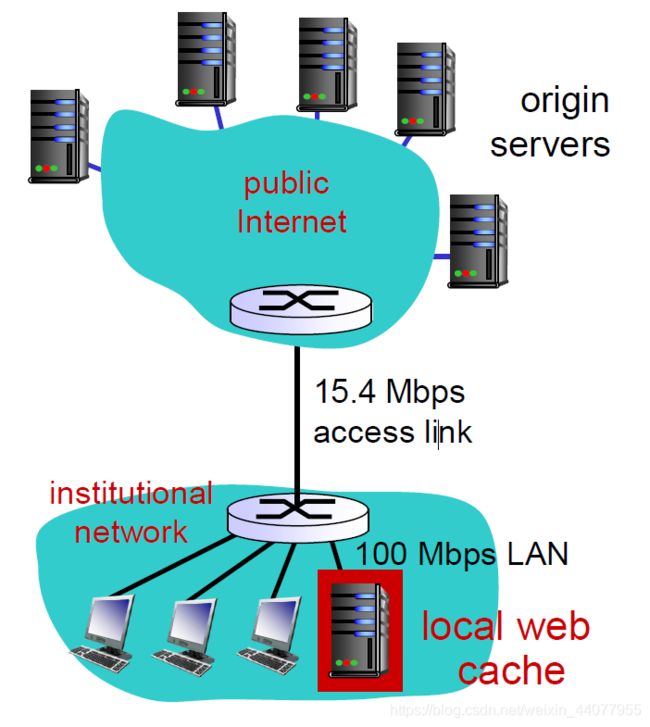
Web caches (proxy server) 缓存器、代理服务器
goal: satisfy client request without involving origin server
if HTTP request in cache:
return HTTP response from cache
else:
cache requests object from origin server
then return object to client
Cache acts as server for original requesting client.
Cache acts as client to origin server.
Lower link utilization, lower delay.
Typically cache is installed by ISP (university, company, residential ISP).
1.减少响应时间 2.减少“交通压力”3.使内容提供商更加有效传输数据Example:
Conditional GET
Goal: don’t send object if cache has up-to-date cached version
cache: specify date of cached copy in HTTP request:
- If-modified-since:
server: response contains no object if cached copy is up-to-date:
- HTTP/1.0 304 Not Modified
2.3 electronic mail: SMTP,POP3,IMAP
Electronic mail:
-
Three major components:
- user agent;
- mail server;
- SMTP (simple mail transfer control);
-
User agent:
-
composing, editing, reading mail messages;
-
outgoing, incoming messages stored on server;
mailbox : incoming messages
message queue: outgoing messages
-
-
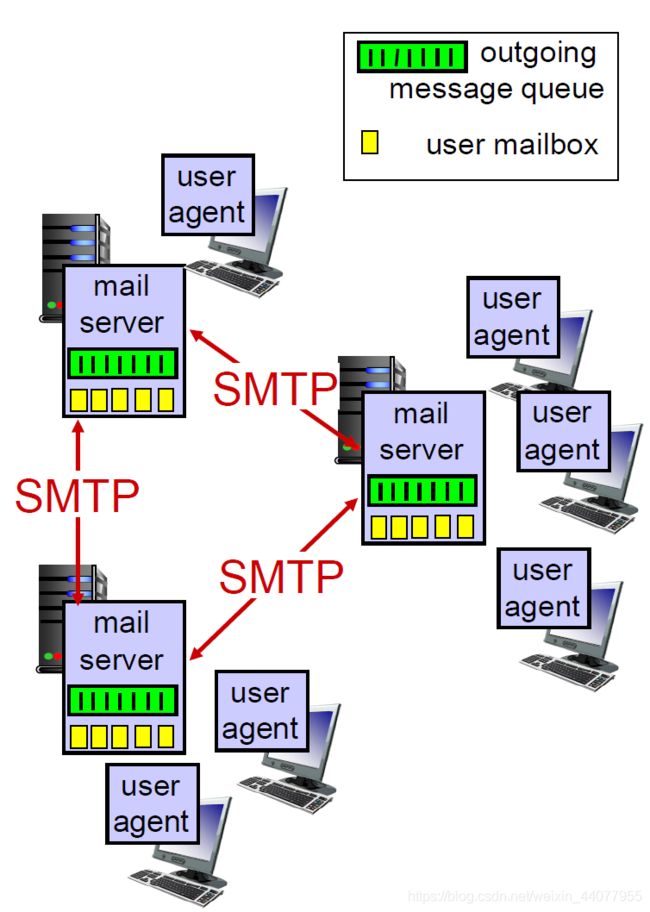
Mail server:
- mailbox contains incoming messages for user;
- message queue of outgoing (to be sent) mail messages;
- SMTP protocol between mail servers to send email messages;
Scenario:
(1)Alice uses UA to compose message to [email protected];
(2)Alice’s UA sends message to her mail server; message placed in message queue;
