Andriod: 在xml布局中使用自定义属性
今天在看android froyo的launcher2 源码的时候,在launcher.xml中看到有这么一段代码:
<com.android.launcher2.DragLayer
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:launcher="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.android.launcher"
android:id="@+id/drag_layer"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<include layout="@layout/all_apps" />
<!-- The workspace contains 3 screens of cells -->
<com.android.launcher2.Workspace
android:id="@+id/workspace"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:scrollbars="horizontal"
android:fadeScrollbars="true"
launcher:defaultScreen="2">
注意到其中的两处:
xmlns:launcher=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.android.launcher”
和
launcher:defaultScreen="2"
可以看出在这个布局文件中,使用了自定义属性。
以前没遇到过,既然这里碰到了,就顺便学习下,下面就写个简单的示例,权当学习笔记,便于以后查阅。
1. 定义一些自定义属性
建立一个属性xml文件: values/attrs.xml, 内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<resources>
<!-- the relation between the icon and text. -->
<attr name="relation">
<enum name="icon_left" value="0" />
<enum name="icon_right" value="1" />
<enum name="icon_above" value="2" />
<enum name="icon_below" value="3" />
</attr>
<skip />
<declare-styleable name="IconText">
<attr name="relation" />
<attr name="icon" format="reference" />
<attr name="text" format="string" />
<attr name="text_size" format="dimension" />
<attr name="text_color" format="integer" />
<attr name="space" format="dimension" />
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
解释如下:
属性relation有4种可选值:icon_left, icon_right, icon_above,icon_below.
属性icon的可选值为引用: 例如:"@/drawbable/icon".
属性text的可选值为string, 例如: "Hello world", 也可是string的引用"@string/hello".
属性text_size的可选值为尺寸大小,例如:20sp、18dip、20px等.
属性text_color的可选值为整数,例如:"0xfffffff", 也可以是color的引用"@color/white".
2. 定义一个能够处理这些属性值的view或者layout类
package com.braincol.viewattrs;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class IconTextView extends LinearLayout {
private final static String TAG = "IconTextView";
private final int ICON_LEFT = 0;
private final int ICON_RIGHT = 1;
private final int ICON_ABOVE = 2;
private final int ICON_BELOW = 3;
private TextView mTextView;
private ImageView mImageView;
private int mRelation = ICON_LEFT;
private String mText = "";
private int mIconId;
private float mTextSize;
private int mSpace;
public IconTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs){
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.IconText);
mRelation = a.getInt(R.styleable.IconText_relation, ICON_LEFT);
Log.d(TAG,"mRelation: "+mRelation);
mText = a.getString(R.styleable.IconText_text);
Log.d(TAG,"mText: "+mText);
mTextSize = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.IconText_text_size, 12);
Log.d(TAG,"mTextSize: "+mTextSize);
mSpace = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.IconText_space, 5);
Log.d(TAG,"mSpace: "+mSpace);
mIconId = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.IconText_icon, R.drawable.icon);
Log.d(TAG,"mIconId: "+mIconId);
a.recycle();
mTextView = new TextView(context);
mTextView.setText(mText);
mTextView.setTextSize(mTextSize);
mImageView = new ImageView(context);
mImageView.setImageResource(mIconId);
int left = 0;
int top = 0;
int right = 0;
int bottom = 0;
int orientation = HORIZONTAL;
int textViewIndex = 0;
switch(mRelation){
case ICON_ABOVE:
orientation = VERTICAL;
bottom = mSpace;
textViewIndex = 1;
break;
case ICON_BELOW:
orientation = VERTICAL;
top = mSpace;
break;
case ICON_LEFT:
right = mSpace;
textViewIndex = 1;
break;
case ICON_RIGHT:
left = mSpace;
break;
}
this.setOrientation(orientation);
this.addView(mImageView);
mImageView.setPadding(left, top, right, bottom);
this.addView(mTextView, textViewIndex);
}
}
可以看出这个LinearLayout 子类IconTextView中只有两个元素,ImageView 和mTextView,通过从xml配置文件中读取属性值来决定icon和text的内容、相对位置及其它属性。
3. 在layout布局文件中使用这个自定布局及其属性
layout/main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<com.braincol.viewattrs.IconTextView
android:id="@+id/icontext_01"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:icontext="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.braincol.viewattrs"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
icontext:relation="icon_left"
icontext:icon="@drawable/hi"
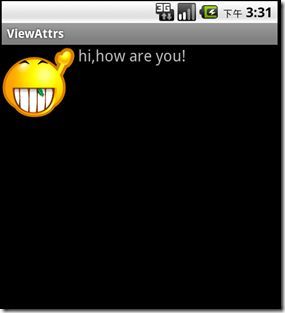
icontext:text="hi,how are you!"
icontext:text_size="12sp"
/>
</LinearLayout>
可以看到我们在这个布局文件中加入了一个新的命名空间:
xmlns:icontext="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.braincol.viewattrs"
并使用我们自定义的那些属性:
icontext:relation="icon_left"
icontext:icon="@drawable/hi"
icontext:text="hi, how are you !"
icontext:text_size="30sp"
4. 在Activity中使用该布局
package com.braincol.viewattrs;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class ViewAttrs extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
}
}
运行效果: