ThreadLocal源码分析
ThreadLocal源码分析
-
- ThreadLocal简介
- ThreadLocal结构图
- ThreadLocal中的变量定义以及说明
- ThreadLocalMap中的变量定义以及说明
- Hash算法简单认识
- Thread中散列表的应用
-
- Hash碰撞的解决办法
- ThreadLocal.set()
-
- ThreadLocalMap.set()
- ThreadLocalMap.replaceStaleEntry()
- ThreadLocalMap.expungeStaleEntry()
- ThreadLocalMap.cleanSomeSlots()
- ThreadLocalMap.rehash()
- ThreadLocalMap.resize()
- ThreadLocal.get()
-
- ThreadLocalMap.getEntry()
- ThreadLocalMap.getEntryAfterMiss()
- ThreadLocal.remove()
- 总结
ThreadLocal简介
源码注释第一句:This class provides thread-local variables.
第一句话就概括了该类的用途,即此类提供线程局部变量
这些局部变量的不同之处在于:每个线程都拥有私有的独立初始化副本
通常存储与线程相关联类中的静态字段,例如:用户id、订单id等等。
线程的ID是在第一次调用{@code ThreadId.get()}时分配的并在后续使用中保持不变
一句话总结:线程私有变量副本,且该线程后续可以继续使用这些变量
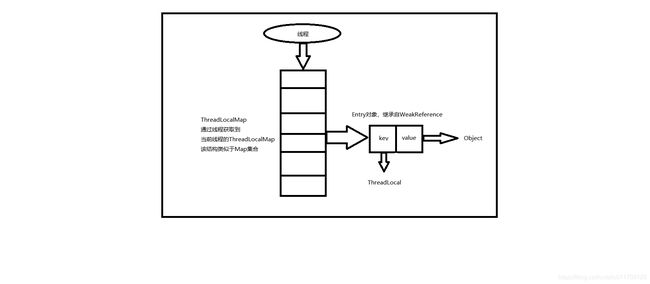
ThreadLocal结构图
ThreadLocal中的变量定义以及说明
/**
* ThreadLocals rely on per-thread linear-probe hash maps attached
* to each thread (Thread.threadLocals and
* inheritableThreadLocals). The ThreadLocal objects act as keys,
* searched via threadLocalHashCode. This is a custom hash code
* (useful only within ThreadLocalMaps) that eliminates collisions
* in the common case where consecutively constructed ThreadLocals
* are used by the same threads, while remaining well-behaved in
* less common cases.
*/
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
/**
* The next hash code to be given out. Updated atomically. Starts at
* zero.
*/
private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode =
new AtomicInteger();
/**
* The difference between successively generated hash codes - turns
* implicit sequential thread-local IDs into near-optimally spread
* multiplicative hash values for power-of-two-sized tables.
*/
private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
/**
* Returns the next hash code.
*/
private static int nextHashCode() {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);
}
| 项目 | Value |
|---|---|
| threadLocalHashCode | 相同的线程使用自定义的哈希码,在ThreadLocalMaps中消除冲突,ThreadLocal对象充当键,通过threadLocalHashCode搜索,解决hash碰撞; |
| AtomicInteger | CAS方式原子操作,位于java.util.concurrent.atomic; |
| HASH_INCREMENT | 连续生成的哈希码之间的区别-将隐式顺序线程本地ID转换为几乎最佳的散布,二乘幂表的乘法哈希值 ,此数值用于做散列hashCode,此数值是一个黄金分割比例数值,需要了解斐波那契数列; |
| nextHashCode | 以CAS原子操作的方式,生成下一个hash code,也就是累加 HASH_INCREMENT |
ThreadLocalMap中的变量定义以及说明
/**
* The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using
* its main ref field as the key (which is always a
* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()
* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the
* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to
* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.
*/
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
/**
* The initial capacity -- MUST be a power of two.
*/
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
/**
* The table, resized as necessary.
* table.length MUST always be a power of two.
*/
private Entry[] table;
/**
* The number of entries in the table.
*/
private int size = 0;
/**
* The next size value at which to resize.