(3)client side of SMTP opens TCP connection with Bob’s mail server;
(4)SMTP client sends Alice’s message over the TCP connection;
(5)Bob’s mail server places the message in Bob’s mailbox;
(6)Bob invokes his user agent to read message;
Electronic Mail: SMTP
-
uses TCP to reliably transfer email message from client to server, port 25;
-
direct transfer: sending server to receiving server;
-
three phases of transfer:
-
handshaking (greeting);
-
transfer of messages;
-
closure;
-
-
command/response interaction (like HTTP):
- commands: ASCII text
- response: status code and phrase
-
messages must be in 7-bit ASCII;
-
SMTP uses persistent connections;
-
\r\n.\r\ndetermines end of message.
三次握手以后,连接建立成功,服务器推送就绪信息:
- 220: 服务就绪
server: 交代认证服务器域名,发件者邮箱,收件者邮箱:
- 250
client: 发送
DATA\r\nserver: 服务器返回354,表示自己已经作好接受邮件的准备.
client: 客户端发送邮件正文
client: 正文结束符
.server: 服务端返回250表示成功。
client: 邮件发送结束,客户端请求断开连接。 发送
QUIT\r\nserver: 服务器返回211,提示断开申请被采纳,并主动断开连接,整个邮件发送过程结束。
SMTP vs HTTP
-
SMTP: push (推协议)
HTTP: pull (拉协议)
-
both have ASCII command/response interaction, status codes;
-
HTTP: each object encapsulated in its own response message;
网页上每个object都有自己的url链接?
-
SMTP: multiple objects sent in multipart message;
邮件很多附件?
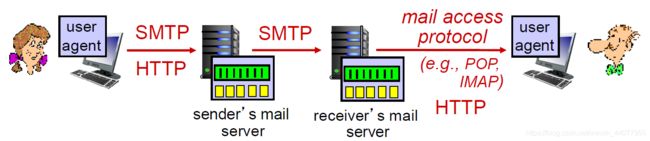
Mail access protocols (邮件访问协议)
-
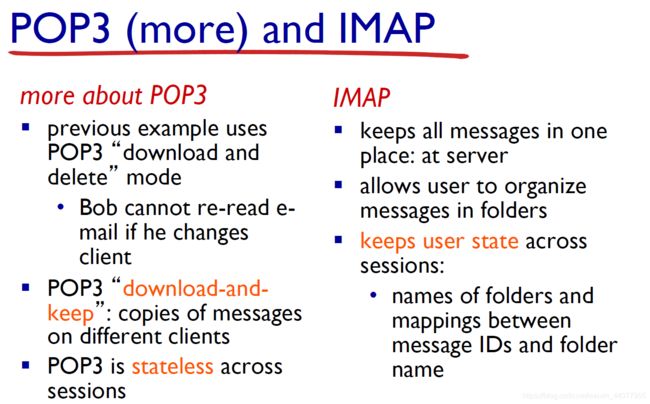
POP: Post Office Protocol [RFC 1939]: authorization, download.
-
IMAP: Internet Mail Access Protocol [RFC 1730]: more features, including manipulation of stored messages on server.
