SLR语法分析器-编译原理
语法分析器
完整代码及图形化界面演示详见github:编译器前端
JavaFx项目,运行Main可看到图形界面,若要测试请按照文法,举几个栗子:
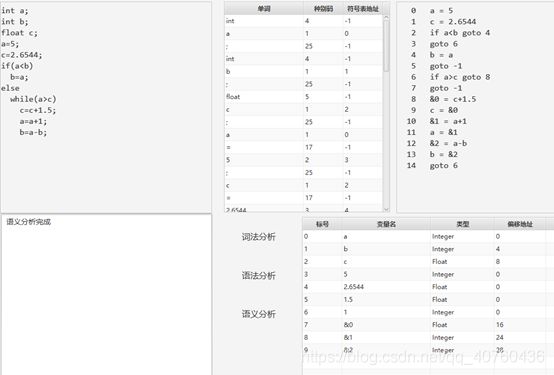

数据结构定义
单词和单词token表
package compiler;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* @author jpf
* 词法分析结果
* value 文法符号名
* type 符号类型
* typeCOde 种别码
* addr 符号表中所在位置
*/
public class Word implements java.io.Serializable {
private String typeCode;
private String type;
private String value;
private int addr;
public Word(String value, String typeCode, String type, int addr) {
this.value = value;
this.typeCode = typeCode;
this.type = type;
this.addr = addr;
}
public static ArrayList<Word> token = new ArrayList<>();
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getTypeCode() {
return typeCode;
}
public void setTypeCode(String typeCode) {
this.typeCode = typeCode;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getAddr() {
return addr;
}
public void setAddr(int addr) {
this.addr = addr;
}
public void printToken(){
System.out.println("{"+this.value+","+this.type+","+this.typeCode+","+this.addr+"}");
}
}
符号和符号表
package compiler;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* @Author: jpf
* @Date: 2020/6/12 0012 15:25
* 符号表
* name 变量名 如id的值,digit的值
* type 变量类型
* val 变量值,暂为null
* addr 相对地址
*
*/
public class Symbol implements java.io.Serializable {
private String name;
private String type;
private int val;
private int addr;
public static int offset;
public static int temp = 0;
public static ArrayList<Symbol> symbolsTable = new ArrayList<>();
public Symbol(String name) {
this.name = name;
this.index = symbolsTable.size();
this.val = -1;
}
/**获取单词在符号表中的位置 */
public static int wordLocate(String word){
for(int i=0; i<symbolsTable.size(); i++){
if(symbolsTable.get(i).name.equals(word)){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**新建一个临时变量,返回其位置*/
public static int newTemp(String type){
symbolsTable.add(new Symbol("&"+temp));
symbolsTable.get(symbolsTable.size()-1).type = type;
symbolsTable.get(symbolsTable.size()-1).addr = offset;
if("Integer".equals(type)){
offset += 4;
}else if("Float".equals(type)){
offset += 8;
}
temp++;
return symbolsTable.size()-1;
}
/**类型判断,即只能Integer给Integer和Float赋值,而不能反过来*/
public static boolean typeCheck(int addr1, int addr2){
return symbolsTable.get(addr1).type.equals(symbolsTable.get(addr2).type) || "Float".equals(symbolsTable.get(addr1).type);
}
public static void printSt(){
for(Symbol x : symbolsTable){
String mes = String.format("%2d %5s %s %3s",x.index,x.name,x.type,x.addr);
System.out.printf("%s\n",mes);
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public int getVal() {
return val;
}
public void setVal(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public int getAddr() {
return addr;
}
public void setAddr(int addr) {
this.addr = addr;
}
public int getIndex() {
return index;
}
public void setIndex(int index) {
this.index = index;
}
}
产生式右部
package compiler;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @Author: jpf
* @Date: 2020/6/17 0017 9:50
*/
public class Rproduct implements Serializable {
/**
* 产生式右部数据结构,pointer指明了下一个待移入文法符号
* len表示有多少个文法符号
* no表明该产生式编号
* */
public String[] symbol;
public int pointer;
public int len;
public int no;
public Rproduct(String[] symbol, int pointer, int no) {