*/
private int threshold; // Default to 0
| 项目 | Value |
|---|---|
| Entry | ThreadLocal中定义的存储结构,也就是key::value键值对,其中key是ThreadLocal对象本身,value是Object基类,由于Entry继承自WeakReference并且将ThreadLocal设置为弱引用,这会是导致内存溢出的关键所在,举个例子,key被gc回收了,value并没有被回收,大量使用就会导致内存越来越大,也并不会被回收释放资源,就会导致内存溢出; |
| INITIAL_CAPACITY | 默认设置Entry数组大小,默认值=16; |
| table | 可调整数组大小,但是长度必须为2的幂,也就是2^n。; |
| size | 表中的条数,有1条数据就是1,2条数据就是2; |
| threshold | 下一个要调整大小的大小值,当size条数达到该值时,需要调整table的大小,该值通常为table.size()值的三分之二的大小,如table容量为16,则该值为10.66…6无限; |
Hash算法简单认识
简单介绍一下Hash算法的原理,深入探究请移步隔壁
Hash,一般翻译做散列、杂凑,或音译为哈希,是把任意长度的输入(又叫做预映射pre-image)通过散列算法变换成固定长度的输出,该输出就是散列值。这种转换是一种压缩映射,也就是,散列值的空间通常远小于输入的空间,不同的输入可能会散列成相同的输出,所以不可能从散列值来确定唯一的输入值。简单的说就是一种将任意长度的消息压缩到某一固定长度的消息摘要的函数。
Hash算法特点
- Hash算法可以将一个数据转换为一个标志,这个标志和源数据的每一个字节都有十分紧密的关系。Hash算法还具有一个特点,就是很难找到逆向规律。
- Hash算法是一个广义的算法,也可以认为是一种思想,使用Hash算法可以提高存储空间的利用率,可以提高数据的查询效率,也可以做数字签名来保障数据传递的安全性。所以Hash算法被广泛地应用在互联网应用中。
- Hash算法也被称为散列算法,Hash算法虽然被称为算法,但实际上它更像是一种思想。Hash算法没有一个固定的公式,只要符合散列思想的算法都可以被称为是Hash算法。
散列表(Hash table,也叫哈希表),是根据关键码值(Key value)而直接进行访问的数据结构。也就是说,它通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。这个映射函数叫做散列函数,存放记录的数组叫做散列表
散列表的查找过程基本上和造表过程相同。一些关键码可通过散列函数转换的地址直接找到,另一些关键码在散列函数得到的地址上产生了冲突,需要按处理冲突的方法进行查找。在介绍的三种处理冲突的方法中,产生冲突后的查找仍然是给定值与关键码进行比较的过程。所以,对散列表查找效率的量度,依然用平均查找长度来衡量。
查找过程中,关键码的比较次数,取决于产生冲突的多少,产生的冲突少,查找效率就高,产生的冲突多,查找效率就低。因此,影响产生冲突多少的因素,也就是影响查找效率的因素。
影响产生冲突多少有以下三个因素:
- 散列函数是否均匀;
- 处理冲突的方法;
- 散列表的装填因子。
Thread中散列表的应用
// 定义结构体,key-value结构的,而且key是弱引用类型
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
/**
* ThreadLocalMap的构造方法,也是初始赋值填充
*/
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];//Entry数组 INITIAL_CAPACITY 默认=16
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1); // 计算第一个hash值作为第一个key的下标
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue); // Entry数组填充数据
size = 1; // size为当前Entry数组中有效数据的大小
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY); // 当前Entry数组大小的2/3,也就是16的2/3
}
/**
* Set the resize threshold to maintain at worst a 2/3 load factor.