2.4 DNS
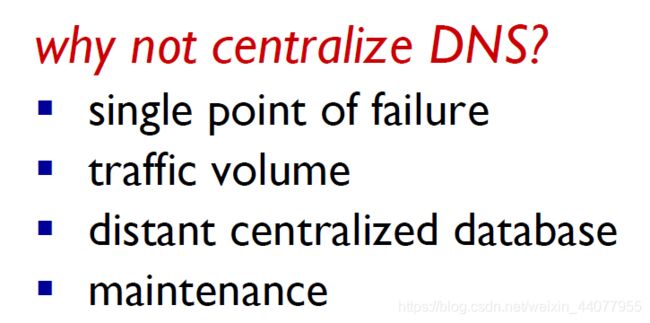
Domain Name system:
-
distributed database implemented in hierarchy of many name servers.
-
application-layer protocol: hosts, name servers communicate to resolve names (address/name translation)
域名,ip映射
DNS service:
-
Host name to ip address translation.
-
Host aliasing.
-
Mail server aliasing.
-
Load distribution.
replicated Web servers: many IP addresses correspond to one name.
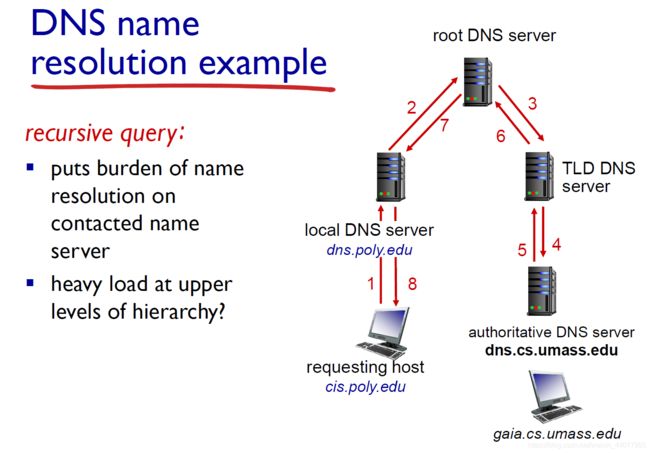
DNS: a distributed, hierarchical database:

查询 www.amazon.com ip地址:
- 查询root dns server返回com DNS server
- 查询 .com DNS server返回 amazon.com DNS server;
- 查询 amazon.com DNS server 得到 www.amazon.com ip地址;
查询 www.sustech.edu.cn ip地址:
- root dns server 返回 cn;
- top 返回 edu.cn;
- authoritative 返回 sustech.edu.cn ➡️ www.sustech.edu.cn;
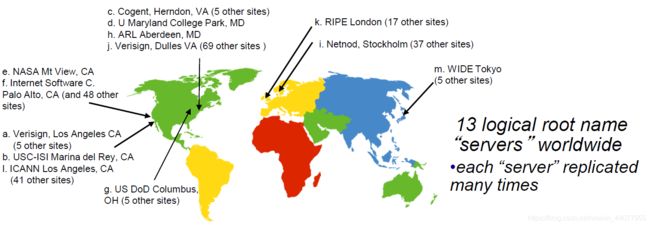
DNS servers
-
root name servers (根DNS服务器);
- contacts authoritative name server if name mapping not known
- gets mapping
- returns mapping to local name server
-
top-level domain (TLD) servers (顶级域服务器);
com org net edu aero cn
-
Authoritative DNS servers(权威DNS服务器);
- organization’s own DNS servers
- providing authoritative hostname to IP mappings for organization’s named hosts
- can be maintained by organization or service provider
-
Local DNS name server. (default name server)
2.5 P2P applications
Pure P2P architecture:
-
no always on server;
-
arbitrary end systems;
-
peers are intermittently connected and change IP addresses(断续连接,改变ip; )
-
self-scalability.
