java爬虫.HttpClient.Post请求
HttpClient.Post请求
HttpPost请求响应的一般步骤:
1). 创建HttpClient对象,可以使用HttpClients.createDefault();
2).
如果是无参数的GET请求:
则直接使用构造方法HttpPost(String url)创建HttpPost对象即可;
如果是带参数POST请求:
先构建HttpEntity对象并设置请求参数,
然后调用setEntity(HttpEntity entity)创建HttpPost对象。
3). 创建HttpResponse:
调用HttpClient对象的execute(HttpUriRequest request)发送请求,该方法返回一个HttpResponse。
调用HttpResponse的getAllHeaders()、getHeaders(String name)等方法可获取服务器的响应头;
调用HttpResponse的getEntity()方法可获取HttpEntity对象,该对象包装了服务器的响应内容。
程序可通过该对象获取服务器的响应内容。
通过调用getStatusLine().getStatusCode()可以获取响应状态码。
4). 释放连接。
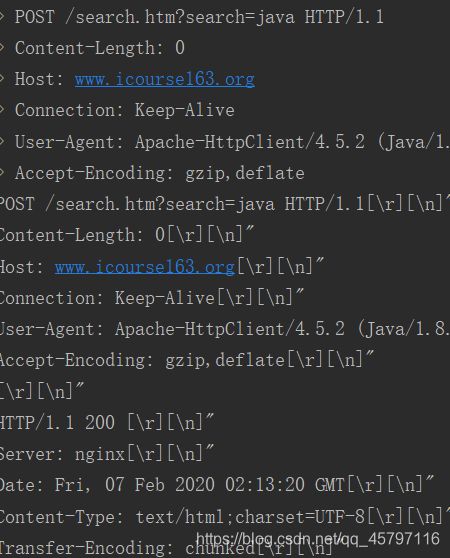
无参
package cn.csdn.crawlar.test;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
import org.apache.http.client.utils.URIBuilder;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import java.io.IOException;
public class HttpPostTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建HttpClient对象
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault();
//设置请求地址是:https://www.icourse163.org/search.htm?search=java#/
//创建URI地址
String string="https://www.icourse163.org/search.htm";
URIBuilder uriBuilder = new URIBuilder( string );
//设置参数
String param="search",value="java";
uriBuilder.setParameter(param,value );
//创建HttpPost对象,设置url访问地址
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(uriBuilder.build());
//发起请求
System.out.println("发起请求的信息"+httpPost);
//try/catch/finally : Ctrl+Alt+T
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
//使用HttpClient发起请求,获取response
response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
//解析响应
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) {
String content = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "utf8");
System.out.println(content.length());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭response
try {
response.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
httpClient.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
含参
package cn.csdn.crawlar.test;
import org.apache.http.NameValuePair;
import org.apache.http.client.entity.UrlEncodedFormEntity;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients;
import org.apache.http.message.BasicNameValuePair;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class HttpPostTest含参 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建HttpClient对象
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault();
//设置请求地址是:https://www.icourse163.org/search.htm?search=java#/
//创建URI地址
String string="https://www.icourse163.org/search.htm";
//创建HttpPost对象,设置url访问地址
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(string);
//声明list集合,封装请求集合,封装表单中的参数
List<NameValuePair> params = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>();
String name="search",value="java";
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair(name, value ) );
//创建表单的Entity对象
String charst="utf8";
UrlEncodedFormEntity formEntity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(params,charst);
//设置表单Entity对象到POST请求中
httpPost.setEntity(formEntity);
//发起请求
System.out.println("发起请求的信息"+httpPost);
//try/catch/finally : Ctrl+Alt+T
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
//使用HttpClient发起请求,获取response
response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
//解析响应
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) {
String content = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "utf8");
System.out.println(content.length());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭response
try {
response.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
httpClient.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
点开网址链接就可以进入学习视频啦!
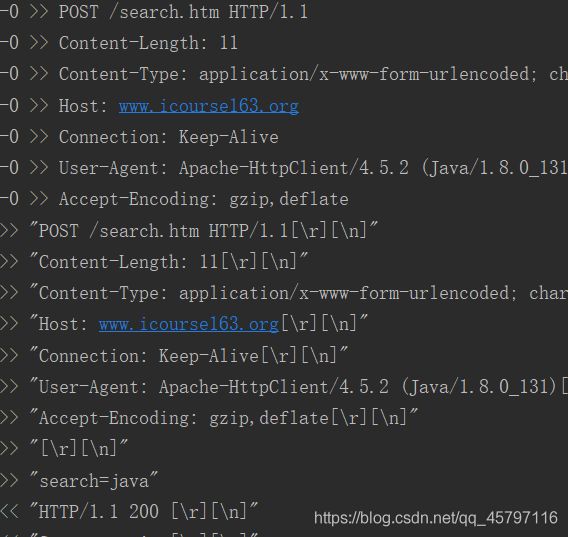
与Get含参请求方法相比较,Post含参请求方法主要区别在于一下几步:
声明list集合,封装请求集合,封装表单中的参数
创建表单的Entity对象
设置表单Entity对象到POST请求中