*/
private void setThreshold(int len) {
//threshold 设置为当前Entry数组大小的2/3,扩容阈值
threshold = len * 2 / 3;
}
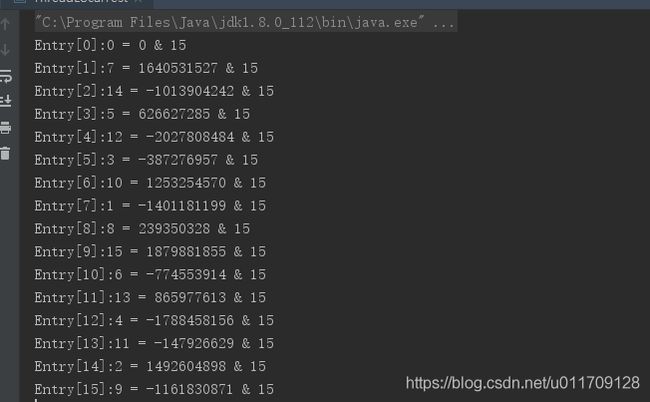
手写代码ThreadLocal计算Hash分布值
使用ThreadLocal的计算方式,给某数组进行下标计算
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* @author Alex
* @description: ThreadLocal计算Hash分布值
* @date 2020/12/18 18:20
*/
public class ThreadLocalTest {
static int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647; // 黄金比例分割数
private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode = new AtomicInteger();
/**
* 进行累计相加HASH_INCREMENT
*
* @return
*/
private static int nextHashCode() {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
getHash(16);
}
public static void getHash(int length) {
int threadLocalHashCode;
int hashLen = length - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
int nextLength = threadLocalHashCode & hashLen ; // 将两个数据转换二进制,“按位与”计算,相同得1不同得0 ,然后将二进制转换为十进制
System.out.println("Entry[" + i + "]:" + nextLength + " = " + threadLocalHashCode + " & " + hashLen);
}
}
}
数组Entry[i]的分布相当均匀,但是如果出现元素下标相同的怎么办呢?就会出现Hash碰撞的问题。
Hash碰撞的解决办法
- 开放寻址法 : 当发生地址冲突时,按照某种方法继续探测哈希表中的其他存储单元,直到找到空位置为止。适用冲突比较少的情况(ThreadLocal用的开放寻址法)
- 再散列法
- 链地址法(拉链法):HashMap中有实现,该方法适用冲突比较多的情况
- 建立一个公共溢出区
ThreadLocal中扩容的时候解决碰撞问题
private void resize() {
/**省略上面部分代码**/
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1); // 重新计算Hash
// 线性探测与赋值
while (newTab[h] != null) //线性探测,若h元素冲突,则h+1,直到找到空的位置
h = nextIndex(h, newLen); // h+1
newTab[h] = e; // 赋值
/**省略下面部分代码**/
}
/**
* Increment i modulo len.
* 判断元素下标i 与 数组长度len
* 三元运算,若i+1 小于 len 长度,则 i + 1 作为元素下标, 否则为下标为0
*/
private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) {
return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0);
}
ThreadLocal.set()中还有针对碰撞的逻辑,下面介绍ThreadLocal.set()
ThreadLocal.set()
此处大量注释,注意跟踪方法顺序,每个方法上都会写一些主要跟踪方法,主要跟踪方法
ThreadLocal.set()方法中相对比较简单,仅是判断线程中是否有ThreadLocalMap对象
如果有就往里面添加当前ThreadLocal
没有就创建一个新的对象,并赋予初始值ThreadLocal
/**
* 获取线程中的ThreadLocalMap对象
* Thread对象中定义了一个 ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
* 主要跟踪方法: map.set(this, value)
*/
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); // 获取当前线程
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); // Thread线程中存储了ThreadLocalMap对象,方便线程直接可以获取该对象
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value); // 调用的是ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap.set()方法
else
createMap(t, value); // 直接调用ThreadLocalMap的构造方法
}
/**
* 获取线程中的ThreadLocalMap对象
* Thread对象中定义了一个 ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
*/
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
/**
* ThreadLocalMap的构造方法,主要是初始化和填充第一个value
*/
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
ThreadLocalMap.set()
ThreadLocalMap.set()方法的前提是已经存在有ThreadLocalMap
在原有的ThreadLocalMap基础上进行赋值操作,往table里面添加数据
1、int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); // 计算当前ThreadLocal的元素下标
2、for循环,从i下标开始遍历数组,数组中i元素值,为空跳出循环,若Hash均匀没有碰撞,则不进循环
3、 if (k == key) 判断是否同一个ThreadLcocal,若是相同的,直接覆盖
4、replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);//是用来回收key = null的数据,否则不进该方法
5、有个隐藏的逻辑,就是出现碰撞,但不是同一个ThreadLocal,k!=key,直接Entry覆盖
6、tab[i]赋值,并且size+1
7、最后if(清除“i”至“size”之间的插槽后 ,并且table数据达到threshold阈值) 重新整理table
/**
* ThreadLocal中给map赋值的set
* 主要跟踪方法:
* replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i)
* cleanSomeSlots(i, sz)