examples:
- file distribution (BitTorrent)
- Streaming (KanKan)
- VoIP (Skype)
File distribution:
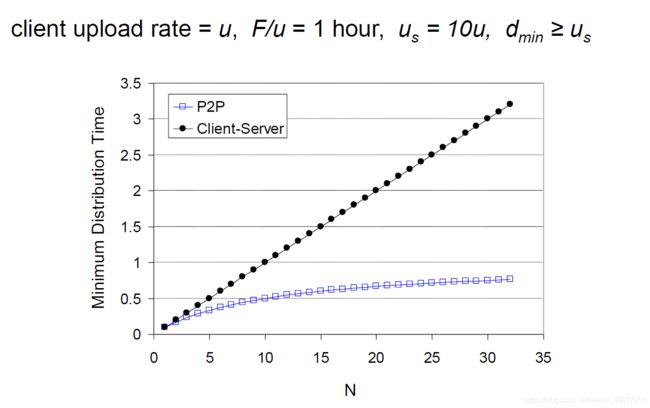
Question: how much time to distribute file (size F) from one server to N peers?
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| u s u_s us | server upload capacity |
| u i u_i ui | peer i i i upload capacity |
| d i d_i di | peer i i i download capacity |
| d m i n d_{min} dmin | minimum download capacity: d m i n = m i n { d 1 , d 2 , . . . , d N } d_{min}=min\{d_1,d_2,...,d_N\} dmin=min{ d1,d2,...,dN} unit: b i t s / s e c bits/sec bits/sec |
| D c − s D_{c-s} Dc−s | time to distribute F F F to N N N clients |
| F F F | File size |
- For client server model:
D c − s ≥ m a x { N F / u s , F / d m i n } D_{c-s}\geq max\{NF/u_s,F/d_{min}\} Dc−s≥max{ NF/us,F/dmin}
N 足够大,由 N F / u S NF/u_S NF/uS决定
- For P2P model:
D c − s ≥ m a x { F / u s , F / d m i n , N F / ( u s + ∑ u i ) } D_{c-s}\geq max\{F/u_s,F/d_{min},NF/(u_s+\sum u_i)\} Dc−s≥max{ F/us,F/dmin,NF/(us+∑ui)}
极限为: m a x { F / u s , F / d m i n , F / u i m i n } max\{F/u_s,F/d_{min},F/u_{i_{min}}\} max{ F/us,F/dmin,F/uimin}
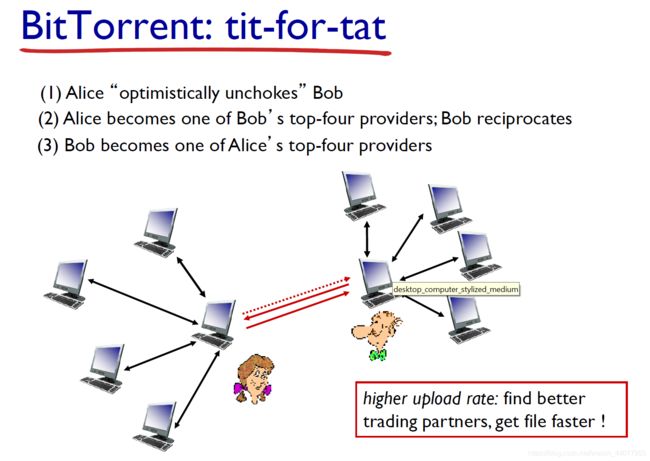
P2P file distribution: BitTorrent
- file divided into 256 Kb chunks.
- peers in torrent send/receive file chunks.
