2018科大讯飞营销广告算法大赛
2018讯飞广告营销算法
本次的最终是一个分类任务,评价指标选择为logloss,以前虽然做过一些分类性的任务,但任务本身难度不大,而本次第一个主要的问题就是数据量大,尤其是在最终的建模中,以前靠只靠cpu版本的XGBoost和Stacking就能得到一个不错的trade-off,而本次任务在Cpu的情况下,就需要花费更多的时间了,所以,重新编译安装了GPU版本的XGBoost,并首次尝试使用了LightGBM(GPU),其性能多方面优先与XGBoost,所以,最后选择使用了LightGBM模型,注:文中张贴非完整代码,完整代码及参考见文末。
赛题背景
讯飞AI营销云在高速发展的同时,积累了海量的广告数据和用户数据,如何有效利用这些数据去预测用户的广告点击概率,是大数据应用在精准营销中的关键问题,也是所有智能营销平台必须具备的核心技术。
本次大赛提供了讯飞AI营销云的海量广告投放数据,参赛选手通过人工智能技术构建预测模型预估用户的广告点击概率,即给定广告点击相关的广告、媒体、用户、上下文内容等信息的条件下预测广告点击概率。希望通过本次大赛挖掘AI营销算法领域的顶尖人才,共同推动AI营销的技术革新。
EDA
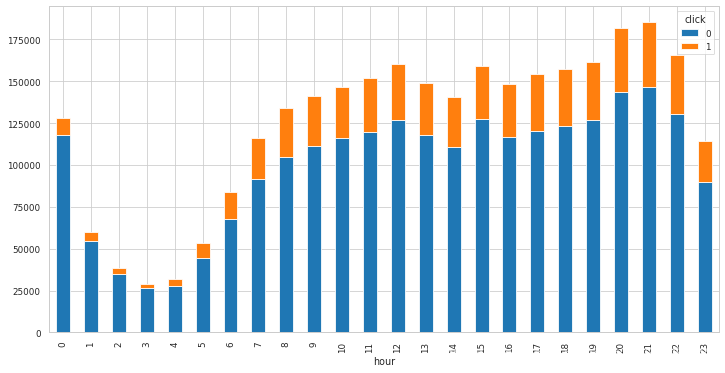
查看时间与点击量的相关信息
# 处理时间戳函数
def get_time(attr):
"""从时间戳获得具体的时间信息"""
day = []
hour = []
for time in attr:
t = datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(time + 3600*24*5) #加5天
day.append(t.day)
hour.append(t.hour)
return day, hour
train_df = train.copy()
train_df["day"], train_df["hour"] = get_time(train_df.time.values)
# 绘制不同时刻的点击情况
hour_info = train_df.groupby(["hour", "click"])["hour"].count()
hour_info = hour_info.unstack() #构成数映射表
hour_info[[0, 1]].plot(kind="bar", stacked=True, figsize=(12, 6)) # stacked堆叠显示
plt.show()
hour_info.plot(figsize=(12,6))
plt.xticks(np.arange(0, 24, 6))
plt.title("The plot of click in different hour", fontsize=15)
plt.show()
结论: 具体每一个时间的点击率有所不同(将连续的时间离散化),可以将时间划分为四个不同的时间间隔,间隔六小时
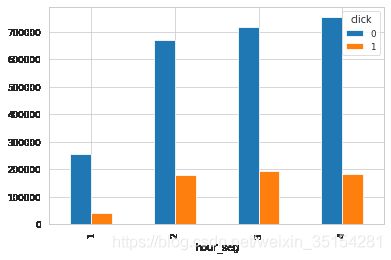
不同时间段的点击情况
def seg_hour(x):
"""划分时间间隔"""
if x > 0 and x <= 6:
return 1
elif x > 6 and x <= 12:
return 2
elif x > 12 and x <= 18:
return 3
else:
return 4
train_df["hour_seg"] = train_df.hour.apply(lambda x:seg_hour(x))
seg_hour = train_df.groupby(["hour_seg", "click"]).hour_seg.count().unstack()
seg_hour[[0, 1]].plot(kind="bar")
plt.show()
结论:对用户的分时段之后可以看出用户时间分布情况。
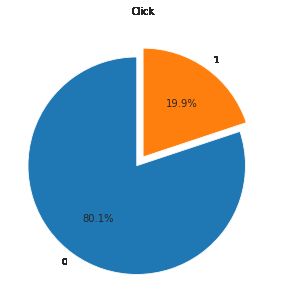
查看样本的均衡情况
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
cnt_click = train_df.click.value_counts()
plt.pie(x=cnt_click
, labels=[0, 1]
, autopct="%1.1f%%"
, explode=[0.1, 0]
, startangle=90
)
plt.title("Click")
plt.show()
结论:样布不均衡,正负样本1:4,少数类为点击,希望捕获少数类。
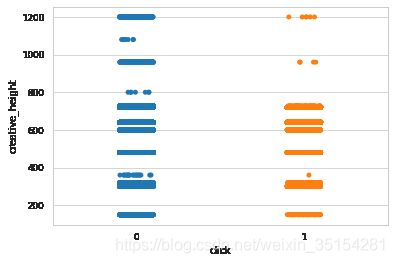
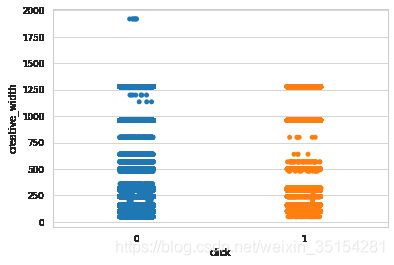
广告长宽与点击情况
sns.stripplot(x="click", y="creative_height", data=train_df)
plt.show()
sns.stripplot(train_df.click, train_df.creative_width)
plt.show()
结论:人们趋向于点击广告大小适中的广告,长宽在500以下比较集中
探索布尔型变量对结果的影响
