R语言拟合ARIMA模型
对于时间序列数据,常常需要用ARIMA模型作出拟合。本文使用R语言对客运量数据作出ARIMA拟合,提供一个一般化的ARIMA模型模板。
在开始前,安装并导入必要的包
install.packages('fUnitRoots')#安装单位根检验包
library(fUnitRoots)
install.packages('tseries')
library(tseries)
install.packages('forecast')#安装预测用的包
library(forecast)
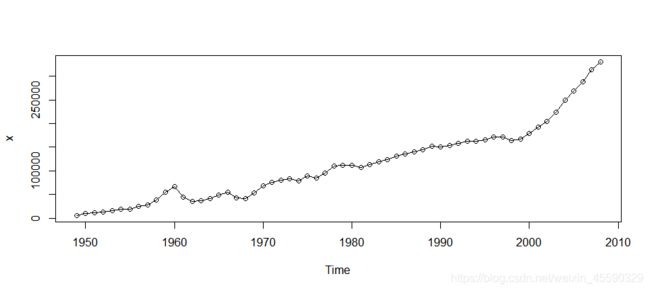
1.读取数据并画图
data_1=read.csv('E:/R_project/ARIMA/数据_1.csv')#路径务必使用 / ,且不要包含汉字!
x=ts(data_1$TLHYL,start = 1949,end=2008)#将数据转化为时间序列格式
plot(x,type='o')#画图
本文所使用的客流量时间序列数据:https://download.csdn.net/download/weixin_45590329/14143811
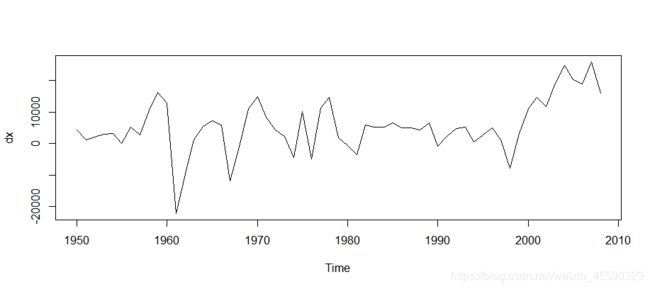
时间序列折线图如下所示,显然数据有递增趋势,初步判断数据不平稳
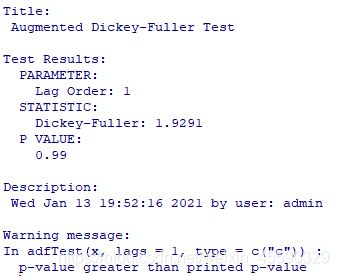
2.平稳性检验
adfTest(x,lags=1,type = c("c"));adfTest(x,lags=2,type = c("c"));adfTest(x,lags=3,type = c("c"))
adfTest(x,lags=1,type = c("nc"));adfTest(x,lags=2,type = c("nc"));adfTest(x,lags=3,type = c("nc"));
adfTest(x,lags=1,type = c("ct"));adfTest(x,lags=2,type = c("ct"));adfTest(x,lags=3,type = c("ct"));
进行三种形式的ADF单位根检验,p值较大(如部分结果所示),发现序列不平稳
3.对数据作一阶差分处理
dx=diff(x)
plot(dx)
4.对一阶差分数据进行平稳性检验
adfTest(dx,lags=1,type = c("c"));adfTest(dx,lags=2,type = c("c"));adfTest(dx,lags=3,type = c("c"))
adfTest(dx,lags=1,type = c("nc"));adfTest(dx,lags=2,type = c("nc"));adfTest(dx,lags=3,type = c("nc"));
adfTest(dx,lags=1,type = c("ct"));adfTest(dx,lags=2,type = c("ct"));adfTest(dx,lags=3,type = c("ct"));
5.序列的白噪声检验:LB检验
Box.test (dx, lag = 6, type = "Ljung")
Box.test (dx, lag = 12, type = "Ljung")
6.确定ARMA(p,q)阶数
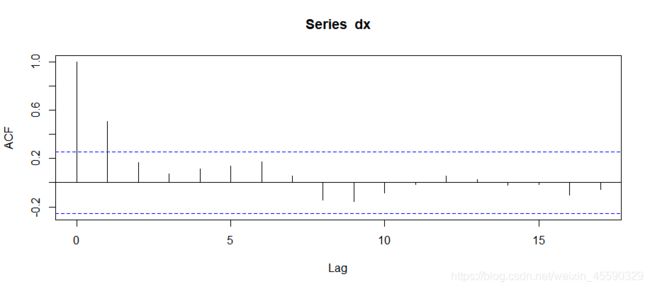
acf(dx) # 自相关系数图1阶截尾,决定MA(1)