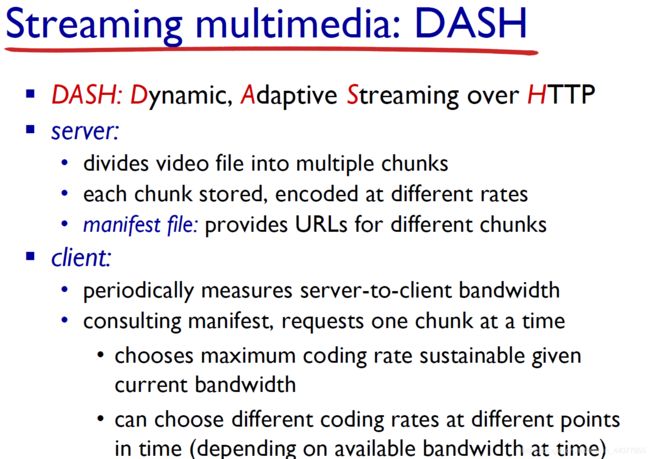
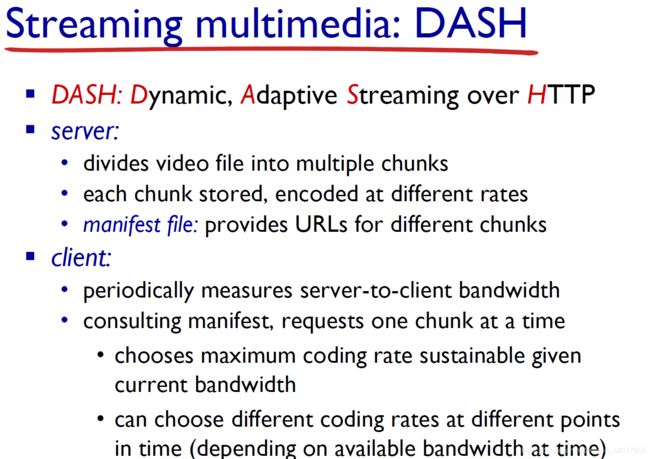
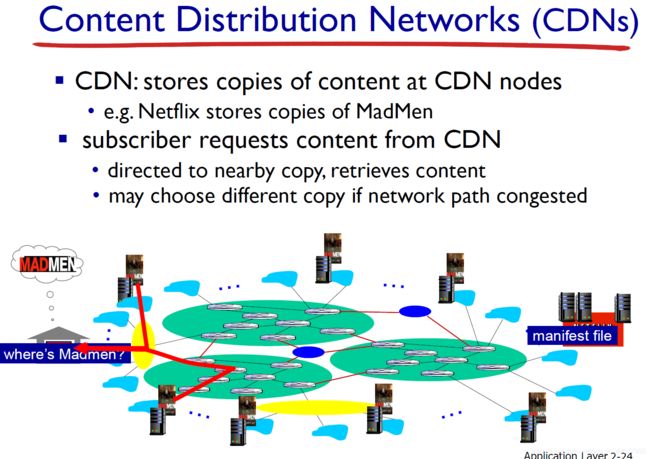
2.6 Video streaming and content distribution networks (CDNs)
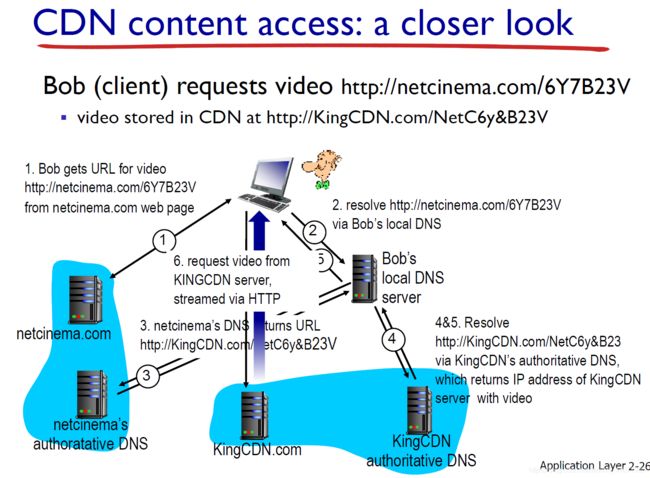
Bob通过local dns server访问netcinema,netcinema给了他一个新的url --> Bob 通过新的url 访问资源。
2.7 socket programming with UDP and TCP
略
- 转载请注明出处:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44077955/article/details/112125922
文章难免有疏漏错误之处,欢迎私信博主及时更正,大家共同进步。
Reference:
①:计算机网络-自顶向下方法
②:http://gaia.cs.umass.edu/kurose_ross/ppt.htm