# 打印bool类型数据
bool_feture = []
cols = data.columns
for col in cols:
if str(train_df[col].dtype) == 'bool':
print(col)
bool_feture.append(str(col))
creative_is_jump
creative_is_download
creative_is_js
creative_is_voicead
creative_has_deeplink
app_paid
def plot_ratio(df, name1, name2):
gropy_n = df.groupby([name1, name2])[name1].count().unstack()
print(gropy_n)
print()
gropy_n[[0, 1]].plot(kind="bar")
plt.xlabel(name1)
plt.ylabel(name2 + "_" + "counts")
plt.show()
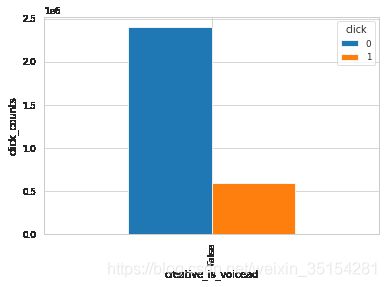
# 是否是语音广告
plot_ratio(train_df, "creative_is_voicead", "click")
click 0 1
creative_is_voicead
False 2397237 595402
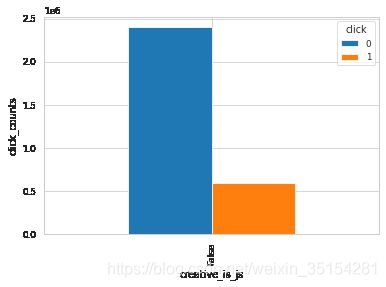
# 是否是js素材
plot_ratio(train_df, "creative_is_js", "click")
click 0 1
creative_is_js
False 2397237 595402
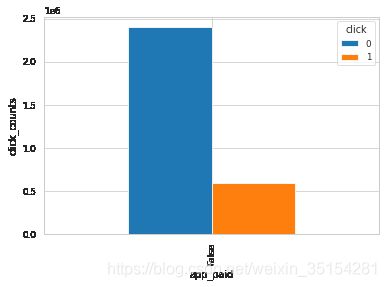
# app是否收费
plot_ratio(train_df, "app_paid", "click")
click 0 1
app_paid
False 2397237 595402
# 是否落地页跳转
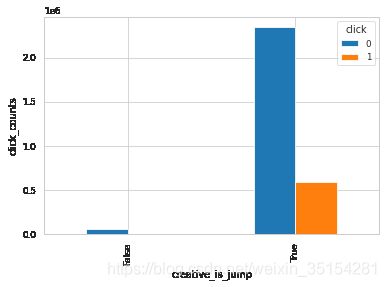
plot_ratio(train_df, "creative_is_jump", "click")
click 0 1
creative_is_jump
False 56805 690
True 2340432 594712
# 是否落地页下载
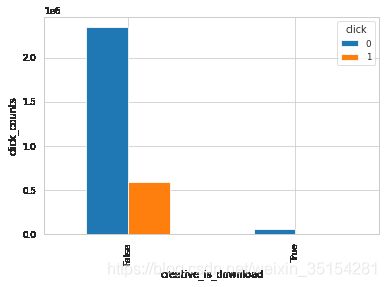
plot_ratio(train_df, "creative_is_download", "click")
click 0 1
creative_is_download
False 2340432 594712
True 56805 690
# 是否有deeplink
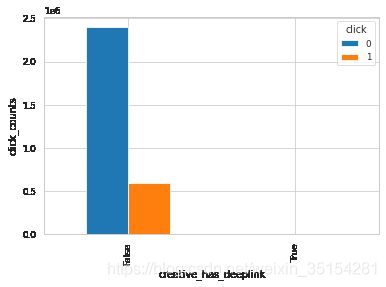
plot_ratio(train_df, "creative_has_deeplink", "click")
click 0 1
creative_has_deeplink
False 2396401 595348
True 836 54
结论:从生成的结果来看,这三种(creative_is_voicead、creative_is_js、 app_paid)bool型特征的值为单个值,无法通过变化来影响是否点击,所以,理论上可以删除。而对于creative_is_jump和creative_is_download是互补关系,可以选择保留其中一个特征
数据预处理
删除冗余数据
del data["instance_id"]
del data["creative_is_js"]
del data["app_paid"]
del data["creative_is_voicead"]
del train
del test
处理时间变量
将时间戳类型的输出抽取为更细的时间参数,并分区
def seg_hour(x):
"""划分时间间隔"""
if x > 0 and x <= 6:
return 1
elif x > 6 and x <= 12:
return 2
elif x > 12 and x <= 18:
return 3
else:
return 4
# 时间向下细分
data["day"], data["hour"] = get_time(data.time.values)
data["hour_part"] = data["hour"].apply(lambda x: seg_hour(x)) # 组合特征
# 删除时间列
del data["time"]
手机品牌处理
清洗手机品牌和机型字段,对同类型进行合并(redmi->xiaomi, honour->huawei)
# 名称装换为小写
col = []
for va in data["make"].values:
va = str(va)
if "," in va:
col.append(va.split(",")[0].lower())
elif "-"in va:
col.append(va.split("-")[0].lower())
elif " " in va:
col.append(va.split(" ")[0].lower())