this.symbol = symbol;
this.pointer = pointer;
this.len = symbol.length;
this.no = no;
}
/**将symbol第i个位置之后的字符串数组返回*/
public ArrayList<String> divideR(int i){
ArrayList<String> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if(i<len){
ret.addAll(Arrays.asList(symbol).subList(i, len));
}
return ret;
}
/**返回指针指向的符号,即待移进符号*/
public String getNext(){
if(pointer < len){
return this.symbol[pointer];
}else{
return null;
}
}
/**输出产生式右部*/
public String printProduct(){
String ret = "";
for(int i=0; i<len; i++){
ret += symbol[i]+" ";
}
return ret;
}
/**重写equals方法,symbol和pointer相同即认为相等*/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj == null || this.getClass()!=obj.getClass()){
return false;
}
Rproduct rproduct = (Rproduct) obj;
return Arrays.equals(this.symbol, rproduct.symbol) && this.pointer == rproduct.pointer;
}
}
增广文法,规范项集族,SLR分析表,终结符集合,非终结符集合
/**M N X Y为附加状态*/
public static String[] vt = {
"id","Integer","Float","int","float","if","(",")","else","while",">","<","==","=","+","-","*","/",";","$"};
public static String[] vn = {
"G","P","D","S","L","C","E","T","F","M","N","X","Y"};
/**G的增广文法*/
public static HashMap<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> GPLUS = new HashMap<>();
/**项集规范族*/
public static HashMap<Integer,HashMap<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>>> C = new HashMap<>();
/**slr分析表*/
public static HashMap<HashMap<Integer,String>, String> ACTION = new HashMap<>();
public static HashMap<HashMap<Integer,String>, Integer> GOTO = new HashMap<>();
/**归约情况,即用那些产生式归约*/
public static ArrayList<String> reduce = new ArrayList<>();
静态初始化增广文法
static {
GPLUS.put("G",new ArrayList<Rproduct>(){
{
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"P"},0,0));
}});
GPLUS.put("P",new ArrayList<Rproduct>(){
{
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"M","D","S"},0,0));
}});
GPLUS.put("D",new ArrayList<Rproduct>(){
{
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"L","id",";","N","D"},0,0));
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"epsilon"},0,1));
}});
GPLUS.put("L",new ArrayList<Rproduct>(){
{
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"int"},0,0));
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"float"},0,1));
}});
/*---语义分析额外加入产生式*/
GPLUS.put("M",new ArrayList<Rproduct>(){
{
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"epsilon"},0,0));
}});
GPLUS.put("N",new ArrayList<Rproduct>(){
{
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"epsilon"},0,0));
}});
/*-----------------------*/
GPLUS.put("S",new ArrayList<Rproduct>(){
{
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"id","=","E",";"},0,0));
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"if","(","C",")","X","S"},0,1));
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"if","(","C",")","X","S","Y","else","X","S"},0,2));
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"while","X","(","C",")","X","S"},0,3));
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"S","X","S"},0,4));
}});
/*---语义分析额外加入产生式*/
GPLUS.put("X",new ArrayList<Rproduct>(){
{
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"epsilon"},0,0));
}});
GPLUS.put("Y",new ArrayList<Rproduct>(){
{
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"epsilon"},0,0));
}});