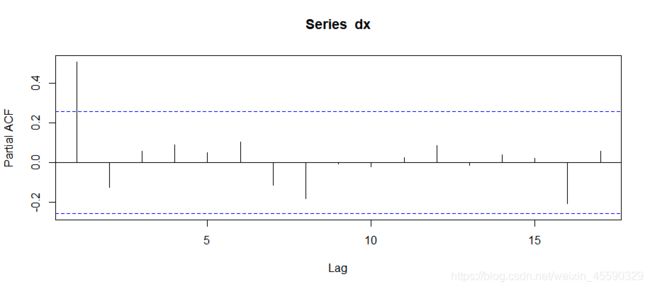
pacf(dx) # 偏相关系数图1阶截尾,决定AR(1)
根据自相关系数图ACF和偏自相关系数图PACF,将原始数据确定为ARIMA(1,1,1)模型
7.参数估计
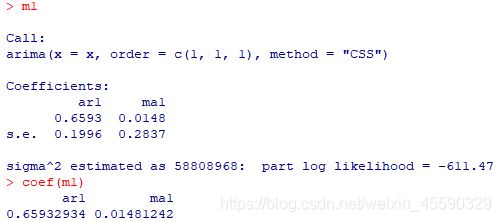
m1 = arima(x,order=c(1,1,1),method="CSS") # CSS为条件最小二乘法
m1
coef(m1)
m2=arima(x,order=c(1,1,1), method="ML") # ML为极大似然估计法
m2
coef(m2)
8.模型检验:检验序列残差是否为白噪声
e1=residuals(m1)#提取拟合的残差,并进行白噪声检验
Box.test(e1, lag = 6, type = "Ljung")
Box.test (e1, lag =12, type = "Ljung")
e2=residuals(m2)#提取拟合的残差,并进行白噪声检验
Box.test(e2, lag = 6, type = "Ljung")
Box.test (e2, lag =12, type = "Ljung")
最终检验结果显示无法拒绝原假设,说明残差序列为白噪声,模型拟合良好

9.模型优化:AIC和BIC准则
aic1=m1$loglik + (0+2+1)/length(x)
sbc1=m1$loglik + log(length(x))*(0+2+1)/length(x)
aic1;sbc1
aic2=m2$loglik + (0+2+1)/length(x)
sbc2=m2$loglik + log(length(x))*(0+2+1)/length(x)
aic2;sbc2
模型1的aic和sbc均小于模型2,故模型1拟合更好
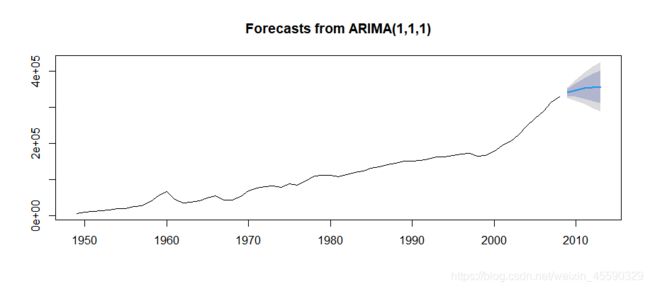
10.模型预测
predict(m1,n.ahead = 5)
往后预测5个值,得到340962.1 347956.4 352567.9 355608.4
11.预测并画图
data_1.TLHYL = forecast(m1,h=5)
data_1.TLHYL
plot(data_1.TLHYL)
install.packages('fUnitRoots')#安装单位根检验包
library(fUnitRoots)
install.packages('tseries')
library(tseries)
install.packages('forecast')#安装预测用的包
library(forecast)
#1.读取数据
data_1=read.csv('E:/R_project/ARIMA/数据_1.csv')
x=ts(data_1$TLHYL,start = 1949,end=2008)#将数据转化为时间序列格式
plot(x,type='o')
#画图,数据有明显递增趋势,初步判断不平稳
#2.平稳性检验
adfTest(x,lags=1,type = c("c"));adfTest(x,lags=2,type = c("c"));adfTest(x,lags=3,type = c("c"))
adfTest(x,lags=1,type = c("nc"));adfTest(x,lags=2,type = c("nc"));adfTest(x,lags=3,type = c("nc"));
