- 类所描述的是对象知道什么与执行什么, 任意类得每个实例都带有相同的方法, 但是方法可以根据实例变量的值来表现不同的行为。
知道什么: 实例变量, 执行什么: 方法. 例如:


一个方法执行不同void play() {
soundPlayer.playSound( title );
}
Song t2 = new Song();
t2.setArtist( "Travis" );
t2.setTitle("Sing");
Song s3 = new Song();
s3.setArtist( "Sex Pistols");
s3.setTitle("My way");
// 可见上边的方法, playSound要把实例变量 title 作为参数, 执行起来肯定返回不同结果.
- 参数传递的真谛
Java 是通过传值传递的, 也就是说通过拷贝传递.


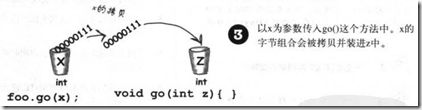
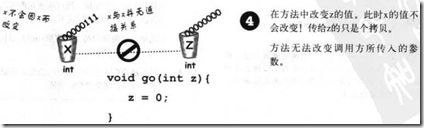
注意: 引用类型也是一样, 传递的拷贝, 只不过因为它是指针, 是间接的, 所以才会出现在函数内修改也会影响到函数外.
方法只能返回一个值, 如果你想返回多个就要用到数组, 如果是同类型的就用普通数组, 如果是不同类型的, 要用 arraylist.
- 封装
类似, cat.height = 27; 这种直接修改实例变量, 有什么不妥呢? 比如 cat.height = 0; 这是一个严重的逻辑错误, 但是没有办法,
你准许别人这样修改. 如果调用 setter方法, 就没关系, 因为可以增加逻辑判断, 使该值在合理的范围以内.
原则: 将你的实例变量标记为私有的, 并提供getter, setter方法来控制存取.
备注: 有些变量在 setter中什么也没限制, 是不是增加负担? 这样做还是有好处的, 就是在将来你想增加这个实例变量的设置时, 哈哈,
只要在 setter 中增加就可以了.
- 所有实例变量都有默认值
integer 0
float 0.0
boolean false
reference null
- 实例变量与局部变量差别
实例变量声明在类内而不是方法中
局部变量没有默认值, 必须要初始化
- 变量的比较, 包括reference类型
基本变量比较是否相等: ==

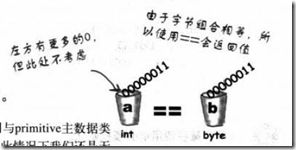
refernence是否指向同一个堆: ==

reference指向的堆的值是否相等: equals(), 即这两个对象是否在意义上相等.
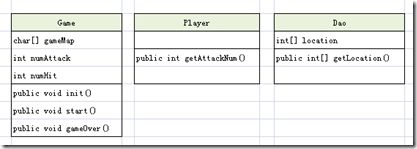
- 问题求解步骤 ( 游戏为例 )


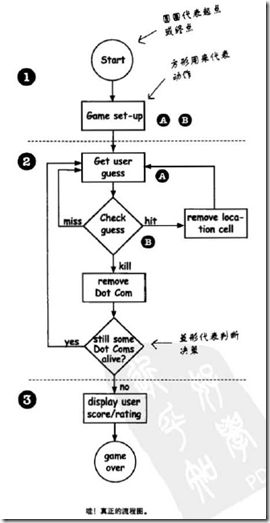

简化版游戏: 只是横排的达康公司…
开发类得过程:
- 找出类应该做的事情
- 列出实例变量和方法
- 编写方法伪码 ( 帮助你专注逻辑而不需要顾虑到程序语法 )
- 编写方法测试程序
- 实现类
- 测试方法
- 除错或重新设计
- 邀请辣妹参加庆功派对
1. 伪码设计:

说明实例变量用途: 大致逻辑上实现方法. ( 高手基本上可以不用了, 直接编码 )
2. 编写测试代码: 来自极限编程(XP)
即编写一个类, 带main方法, 并调用刚刚创建的对象, 思索该对象中那些地方需要测试, 思索的过程中, 就会对这个类有个更深刻的认识.
3. 真实码
- for 循环
从 java 5.0(Tiger)开始, java提供加强版得for循环, 它能够很容易的逐个运行数组或其他集合(collection)的元素.
for( String name: nameArray) {} 其中String 是指数组元素类型,必须与循环变量类型一致. 另外中间是 冒号: 而不是分号;
nameArray: 必须是对数组或其他集合的引用(reference).
- 以上小游戏的 Java 源码


GameTest/* * File: GameTest.java * ----------------------------- * This class is for testing, only has main method. */
public class GameTest {
/** * @param args */
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Game game = new Game();
game.init();
game.start();
game.gameOver();
}
}


Game/* * File: Game.java * ---------------------------- * This class is for the main game. * Game initialize, start and so on. * */
import java.util.*;
public class Game {
/* initialize the game */
public void init() {
gameMap = new char[7];
Dao dao = new Dao();
daoLocation = dao.getLocation();
for (int i: daoLocation) {
gameMap[i] = 'D';
}
}
/* start the game */
public void start() {
Player player = new Player();
int num = -1;
while (numHit < 3) {
System.out.println("Please guess the number: ^_^");
num = player.getAttackNum();
for (int i: daoLocation) {
if (num == i && gameMap[i] == 'D') {
gameMap[i] = 'A';
numHit++;
result = "Hit";
break;
}
}
System.out.println(result);
result = "Miss";
numAttack++;
}
}
public void gameOver() {
System.out.println("Congatulation, you finish your game, the detail as below:");
System.out.println("Total attack times: "+numAttack);
}
/* private instance values */
private String result = "Miss"; // every time, you attack and the result.
private int[] daoLocation; // The location of the company.
private char[] gameMap ; // The graph map for the game.
private int numAttack = 0; // count the attack number.
private int numHit = 0; // count the hit number.
}


Player/* * File: Player.java * ----------------------------------- * This class is player, player can guess the game. */
import java.io.*;
public class Player {
public int getAttackNum() {
String inputLine = null;
try {
BufferedReader is = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in));
inputLine = is.readLine();
if (inputLine.length() == 0) return -1;
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IoException:" + e);
}
int num = Integer.parseInt(inputLine);
return num;
}
}


Dao/* * File: Dao.java * ------------------------ * This class is for the company Dao. * it will show on the Game map. */
import java.util.*;
public class Dao {
/* create the location for the company */
public int[] getLocation() {
return location;
}
/* private instance values */
private int[] location = {2, 3, 4};
}
类得结构