else:
col.append(va.lower())
# 修改同类品牌的下的子品牌
for index in range(len(col)):
if "apple" in col[index]:
col[index] = "apple"
elif "redmi" in col[index]:
col[index] = "xiaomi"
elif "honor" == col[index]:
col[index] = "huawei"
elif col[index] == "mi":
col[index] = "xiaomi"
elif col[index] == "nan":
col[index] == np.nan
elif col[index] == "meitu":
col[index] == "meizu"
elif col[index] == "le" or col[index] == "letv" or col[index] == "lemobile" or col[index] == "blephone":
col[index] == "leshi"
data["new_make"] = col
手机机型处理
# 机型数据统一化处理
lst = []
for va in data.model.values:
va = str(va)
if "-" in va:
lst.append(va.replace('-', " "))
elif "+" in va:
lst.append(va.replace("+", " "))
elif "," in va:
lst.append(va.replace(",", " "))
elif va == "nan":
lst.append(np.nan)
else:
lst.append(va)
data["new_model"] = lst
广告主行业划分
形式:教育_培训(划分)
lst1 = []
lst2 = []
for va in data.advert_industry_inner.values:
lst1.append(va.split("_")[0])
lst2.append(va.split("_")[1])
data["advert_industry_inner1"] = lst1
data["advert_industry_inner2"] = lst2
媒体广告位置划分
如xf, iqy
lst = []
for va in data.inner_slot_id.values:
lst.append(va.split("_")[0])
data["inner_slot_id1"] = lst
操作系统
# plt.pie(data.os.value_counts())
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
percent = data.os.value_counts()
plt.pie(x=percent
, labels=["Andiord", "iOS", "Other"]
, autopct="%1.2f%%"
, startangle=90
, rotatelabels=True
)
plt.show()
# 其他类型操作系统比重极少,可将其归为安卓类
data.os.replace(0, 2, inplace=True)
…
查看缺失值情况
Total = data.isnull().sum().sort_values(ascending=False)
Percent = (data.isnull().sum()/data.isnull().count()).sort_values(ascending=False)*100
missing_data = pd.concat([Total, Percent], axis=1, keys=["Total", "Percent"])
# 可视化缺失值
index = 10
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 6))
sns.barplot(x=missing_data[:index].index, y=missing_data.Percent[:index], hue_order=True)
plt.xticks(rotation=90)
plt.xlabel("missing_features", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("Percent", fontsize=14)
plt.title("The percent of missing_feature", fontsize=16)
plt.show()
特征编码
特征类型分析
use_tags表示唯一性,不要编码
creative_width, creative_height :属于数值型特征变量不需要进行编码
creative_is_jump, creative_is_download, creative_has_deeplink :0, 1
day :一周
click :目标 [0, 1]
hour_part :[1, 2, 3, 4]
osv1, osv2, osv3 :类别型数值变量