* rehash()
*/
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table; // 获得对象数组
int len = tab.length; // 获得当前数组长度
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); // 计算当前ThreadLocal的元素下标
// 从i下标开始遍历数组,数组中i元素值,为空跳出循环,若Hash均匀没有碰撞,则不进循环
// 此处for循环是用于解决碰撞冲突使用的,若无冲突,则不进循环
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
// Entry[i+1 or 0] 出现碰撞,则i+1 or 0
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
// 比较数组中 k == 当前set的 key ,它们都是ThreadLocal
if (k == key) {
e.value = value; // 简单粗暴,相同key则直接value覆盖,return
return;
}
if (k == null) {
//数组中k(Entry[i].get())为空,也就是Entry中的key为空
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);//回收陈旧数据
return;
}
//有个隐藏的逻辑,就是出现碰撞,但不是同一个ThreadLocal,k!=key,直接Entry覆盖
}
// 给数组下标i赋值,直接覆盖
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;//数组长度+1 ++size是先加1后赋值 size++是先赋值后加1
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold) // 若清理过table中的数据,并且数组大小超过threshold阈值,则需要重新整理
rehash();// 重新整理table
}
ThreadLocalMap.replaceStaleEntry()
ThreadLocalMap.replaceStaleEntry() 替换陈旧的Entry,Entry.key=null被回收掉的,key是ThreadLocal对象,弱引用对象会被GC自动回收
第一个for循环,“i”元素递减获取e.get = null 的最小元素“i” ,赋值给slotToExpunge
第二个for循环,“i”元素递增,table遍历匹配Entry.get() == key
/**
*
* 主要跟踪方法:
* cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len)
* expungeStaleEntry()
* cleanSomeSlots()
*/
private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value,int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
Entry e;
int slotToExpunge = staleSlot; // 默认设置为staleSlot
/** 从staleSlot开始,向前遍历,第一次是staleSlot-1,获得key=null的最小下标,并赋予slotToExpunge **/
for (int i = prevIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = prevIndex(i, len))
if (e.get() == null)
slotToExpunge = i;
/**从staleSlot开始,向后遍历,第一次是staleSlot+1,仅遍历当tab[i]!=null **/
for (int i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value; // 与Hash计算下标staleSlot相同key时,覆盖其value
// staleSlot是Hash计算的下标,将覆盖值后的Entry与其交换位置
tab[i] = tab[staleSlot];
tab[staleSlot] = e; // 相当于set(key,value)到Hash指定位置
/** 当向前遍历,与向后遍历,找到的都是同一个 **/
if (slotToExpunge == staleSlot) // 如果key=null是同一个Entry[i]
slotToExpunge = i;
cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);
return;
}
/** 若当前元素k=null,且向前遍历,与向后遍历,找到的都是同一个 **/
if (k == null && slotToExpunge == staleSlot)
slotToExpunge = i;
}
tab[staleSlot].value = null; // 清空陈旧数据
tab[staleSlot] = new Entry(key, value);
/** 如果运行中还有其他任何陈旧的条目,请清除它们 **/
if (slotToExpunge != staleSlot)
cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);
}
/**
* Decrement i modulo len.
* 递减i值,直至i为0
*/
private static int prevIndex(int i, int len) {
return ((i - 1 >= 0) ? i - 1 : len - 1);
}
ThreadLocalMap.expungeStaleEntry()
ThreadLocalMap.expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) 清理过期Entry
staleSlot为清理标记点
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// 元素[staleSlot] 里的数据清空,且table.size-1
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = null;
size--;
Entry e;
int i;
// 向后遍历table,第一次 i = staleSlot+1
for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
// 遍历时,遇到key = null,清空数据
e.value = null;
tab[i] = null;
size--;
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1); // 重新计算hsah
if (h != i) {
// 重新计算后与当前下标不冲突
tab[i] = null;// 原数据设置为null
// Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until
// null because multiple entries could have been stale.