/*-----------------------*/
GPLUS.put("C",new ArrayList<Rproduct>(){
{
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"E",">","E"},0,0));
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"E","<","E"},0,1));
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"E","==","E"},0,2));
}});
GPLUS.put("E",new ArrayList<Rproduct>(){
{
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"E","+","T"},0,0));
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"E","-","T"},0,1));
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"T"},0,2));
}});
GPLUS.put("T",new ArrayList<Rproduct>(){
{
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"F"},0,0));
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"T","*","F"},0,1));
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"T","/","F"},0,2));
}});
GPLUS.put("F",new ArrayList<Rproduct>(){
{
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"(","E",")"},0,0));
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"id"},0,1));
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"Integer"},0,2));
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"Float"},0,3));
}});
}
文法
G → P
P → D S
D →L id ; D |ε
L → int | float
S → id = E;
S → if ( C ) S1
S → if ( C ) S1 else S2
S → while ( C ) S1
S → S S
C → E1 > E2
C → E1 < E2
C → E1 == E2
E → E1 + T
E → E1 – T
E → T
T → F
T → T1 * F
T → T1 / F
F → ( E )
F → id
F → Integer
F → Float
注:由于语义翻译部分需要对文法就行修改,故代码中初始化文法为修改后的文法,加入了几个空产生式。epsilon表示空。
SLR分析器的实现
判断一组产生式是否包含在在状态集的某个状态中,返回状态值
public static int isinC(HashMap<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> item){
for(Map.Entry<Integer,HashMap<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>>> entry : C.entrySet()){
int key = entry.getKey();
HashMap<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> value = entry.getValue();
boolean flag = true;
for(Map.Entry<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> entry2 : item.entrySet()){
String key2 = entry2.getKey();
ArrayList<Rproduct> value2 = entry2.getValue();
if(value.containsKey(key2)){
if(!value.get(key2).containsAll(value2)){
flag = false;
}
}else {
flag = false;
}
}
if(flag){
return key;
}
}
return -1;
}
判断一组产生式是否在状态集的某个状态中,若在,返回状态值,否则返回-1。该函数在生成状态集时使用,作用是对于一个状态集的每一个产生式,在接收任何一个文法符号后得到的项目集闭包是否在已生成的状态集中,若在则不必新建状态,若不在则需要新加一个状态。
求文法符号的first集
public static HashSet<String> first(String x){
HashSet<String> ret = new HashSet<>();
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
boolean flag = false;
if(!Arrays.asList(vn).contains(x)){
ret.add(x);
return ret;
}
if(GPLUS.containsKey(x)){
ArrayList<Rproduct> value = GPLUS.get(x);
if(value.contains(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"epsilon"},0,0))){
flag = true;
}
for(Rproduct rproduct : value){
if(!rproduct.symbol[0].equals(x)){
if(Arrays.asList(vn).contains(rproduct.symbol[0])){
stack.push(rproduct.symbol[0]);
}else {
ret.add(rproduct.symbol[0]);
}
}else if(flag && rproduct.len>1){
stack.push(rproduct.symbol[1]);
}
}
while (!stack.empty()){
String firstVn = stack.pop();
ret.addAll(first(firstVn));
}
}
return ret;
}
求文法符号x的first集,这里的x是单个文法符号,而不是符号串,思路为若x是终结符,则在返回的集合中加入该终结符并返回。否则对所有以该非终结符为左部的产生式,若产生式中包含直接推出epsilon产生式,则将flag设为true,然后遍历这些产生式右部的第一个文法符号,若是x本身,flag为true且该产生式右部文法符号数大于1,则将x的后一个文法符号压入堆栈;若不是x本身,若是非终结符号,则压入堆栈,若是终结符号,则加入返回集合。遍历结束后查看堆栈,当堆栈不为空的时候,依次将这些非终结符号弹出堆栈并将将这些非终结符号的first集加入返回集合,利用递归实现。