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
# 打印object类型数据
bool_feture = []
cols = data.columns
for col in cols:
if str(data[col].dtype) == 'object':
print(col)
bool_feture.append(str(col))
type_feature = ['city', 'province', 'carrier', 'devtype', 'make', 'model',
'nnt', 'os', 'osv', 'os_name', 'adid', 'advert_id', 'orderid',
'advert_industry_inner', 'campaign_id', 'creative_id',
'creative_tp_dnf', 'app_cate_id', 'f_channel', 'app_id',
'inner_slot_id', 'creative_type',
'advert_name', 'hour', 'new_make',
'advert_industry_inner1', 'advert_industry_inner2',
'inner_slot_id1', 'user_id', 'new_model', 'os_name1']
# 标签编码
for feature in type_feature:
try:
data[feature] = LabelEncoder().fit_transform(data[feature].fillna(-1).apply(int)) # 字符型数值转为int类型
except:
data[feature] = LabelEncoder().fit_transform(data[feature].fillna("-1"))
处理数据
# 取出训练集数据索引
train_index = data[data.click != -1].index
test_index = data[data.click == -1].index
train_y = pd.Series(data=data.loc[train_index, "click"])
train = data.iloc[train_index, :]
test = data.iloc[test_index, :]
del test["click"]
del train["click"]
建模
LightGBM
- 确定任务类型(回归、分类、排序等),以及基学习器的类型(dark, gbdt、RF)
- 首先选择较高的学习率,大概0.1附近,这样是为了加快收敛的速度。这对于调参是很有必要的。
- 对决策树基本参数调参
- 正则化参数调参
- 最后降低学习率,这里是为了最后提高准确率
data_train = lgb.Dataset(train_df, y)
初始化状态(未调参)
# 参数设定为默认状态
params1 = {
"boosting_type": "gbdt"
, "objective": "binary" # 二分类任务
, "metric": {
"binary_logloss", "auc"}
, "nthread": 4
, "device": "gpu"
, "gpu_device_id": 1
, "verbose": 1
, "learning_rate": 0.1
, "max_depth": 5
, "num_leaves": 31 # 由于lightGBM是leaves_wise生长,官方说法是要小于2^max_depth
, "subsample": 1.0 # 数据采样
, "colsample_bytree": 1.0 # 特征采样
, 'reg_alpha': 0.0 # L1
, 'reg_lambda': 0.0 # L2
}
t0 = time()
cv_result1 = lgb.cv(params=params1, train_set=data_train
, nfold=5
, stratified=True
, shuffle=True
# , metrics="binary_logloss"
, seed=0
)
print("参数处理时间:",datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(time()-t0).strftime("%M:%S:%f"))
参数处理时间: 01:06:799278
调整好的参数状态
num_boost_round = 3000
params2 = {
"boosting_type": "gbdt"
, "objective": "binary" # 二分类任务
, "metric": {
"binary_logloss", "auc"}
, "nthread": 4
, "device": "gpu"
, "gpu_device_id": 1
, "verbose": 1
, "learning_rate": 0.01
, "max_depth": 6
, "num_leaves": 41 # 由于lightGBM是leaves_wise生长,官方说法是要小于2^max_depth