while (tab[h] != null) //线性探测,若h元素冲突,则h+1,直到找到空的位置
h = nextIndex(h, len);
tab[h] = e; //将重新计算Hash后的元素下标赋予新值
}
}
}
return i;//返回遍历最后的元素下标
}
ThreadLocalMap.cleanSomeSlots()
cleanSomeSlots() //清除一些插槽数据
主要判断 e有值,但e的key = null 被回收过的,将其清理
/**
* 清除一些插槽数据
* @return 如果已删除任何过时的条目,则为true
*/
private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) {
boolean removed = false;
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
do {
i = nextIndex(i, len);
Entry e = tab[i];
// 判断 e有值,但e的key = null 被回收过的,将其清理
if (e != null && e.get() == null) {
n = len;
removed = true;
i = expungeStaleEntry(i); // 将该值清除,且内部重新计算hash值
}
} while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0);// n为table长度,n >>>= 1 右移1位并赋值,至到n = 0
return removed;
}
ThreadLocalMap.rehash()
重新整理table
首先首先扫描整个表删除过时的条目。
如果这还不够缩小表的大小,将表的大小增加一倍。
private void rehash() {
expungeStaleEntries();
// Use lower threshold for doubling to avoid hysteresis
if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4) // 扩容判断
resize();// 扩容
}
ThreadLocalMap.resize()
当table达到阈值,则需要扩容增加表的大小,以避免Hash冲突
threshold为扩容阈值
table必须是2的平方倍数大小,这样计算的Hash比较均匀
private void resize() {
Entry[] oldTab = table;
int oldLen = oldTab.length;
int newLen = oldLen * 2;
Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen]; // 创建新的tab
int count = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) {
Entry e = oldTab[j];
if (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
// 遍历旧的tab,当key = null,则清空
e.value = null; // Help the GC
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1);// 重新计算Hash
while (newTab[h] != null) // 线性探测,重复时 h+1 ,直到找到空的位置
h = nextIndex(h, newLen);
newTab[h] = e;
count++;
}
}
}
setThreshold(newLen);//设置新的扩容阈值
size = count;
table = newTab;
}
ThreadLocal.get()
从get方法入手
先判断map是否存在,map不存在直接返回null
map.getEntry(this) map中先计算出当前key的Hash对应的元素下标,然后获取该值
若该Key的Hash对应的元素下标没有找到,则遍历整个表去找,再找不着返回null
/**
* Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this
* thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the
* current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned
* by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method.
*
* @return the current thread's value of this thread-local
*/
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue(); // 没有map的时候,相当于直接返回null
}
// 此处map == null 则直接返回null
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
ThreadLocalMap.getEntry()
getEntry(ThreadLocal key)
计算当前ThreadLocal的Hash对应的元素“i”,判断非空才去赋值
若没找到走getEntryAfterMiss();
/**
* Get the entry associated with key. This method
* itself handles only the fast path: a direct hit of existing
* key. It otherwise relays to getEntryAfterMiss. This is
* designed to maximize performance for direct hits, in part
* by making this method readily inlinable.
*
* @param key the thread local object
* @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such
*/
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
ThreadLocalMap.getEntryAfterMiss()
在没有找到Entry的情况下,先遍历整个tab去寻找当前Threal的值
若e = null ,直接返回null , 当e!=null 才进入下面的循环
碰到k = key ,直接返回寻到的对象
碰到k = null , 直接清除该值
实在找不着,tab[i]设置为e ,当然,此时e!=null
/**
* Version of getEntry method for use when key is not found in
* its direct hash slot.
*
* @param key the thread local object
* @param i the table index for key's hash code
* @param e the entry at table[i]
* @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such
*/
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
while (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key)
return e;
if (k == null)
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
i = nextIndex(i, len);// i+1赋值,再次进入循环遍历
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}
ThreadLocal.remove()
删除引用,调用expungeStaleEntry()清除数据
/**
* Remove the entry for key.
*/
private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
if (e.get() == key) {
e.clear();
expungeStaleEntry(i);
return;
}
}
}
总结
首先了解ThreadLocal的结构,ThreadLocalMap的结构
1.了解Hash算法的计算以及在ThreadLocal中的应用,黄金比例魔数:0x61c88647
2.然后就是ThreadLocalMap.set() 碰撞的计算,若无碰撞,直接可以覆盖Entry ,然后调整tab大小及扩容
3.碰撞的时候,使用开放寻址法,寻找空位赋值Entry,key=null的,替换并清理过期数据
4.扩容的时候,若存在碰撞计算,则使用线性探测来进行赋值,重新设置扩容阈值
1.get方法中若map == null ,则直接返回null
2.最后就是getEntryAfterMiss()没寻到之后的处理,当Entry!=null,遍历整个tab去寻找
3.找到就直接返回,k = null 则清除过期数据,实在找不到,返回null