求文法符号串first集
public static HashSet<String> firstX(ArrayList<String> x){
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();
for (String s : x) {
if (first(s).contains("epsilon")) {
set.addAll(first(s));
set.remove("epsilon");
} else {
set.addAll(first(s));
return set;
}
}
set.add("epsilon");
return set;
}
求文法符号串的first集。该算法比较简单,遍历符号串,将第一个文法符号的first集加入到firstX,若第一个文法符号的first集包含epsilon,则加入第二个文法符号的first集,若第二个能推出空,则加入第三个……以此类推。
求非终结符的follow集
public static HashSet<String> follow(String x) {
HashSet<String> ret = new HashSet<>();
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
if ("G".equals(x)) {
ret.add("$");
return ret;
}else {
for (Map.Entry<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> entry : GPLUS.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
for (Rproduct rproduct : entry.getValue()) {
for (int index = 0; index < rproduct.len; index++) {
if (rproduct.symbol[index].equals(x)) {
if (index < rproduct.len - 1) {
String next = rproduct.symbol[index + 1];
if (Arrays.asList(vt).contains(next)) {
ret.add(next);
} else if (Arrays.asList(vn).contains(next)) {
HashSet<String> set = firstX(rproduct.divideR(index + 1));
if (set.contains("epsilon")) {
set.remove("epsilon");
ret.addAll(set);
stack.add(key);
} else {
ret.addAll(set);
}
}
} else if (index == rproduct.len - 1) {
stack.push(key);
}
}
}
}
}
while (!stack.empty()){
String left = stack.pop();
if(!left.equals(x)){
ret.addAll(follow(left));
}
}
}
return ret;
}
求非终结符号的follow集,若是开始符号G,则将”$”加入集合并返回。否则遍历所有产生式,对每个产生式的右部,依次遍历各个文法符号,当找到与x相等的文法符号,取该符号的后继符号,若后继符号为终结符,则将终结符加入x的follow集,否则若是非终结符,则将产生式中该非终结符及其之后的文法符号构成的符号串的first集元素加入到x的follow集,若该非终结符能推出epsilon,则还要将该非终结符压入堆栈。待遍历完成后,对堆栈中的非终结符,依次出栈并递归的将其follow集加入到x的follow集。
求项集闭包
public static HashMap<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> getClosure(HashMap<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> item){
HashMap<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> rproducts = new HashMap<>();
boolean flag = true;
while (flag){
String x;
/*遍历item,对item中每个产生式右部待移入的文法符号,GPLUS有以其为左部的产生式,若不在item中,则加入*/
for (Map.Entry<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> entry : item.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
ArrayList<Rproduct> value = entry.getValue();
for (Rproduct rproduct : value) {
x = rproduct.getNext();
if (GPLUS.containsKey(x)) {
for (int i = 0; i < GPLUS.get(x).size(); i++) {
if(!item.containsKey(x) && !rproducts.containsKey(x)){
rproducts.put(x, new ArrayList<>());
}
if (!item.containsKey(x)) {
if(!rproducts.get(x).contains(GPLUS.get(x).get(i))){
rproducts.get(x).add(GPLUS.get(x).get(i));
}
} else if (!item.get(x).contains(GPLUS.get(x).get(i))) {
if(!rproducts.containsKey(x)){
rproducts.put(x, new ArrayList<>());
}
if(!rproducts.get(x).contains(GPLUS.get(x).get(i))){
rproducts.get(x).add(GPLUS.get(x).get(i));
}
}
}
}
}
}
if(rproducts.size()>=1){
for(Map.Entry<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> entry : rproducts.entrySet()){
String key = entry.getKey();
ArrayList<Rproduct> value = entry.getValue();
if(value.size() > 0)
{
if(!item.containsKey(key)){
item.put(key,new ArrayList<>());
}
for(Rproduct rproduct : value){