adfTest(x,lags=1,type = c("ct"));adfTest(x,lags=2,type = c("ct"));adfTest(x,lags=3,type = c("ct"));
#进行三种形式的ADF单位根检验,p值较大(如部分结果所示),发现序列不平稳
#3.对数据作一阶差分处理
dx=diff(x)
plot(dx)#作出数据一阶差分后折线图,初步判断平稳
#4.对一阶差分数据进行平稳性检验
adfTest(dx,lags=1,type = c("c"));adfTest(dx,lags=2,type = c("c"));adfTest(dx,lags=3,type = c("c"))
adfTest(dx,lags=1,type = c("nc"));adfTest(dx,lags=2,type = c("nc"));adfTest(dx,lags=3,type = c("nc"));
adfTest(dx,lags=1,type = c("ct"));adfTest(dx,lags=2,type = c("ct"));adfTest(dx,lags=3,type = c("ct"));
#拒绝原假设说明序列平稳
#5.序列的白噪声检验:LB检验
#非白噪声序列才有拟合的意义
Box.test (dx, lag = 6, type = "Ljung")
Box.test (dx, lag = 12, type = "Ljung")
#拒绝原假设说明序列为非白噪声
#6.确定ARMA(p,q)阶数
acf(dx) # 自相关系数图1阶截尾,决定MA(1)
pacf(dx) # 偏相关系数图1阶截尾,决定AR(1)
#将原始数据确定为ARIMA(1,1,1)模型
#7.参数估计
m1 = arima(x,order=c(1,1,1),method="CSS") # CSS为条件最小二乘法
m1
coef(m1)
m2=arima(x,order=c(1,1,1), method="ML") # ML为极大似然估计法
m2
coef(m2)
#8.模型检验:检验序列残差是否为白噪声
#最终检验结果显示无法拒绝原假设,说明残差序列为白噪声,模型拟合良好
e1=residuals(m1)#提取拟合的残差,并进行白噪声检验
Box.test(e1, lag = 6, type = "Ljung")
Box.test (e1, lag =12, type = "Ljung")
e2=residuals(m2)#提取拟合的残差,并进行白噪声检验
Box.test(e2, lag = 6, type = "Ljung")
Box.test (e2, lag =12, type = "Ljung")
#9.模型优化:AIC和BIC准则
#模型1的aic和sbc均小于模型2,故模型1拟合更好
aic1=m1$loglik + (0+2+1)/length(x)
sbc1=m1$loglik + log(length(x))*(0+2+1)/length(x)
aic1;sbc1
aic2=m2$loglik + (0+2+1)/length(x)
sbc2=m2$loglik + log(length(x))*(0+2+1)/length(x)
aic2;sbc2
#10.模型预测
predict(m1,n.ahead = 5)#往后预测5个值,得到340962.1 347956.4 352567.9 355608.4
#11.预测并画图
data_1.TLHYL = forecast(m1,h=5)#基于模型1做5期预测
data_1.TLHYL
plot(data_1.TLHYL)