, "subsample": 0.8 # 数据采样
, "colsample_bytree": 0.8 # 特征采样
, 'reg_alpha': 0.0 # L1
, 'reg_lambda': 0.0 # L2
}
t0 = time()
cv_result2 = lgb.cv(params=params2, train_set=data_train
, num_boost_round=num_boost_round
, nfold=5
, stratified=True
, shuffle=True
# , metrics="binary_logloss"
# , early_stopping_rounds=50
, seed=0
)
print("参数处理时间:",datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(time()-t0).strftime("%M:%S:%f"))
参数处理时间: 28:52:279001
# 选择最佳的estimators
print("Best_n_estimators: %d\nBest_cv_score: %.4f"
% (np.array(list(cv_result2.values())).shape[1],
min(np.array(list(cv_result2.values()))[0]))
)
Best_n_estimators: 3000
Best_cv_score: 0.4166
调参数状态
params3 = {
"boosting_type": "gbdt"
, "objective": "binary" # 二分类任务
, "metric": {
"binary_logloss", "auc"}
, "nthread": 4
, "device": "gpu"
, "gpu_device_id": 1
, "verbose": 1
, "learning_rate": 0.01
, "max_depth": 6
, "num_leaves": 31 # 由于lightGBM是leaves_wise生长,官方说法是要小于2^max_depth
, "subsample": 0.8 # 数据采样
, "colsample_bytree": 0.8 # 特征采样
, 'reg_alpha': 0.0 # L1
, 'reg_lambda': 0.0 # L2
}
t0 = time()
cv_result3 = lgb.cv(params=params3, train_set=data_train
, num_boost_round=3000
, nfold=5
, stratified=True
, shuffle=True
# , metrics="binary_logloss"
# , early_stopping_rounds=50
, seed=0
)
print("处理时间:",datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(time()-t0).strftime("%M:%S:%f"))
处理时间: 27:40:536119
可视化指标
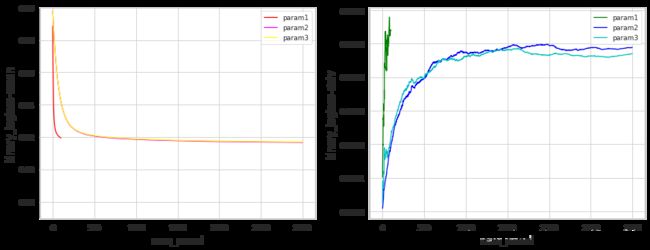
1. logloss指标
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize = (14,5))
length1 = np.array(list(cv_result1.values())).shape[1]
length2 = np.array(list(cv_result2.values())).shape[1]
length3 = np.array(list(cv_result3.values())).shape[1]
ax[0].plot(range(length1), cv_result1[list(cv_result1.keys())[0]], label="param1", c="red")
ax[1].plot(range(length1), cv_result1[list(cv_result1.keys())[1]], label="param1", c="green")
ax[0].plot(range(length2), cv_result2[list(cv_result2.keys())[0]], label="param2", c="magenta")
ax[1].plot(range(length2), cv_result2[list(cv_result2.keys())[1]], label="param2", c="blue")
ax[0].plot(range(length3), cv_result3[list(cv_result3.keys())[0]], label="param3", c="yellow")
ax[1].plot(range(length3), cv_result3[list(cv_result3.keys())[1]], label="param3", c="c")
ax[0].set_xlabel("num_round", fontsize=12)
