SpringBoot(静态资源的映射、模板引擎)
SpringBoot对静态资源的映射规则
如果我们需用给web项目中添加css/js/html文件的话,我们会发现此时没有webapp目录。

由于springboot是以jar包的方式打包程序的因此是没有webapp目录的。
那么我们的css/js/html文件要保存在什么地方啊???
我们要了解一个Java类“WebMvcAuotConfiguration”,因为与web开发相关的自动配置都是由这个类完成的。
spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.4.0.jar —> META-INF —> spring.factories
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
return;
}
Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
CacheControl cacheControl = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**")
.addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/")
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl)
.setUseLastModified(this.resourceProperties.getCache().isUseLastModified()));
}
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(staticPathPattern)
.addResourceLocations(getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()))
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl)
.setUseLastModified(this.resourceProperties.getCache().isUseLastModified()));
}
}
WebProperties.java
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS =
{
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/",
"classpath:/resources/",
"classpath:/static/",
"classpath:/public/" };
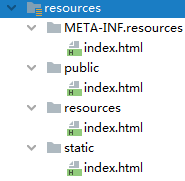
一、 静态资源的保存位置所有“/webjars/**”
webjars:将需要使用的静态资源打成jar包,我们如果需要就将整个jar导入值本项目就可以使用了。
静态资源打成jar包查看位置:
https://www.webjars.org/

以JQuery为例来使用一下webjars方式
1.1 在pom.xml文件中导入JQuery的jar依赖
<!--导入jquery的jar包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>jquery</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
1.2 测试访问我们导入的jquery文件
启动服务,在浏览器的地址栏中直接访问jquery文件
http://localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.5.1/jquery.js

二、默认静态资源文件的位置
WebProperties.java
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS =
{
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/",
"classpath:/resources/",
"classpath:/static/",
"classpath:/public/" };
2.1 "classpath:/META‐INF/resources/",
[src/main/resources/META-INF/resources/]–运行之前需要打包一下

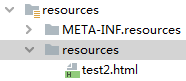
2.2 "classpath:/resources/"=== [src/main/resources/resources]
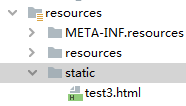
2.3 ”classpath:/static/”==== [src/main/resources/static]
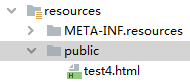
2.4."classpath:/public/"== [src/main/resources/public]
三、欢迎页; 静态资源文件夹下的所有index.html页面;
四、页面图标; 静态资源文件夹下的所有favicon.ico 图标;
可以在application.properties中配置修改静态资源文件夹路径。
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.web.resources", ignoreUnknownFields = false)
public class ResourceProperties implements ResourceLoaderAware {
//可以设置和静态资源有关的参数,缓存时间等
application.properties
spring.web.resources.static-locations=classpath:/test/,classpath:/hello/
http://localhost:8080/test.html
模板引擎
由于springboot是以jar包的方式打包程序的,而不是web项目,再者在springboot中我们用的是嵌入式的tomcat服务器,因此springboot项目是不支持动态页面的运行,所以如果我们都将页面处理成静态页面的话,那么到时候见加载数据的时候就需要大量的js来向后台请求数据回填到静态页面上,这样的话就会比较麻烦。所用springboot才为我们提供了模板引擎。
常见的模板引擎有JSP、Velocity、Freemarker、Thymeleaf

SpringBoot为我们推荐Thymeleaf模板引擎;因为他语法更简单,功能更强大。
Thymeleaf模板引擎的使用:
1. 引入Thymeleaf模板引擎的依赖包【启动器】
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.使用Thymeleaf
先看看自动配置
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING;
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
private boolean checkTemplate = true;
private boolean checkTemplateLocation = true;
private String prefix = "classpath:/templates/"; //模板的位置
private String suffix = ".html"; //静态页面的类型
private String mode = "HTML";
只要我们把HTML页面放在classpath:/templates/,thymeleaf就能自动渲染;
3.创建控制器
package com.wangxing.springboot.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import java.util.Map;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/testHello1")
public String testHello1(Map<String,Object> map){
map.put("id",1001);
map.put("name","张三");
map.put("age",23);
map.put("address","西安");
return "test1";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/testHello2")
public String testHello2(Model model){
model.addAttribute("id",1001);
model.addAttribute("name","张三");
model.addAttribute("age",23);
model.addAttribute("address","西安");
return "test1";
}
}
注意:传递给页面是数据值是通过请求处理方法中的参数设置的,
请求处理方法中的参数的类型:
1.Map
2.Model model
4.创建模板页面,模板页面默认是”.html”
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<ul>
<li><h1 th:text="${id}">h1>li>
<li><h1 th:text="${name}">h1>li>
<li><h1 th:text="${age}">h1>li>
<li><h1 th:text="${address}">h1>li>
ul>
body>
html>
xmlns:th=“http://www.thymeleaf.org”–给html页面引入thymeleaf命名空间,引入thymeleaf命名空间我们就可以在html页面中使用thymeleaf语法,显示动态数据。
thymeleaf语法

th:任意html属性;来替换原生html的属性的值
<span id="span1"></span>
<span th:id="${id}"></span>
例如:
<h1 th:text="${address}"></h1>
th:text—控制h1元素的text属性值,text属性值就是html元素的文本内容
thymeleaf表达式
| #{…} | 国际化消息 |
|---|---|
| ${…} | 变量取值 |
| *{…} | 当前对象/变量取值 |
| @{…} | url表达式 |
| ~{…} | 片段引用 |
判断/遍历:
th:if —th:if=”$ {id}==1001”
th:unless
th:each — th:each=”user:$ {users}” — th:text=”${user}”
th:switch、th:case
测试th:if / th:each
@RequestMapping(value = "/testHello3")
public String testHello3(Model model){
List<UserBean> userBeanList=new ArrayList<UserBean>();
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
UserBean userBean=new UserBean();
userBean.setUserid(1000+i);
userBean.setUsername("zhangsan_"+i);
userBean.setUserage(20+i);
userBean.setUseraddress("address_"+i);
userBeanList.add(userBean);
}
model.addAttribute("userlist",userBeanList);
return "test2";
}
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<table border="1px">
<tr align="center">
<td colspan="4"><h1>用户信息表h1>td>
tr>
<tr th:if="${userlist.size()} != 0" th:each="user:${userlist}">
<td th:text="${user.userid}">td>
<td th:text="${user.username}">td>
<td th:text="${user.userage}">td>
<td th:text="${user.useraddress}">td>
tr>
<tr th:if="${userlist.size()} == 0">
<td colspan="4">没有用户记录!!!td>
tr>
table>
body>
html>