item.get(key).add(rproduct);
}
flag = true;
}else {
flag = false;
}
}
LrParser.printHs(item);
}else {
flag = false;
}
rproducts.clear();
}
return item;
}
求项集的项集闭包,遍历输入item的各个产生式,对item中每个产生式右部待移入的文法符号,若增广文法中有以其为左部的产生式并且不再item中,则把这个产生式加入到item中,最终item是一个项目集闭包。
一个辅助函数:实现深度拷贝
public static <T extends Serializable> T myClone(T obj) {
T clonedObj = null;
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(baos);
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(baos.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bais);
clonedObj = (T) ois.readObject();
ois.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return clonedObj;
}
求项目集闭包item对应于x的后继项目集闭包
public static HashMap<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> go(HashMap<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> item, String x){
HashMap<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> j = new HashMap<>();
HashMap<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> itemClone = myClone(item);
for(Map.Entry<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> entry : itemClone.entrySet()){
String key = entry.getKey();
ArrayList<Rproduct> value = entry.getValue();
for(Rproduct rproduct : value){
if(rproduct.pointer<rproduct.len){
if(!j.containsKey(key) && rproduct.getNext().equals(x)){
j.put(key, new ArrayList<>());
rproduct.pointer++;
j.get(key).add(rproduct);
}else if(rproduct.getNext().equals(x)){
rproduct.pointer++;
j.get(key).add(rproduct);
}
}
}
}
return LrParser.getClosure(j);
}
求一个项目集闭包item对应于x的后继项目集闭包。遍历item的每一个产生式,若产生式的移入指针指向的文法符号为x,则将该产生式的移入指针后移一位,遍历完成后,对新的item用getClosure函数求其对应的项目集闭包。
初始化规范化项集族
public static void initC(){
HashMap<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> item = new HashMap<>();
item.put("G",new ArrayList<Rproduct>(){
{
add(new Rproduct(new String[]{
"P"},0,0));
}});
int i = 0;
Queue<Integer> pointer = new LinkedList<>();
pointer.add(i);
C.put(i,LrParser.getClosure(item));
HashMap<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> gotoix;
while (!pointer.isEmpty()){
int j = pointer.poll();
HashMap<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> cItem = C.get(j);
HashMap<String, Integer> flag = new HashMap<>();
LrParser.printHs(cItem);
for(Map.Entry<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> entry : cItem.entrySet()){
String key = entry.getKey();
ArrayList<Rproduct> value = entry.getValue();
for (Rproduct rproduct : value) {
String x = rproduct.getNext();
if(x!=null){
flag.put(x, 1);
}
System.out.println(x);
}
}
for(Map.Entry<String, Integer> entryflag : flag.entrySet()){
String flagkey = entryflag.getKey();
HashMap<Integer, String> source = new HashMap<>();
if(!"epsilon".equals(flagkey) && flagkey!=null){
gotoix = LrParser.go(C.get(j),flagkey);
int index = LrParser.isinC(gotoix);
if(gotoix != null && index==-1){
C.put(++i,gotoix);
pointer.add(i);
source.put(j,flagkey);
GOTO.put((HashMap<Integer, String>) source.clone(),i);
}else {
source.put(j,flagkey);
GOTO.put((HashMap<Integer, String>) source.clone(),index);
}
source.clear();
}
}
flag.clear();
}
}
初始化规范项集族,首先将开始符号对应的一条产生式作为状态0加入到规范化项集族,将其状态号加入队列,接下来是while循环,当队列不为空的时候,弹出队首状态j,获取该状态对应的项集闭包,然后遍历该项集闭包中产生式,若产生式对应的移入指针指向的文法符号不为空(epsilon也认为空)设为x,则调用go函数求得该j状态对应项目集闭包对应于x的后继项目集闭包,判断后继项目集闭包是否在规范项集族中,若不在则构造新的状态,并将新状态标号加入队列。当队列为空时,规范化项集族便求出。
