Spring boot admin 日志
前言
以前写过Spring Boot Admin的使用教程,还配置了各种路径参数。最近有留言说client的log怎么查看,其实log这个没写是因为,不能满足性能与管理的需要,ELK技术很成熟,搜索也是,备份管理都有现成的,但是估计有些小公司不需要这样的技术,只需要可以快速查看的日志入口就可以了。下面来试试。
1. SBA log示例
此次使用consul + admin + client
1. 1 consul启动
由于我的电脑是macos,只需要./consul agent -dev即可,win更容易,直接双击启动
1.2 admin server
pom依赖
spring-boot-admin
org.example
1.0-SNAPSHOT
4.0.0
admin-derver
de.codecentric
spring-boot-admin-starter-server
2.3.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
2.3.4.RELEASE
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-actuator
2.3.4.RELEASE
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-consul-discovery
2.2.4.RELEASE
org.slf4j
slf4j-api
1.7.30
bootMain类
package com.feng.admin.server;
import de.codecentric.boot.admin.server.config.EnableAdminServer;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAdminServer
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class ServerMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ServerMain.class, args);
}
}
application
server.port=8082
spring.application.name=AdminServer
management.endpoint.health.show-details=always
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
spring.cloud.consul.host=localhost
spring.cloud.consul.port=8500
spring.cloud.consul.discovery.service-name=${spring.application.name}1.3 admin client
client同理,复制AdminServer,即可去除
查看结果
2. client log改造
所谓的log实时查看是client提供一个读取本地文件的接口,然后admin定时调用显示,达到实时展示的效果。需要2步即可
2.1 application增加
management.endpoint.logfile.external-file=/Users/huahua/logs/boot.log
还有其他方式,后面说
2.2 增加logback-spring.xml文件
${APP_Name}
${CONSOLE_LOG_PATTERN}
utf8
${LOG_HOME}/boot.log
${LOG_HOME}/boot-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log
3
%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50}:%L - %msg%n
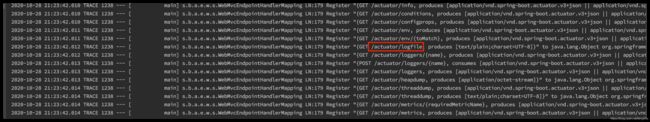
注意这个,必须为trace,可以打印actuator的HTTP requestmapping信息
重点关注logfile接口,这个接口必须配置参数才能出现
2.3 效果如下
F12可以看到,页面在定时请求
3. 原理分析
根源在一个自动配置上
public class LogFile {
public static final String FILE_NAME_PROPERTY = "logging.file.name";
public static final String FILE_PATH_PROPERTY = "logging.file.path";
package org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.logging;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectProvider;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.endpoint.condition.ConditionalOnAvailableEndpoint;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.logging.LogFileWebEndpoint;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionMessage;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionOutcome;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.SpringBootCondition;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.logging.LogFile;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
/**
* {@link EnableAutoConfiguration Auto-configuration} for {@link LogFileWebEndpoint}.
*
* @author Andy Wilkinson
* @author Christian Carriere-Tisseur
* @since 2.0.0
*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnAvailableEndpoint(endpoint = LogFileWebEndpoint.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(LogFileWebEndpointProperties.class)
public class LogFileWebEndpointAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
//条件式,很关键,默认条件是false
@Conditional(LogFileCondition.class)
public LogFileWebEndpoint logFileWebEndpoint(ObjectProvider logFile,
LogFileWebEndpointProperties properties) {
return new LogFileWebEndpoint(logFile.getIfAvailable(), properties.getExternalFile());
}
private static class LogFileCondition extends SpringBootCondition {
@Override
//条件判定
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();
String config = getLogFileConfig(environment, LogFile.FILE_NAME_PROPERTY);
ConditionMessage.Builder message = ConditionMessage.forCondition("Log File");
if (StringUtils.hasText(config)) {
return ConditionOutcome.match(message.found(LogFile.FILE_NAME_PROPERTY).items(config));
}
config = getLogFileConfig(environment, LogFile.FILE_PATH_PROPERTY);
if (StringUtils.hasText(config)) {
return ConditionOutcome.match(message.found(LogFile.FILE_PATH_PROPERTY).items(config));
}
config = environment.getProperty("management.endpoint.logfile.external-file");
if (StringUtils.hasText(config)) {
return ConditionOutcome.match(message.found("management.endpoint.logfile.external-file").items(config));
}
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(message.didNotFind("logging file").atAll());
}
private String getLogFileConfig(Environment environment, String configName) {
return environment.resolvePlaceholders("${" + configName + ":}");
}
}
} 所以logging.file.name、logging.file.path、management.endpoint.logfile.external-file都可以开启条件
logging.file.path配置要注意,这个是个坑,会默认spring.log的文件,logging.file.name不会
public String toString() {
return StringUtils.hasLength(this.file) ? this.file : (new File(this.path, "spring.log")).getPath();
}另外可以看到LogFileWebEndpointProperties这个配置
所以management.endpoint.logfile.externalFile也是可以的,实际上
Spring在解析properties时会在Spring缓存的Map中,把management.endpoint.logfile.external-file的key会转换成management.endpoint.logfile.externalFile。
最终的结果是实例化LogFileWebEndpoint,创建endpoint的requestmapping接口映射
/*
* Copyright 2012-2019 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.boot.actuate.logging;
import java.io.File;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.annotation.Endpoint;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.annotation.ReadOperation;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.web.annotation.WebEndpoint;
import org.springframework.boot.logging.LogFile;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
/**
* Web {@link Endpoint @Endpoint} that provides access to an application's log file.
*
* @author Johannes Edmeier
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Andy Wilkinson
* @since 2.0.0
*/
@WebEndpoint(id = "logfile")
public class LogFileWebEndpoint {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(LogFileWebEndpoint.class);
private File externalFile;
private final LogFile logFile;
public LogFileWebEndpoint(LogFile logFile, File externalFile) {
this.externalFile = externalFile;
this.logFile = logFile;
}
@ReadOperation(produces = "text/plain; charset=UTF-8")
//最终是requestmapping,访问这个方法,本质是读取文件
public Resource logFile() {
Resource logFileResource = getLogFileResource();
if (logFileResource == null || !logFileResource.isReadable()) {
return null;
}
return logFileResource;
}
private Resource getLogFileResource() {
if (this.externalFile != null) {
return new FileSystemResource(this.externalFile);
}
if (this.logFile == null) {
logger.debug("Missing 'logging.file.name' or 'logging.file.path' properties");
return null;
}
return new FileSystemResource(this.logFile.toString());
}
}
总结
其实Spring Boot Admin显示client的日志原理很简单,client暴露HTTP,admin定时调用。client端取日志需要配置才能开启,是读取本地文件。
源码分析也验证了上面的观点。