ax[1].set_xlabel("num_round", fontsize=12)
ax[0].set_ylabel(list(cv_result1.keys())[0], fontsize=12)
ax[1].set_ylabel(list(cv_result1.keys())[1], fontsize=12)
ax[0].set_ylim((0.37, 0.5))
ax[0].legend()
ax[1].legend()
plt.show()
2. AUC指标
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize = (14,5))
length1 = np.array(list(cv_result1.values())).shape[1]
length2 = np.array(list(cv_result2.values())).shape[1]
length3 = np.array(list(cv_result3.values())).shape[1]
ax[0].plot(range(length1), cv_result1[list(cv_result1.keys())[2]], label="param1", c="red")
ax[1].plot(range(length1), cv_result1[list(cv_result1.keys())[3]], label="param1", c="green")
ax[0].plot(range(length2), cv_result2[list(cv_result2.keys())[2]], label="param2", c="magenta")
ax[1].plot(range(length2), cv_result2[list(cv_result2.keys())[3]], label="param2", c="blue")
ax[0].plot(range(length3), cv_result3[list(cv_result3.keys())[2]], label="param3", c="yellow")
ax[1].plot(range(length3), cv_result3[list(cv_result3.keys())[3]], label="param3", c="c")
ax[0].set_xlabel("num_round", fontsize=12)
ax[1].set_xlabel("num_round", fontsize=12)
ax[0].set_ylabel(list(cv_result1.keys())[2], fontsize=12)
ax[1].set_ylabel(list(cv_result1.keys())[3], fontsize=12)
ax[0].set_ylim((0.74, 0.78))
ax[0].legend()
ax[1].legend()
plt.show()
最终预测结果
# 最终预测
t0 = time()
lgb_c = lgb.train(params=params2, train_set=data_train
, num_boost_round=8000
# , nfold=5
# , stratified=True
# , shuffle=True
# , metrics="binary_logloss"
# , early_stopping_rounds=50
# , seed=0
)
print("处理时间:",datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(time()-t0).strftime("%M:%S:%f"))
处理时间: 08:23:193281
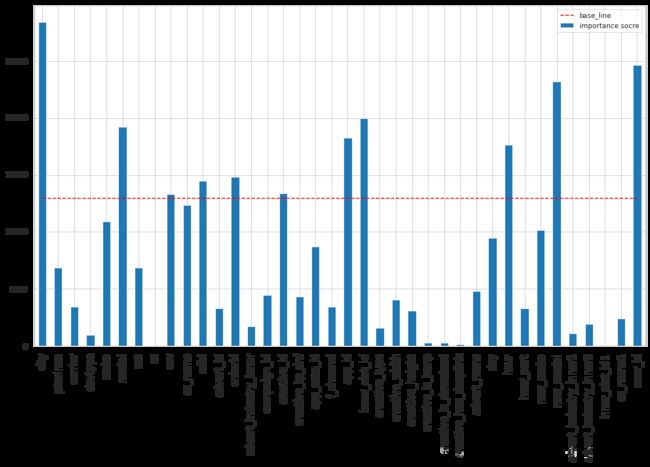
探索性分析
特征重要性
feature_importance = [*zip(lgbc.feature_name(),lgbc.feature_importance())]
df = pd.DataFrame(feature_impoetance, columns=["feature", "importance socre"])
df.plot(kind="bar",figsize = (14, 8))
plt.plot(np.arange(0, 38), [13000]*38, c="r", linestyle="--", label = "base_line")
plt.xticks(np.arange(0, 38), df.feature.tolist(),fontsize=12)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
总结
本次实现过程主要参考该算法比赛第一名的算法思路,在建模阶段由于对原作者的设计思路,自己仍处于研究阶段,所以,后续若更改会随时更新。
参考
2018科大讯飞AI营销算法大赛总结及完整代码(冠军)
2018科大讯飞营销算法大赛(冠军方案)
DC竞赛
2018科大讯飞AI营销算法大赛(31名代码)
pandas之 read_table函数读取txt文件
LightGBM 中文文档
XGBoost Documentation