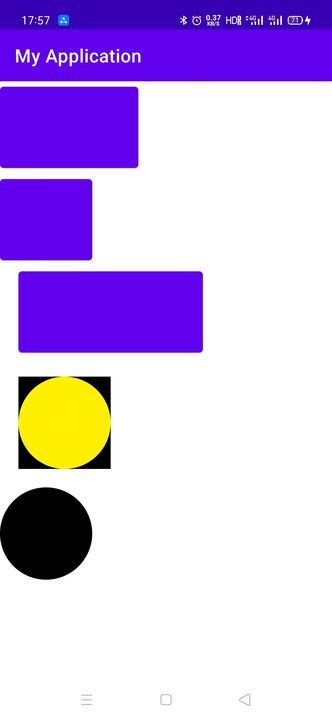
自定义View和自定义ViewGroup实例讲解
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/c84693096e41
自定义View
定义一个自定义View的步骤:
1.需要继承View或者View的子类;
2.重写至少两个构造方法;
3.自定义xml中的属性;
declare-styleable中的format的类型:
reference:引用类型,如@drawable/xxx
color:颜色,如#fff000
dimension:尺寸,如11dp
其他的:float,integer,boolean,string
4.在构造方法中对属性进行赋值;
5.onMeasure方法;
测量当前View
6.onDraw方法;
对View的绘制
下面的例子是一个外侧是正方形内侧为圆形的自定义View
在res中values中新建一个styles.xml,里面写
public class MyView extends View {
private int defaultSize;
private int circleColor;
private Paint paint = new Paint();//在onDraw中会使用,但在onDraw中定义的话会频繁新建,因此放在外面定义
public MyView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
//获取属性
TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MyView);
defaultSize = (int) typedArray.getDimension(R.styleable.MyView_default_size, 100);
circleColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.MyView_circle_color, getResources().getColor(R.color.black));
typedArray.recycle();
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int width = getSize(defaultSize, widthMeasureSpec);
int height = getSize(defaultSize, heightMeasureSpec);
height = width = Math.min(width, height);//将宽和高的小的值边长
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);//设置最后的宽高
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
int radius = getMeasuredWidth() / 2;
//这个x,y是针对view自身的
int centerX = radius;
int centerY = radius;
paint.setColor(circleColor);
paint.setAntiAlias(true);//抗锯齿
canvas.drawCircle(centerX, centerY, radius, paint);
}
private int getSize(int defaultSize, int measureSpec) {
int mySize;
int mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int size = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (mode) {
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
//当为wrap_content或者match_parent,就按系统的去走
mySize = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
mySize = defaultSize;
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected value: " + mode);
}
return mySize;
}
}
xml中使用:
自定义ViewGroup
自定义ViewGroup的步骤
1.构造方法
2.onlayout必须重写
作用:确定子View的位置
3.onMeasure
作用:确定自定义的ViewGroup的宽高
public class MyViewGroup extends LinearLayout {
public MyViewGroup(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
//必实现
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int count = getChildCount();
int curHeight = 0;//当前总高度
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
int childWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();
//加上margin值
childView.layout(l + lp.leftMargin, curHeight + lp.topMargin, l + lp.leftMargin + childWidth, curHeight + childHeight + lp.topMargin);
curHeight += childHeight + lp.topMargin;
}
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//对所有的子View进行测量,触发每一个子View的onMeasure函数
//子view的测量方法在子view里面去自定义,和这里的onMeasure没关系
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int count = getChildCount();
if (count == 0) {
setMeasuredDimension(0, 0);
} else {//对wrap_content的特殊处理
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(getMaxChildWidth(), totalChildHeight());
} else if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(getMaxChildWidth(), heightMeasureSpec);
} else if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(widthMeasureSpec, totalChildHeight());
}
}
}
//返回所有子View宽度的最大值
private int getMaxChildWidth() {
int count = getChildCount();
int maxWidth = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) getChildAt(i).getLayoutParams();
maxWidth = Math.max(getChildAt(i).getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin, maxWidth);//加上左右margin
}
return maxWidth;
}
//返回所有子View的高度的总和
private int totalChildHeight() {
int count = getChildCount();
int totalHeight = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) getChildAt(i).getLayoutParams();
totalHeight += getChildAt(i).getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
}
return totalHeight;
}
}