初始化SLR分析表
public static void initLrTable(){
for(Map.Entry<Integer, HashMap<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>>> entry : C.entrySet()){
int key = entry.getKey();
HashMap<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> value = entry.getValue();
for(Map.Entry<String, ArrayList<Rproduct>> entry2 : value.entrySet()){
String lP = entry2.getKey();
ArrayList<Rproduct> rP = entry2.getValue();
for(int i=0; i<rP.size(); i++){
Rproduct rproduct = rP.get(i);
String variable = rproduct.getNext();
HashMap<Integer,String> actionKey = new HashMap<>();
if(variable != null && !"epsilon".equals(variable)){
if(Arrays.asList(vt).contains(variable)){
actionKey.put(key,variable);
int des = GOTO.get(actionKey);
ACTION.put((HashMap<Integer, String>) actionKey.clone(),"s"+des);
}else if(Arrays.asList(vn).contains(variable)){
/*在初始化规范项集族时已求出*/
actionKey.put(key,variable);
int des = GOTO.get(actionKey);
}
}else {
HashSet<String> followLp = follow(lP);
for(int k=0; k<vt.length; k++){
if(followLp.contains(vt[k])){
if(!"G".equals(lP)){
actionKey.put(key,vt[k]);
ACTION.put((HashMap<Integer, String>) actionKey.clone(),"r"+lP+rproduct.no);
}else {
actionKey.put(key,"$");
ACTION.put((HashMap<Integer, String>) actionKey.clone(),"acc");
}
}
actionKey.clear();
}
}
actionKey.clear();
}
}
}
}
初始化slr分析表,遍历求出的规范化项集族,即遍历每个状态j的每一条产生式p,获取该产生式移入指针指向的文法符号x。若x不为空也不为epsilon,则进一步判断该文法符号是否是终结符号,若x是终结符号,填写ACTION表项,即状态j遇到文法符号x执行移入x并进入状态GO(j,x),若x是非终结符号,填写GOTO表项,即状态j遇到文法符号x进入状态GO(j,x);若x为空或epsilon,首先求产生式p左部文法符号的follow集,对任何在follow集中的终结符号,若p左部不是开始符号G,填写ACTION表项,即状态j遇到文法符号x按产生式p进行归约;若p左部是开始符号G,则表示语法分析完成,填写ACTION表项即状态j遇到末尾符”$”则acc。
SLR分析器
public static void slrParser(){
reduce.clear();
int index = 0;
int state = 0;
Stack<Integer> stateStack = new Stack<>();
stateStack.push(state);
while (true){
state = stateStack.peek();
Word symbol = Word.token.get(index);
HashMap<Integer,String> s1 = new HashMap<>();
s1.put(state,symbol.getType());
if(ACTION.containsKey(s1)){
String action = ACTION.get(s1);
if(action.charAt(0) == 's'){
stateStack.push(Integer.parseInt(action.substring(1)));
int x = stateStack.peek();
index++;
}else if(action.charAt(0) == 'r'){
String leftProduct = action.substring(1,2);
int productNo = Integer.parseInt(action.substring(2));
int popLen;
if("epsilon".equals(GPLUS.get(leftProduct).get(productNo).symbol[0])){
popLen = 0;
}else {
popLen = GPLUS.get(leftProduct).get(productNo).len;
}
for(;popLen>0;popLen--){
stateStack.pop();
int x = stateStack.peek();
}
state = stateStack.peek();
HashMap<Integer,String> s2 = new HashMap<>();
s2.put(state,leftProduct);
stateStack.push(GOTO.get(s2));
reduce.add(leftProduct+"->"+GPLUS.get(leftProduct).get(productNo).printProduct());
int x = stateStack.peek();
}else if("acc".equals(action)){
reduce.add("G->P 语法分析完成");
break;
}else {
reduce.add("语法错误");
break;
}
}else {
reduce.add("语法错误");
break;
}
}
}
slr分析器主程序,初始化一个状态栈,将0状态入栈,进入while(true)循环,获取栈顶状态state,读入词法分析阶段token表第一个单词symbol,若ACTION中存在键(state,symbol),则获取该键对应的值即移入归约动作,若是移入动作,则将移入symbol后进入的状态压入状态栈;若是归约动作,则按归约所用的产生式归约,具体做法为从状态栈中弹出n个状态,n是归约产生式右部文法符号的个数(epsilon产生式右部文法符号个数认为是0个),并用GOTO表获取此时栈顶状态遇到归约所用产生式左部文法符号时进入的后继状态,并将这个后继状态压入状态栈;若是acc动作,输出语法分析完成,表示输入为正确的语法;对于其他情况,输出error,表示语法错误。