Pytorch学习笔记 2.2:线性回归下的梯度下降
线性回归下的梯度下降
The Gradient Descent Of Linear Regression
自学视频PyTorch学这个就够了!:
课件以及代码:Pytorch.zip
这节课(lesson 3)用到的数据集和代码:lesson03代码及数据.zip
我用的Pycharm运行的,大家关注我就能下载了,不用收费 呜呜呜。
学他学他学他!就学他!讲的太透彻了,我刚上初中就能听明白,小白一枚之前看Pytorch的教程死活看不懂,没想到这个一看就明白了!兄弟姐妹们学起来!
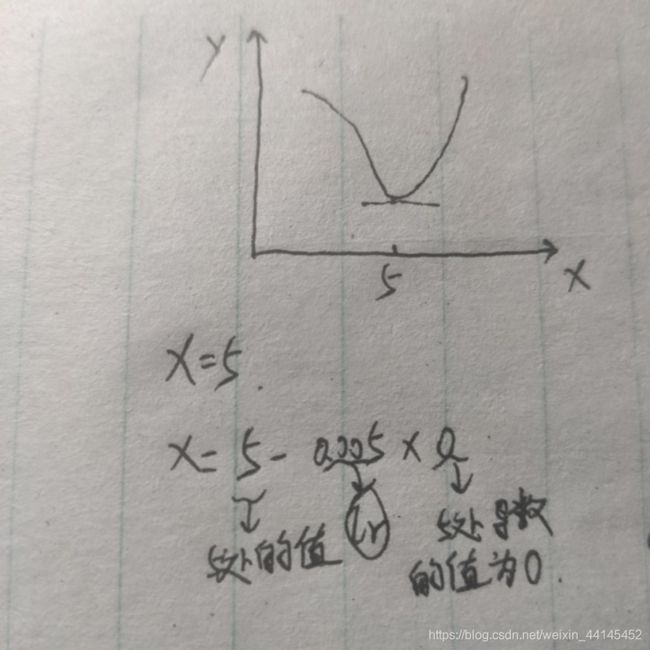
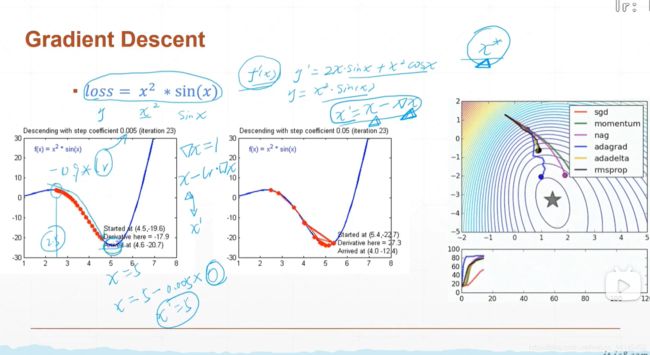 这里有一个loss函数:
这里有一个loss函数:
当loss值最低的时候,就是求得的结果与预期结果最接近的时候。
代码:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import torch
import pandas as pd
# %matplotlib inline
# %config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'svg'
# 绘制 loss 曲线
train_loss_results = [] # 将每轮的loss记录在此列表中,为后续画loss曲线提供数据
points = np.genfromtxt('l3_data.csv',delimiter = ',')
plt.scatter(points[:,0],points[:,1],c = '',edgecolors = 'b',s = 15)
plt.show()
# y = wx + b
def compute_error_for_line_given_points(b, w, points):
"""
计算给定超参数[w,b]的误差值
"""
totalError = 0
for i in range(0, len(points)):
x = points[i, 0]
y = points[i, 1]
totalError += (y - (w * x + b)) ** 2
return totalError / float(len(points))
def step_gradient(b, w, points, lr):
b_gradient = 0
w_gradient = 0
N = float(len(points))
for i in range(len(points)):
x = points[i, 0]
y = points[i, 1]
b_gradient += -(2/N) * (y - ((w * x) + b))
w_gradient += -(2/N) * x * (y - ((w * x) + b))
b_new = b - (lr * b_gradient)
w_new = w - (lr * w_gradient)
return [b_new, w_new]
def gradient_descent_runner(points, b, w, lr, iterations):
"""
梯度下降
"""
for i in range(iterations):
b, w = step_gradient(b, w, np.array(points), lr)
print("iterations {}, loss: {}".format(i, compute_error_for_line_given_points(b,w,points)))
train_loss_results.append(compute_error_for_line_given_points(b,w,points)) # 将4个step的loss求平均记录在此变量中
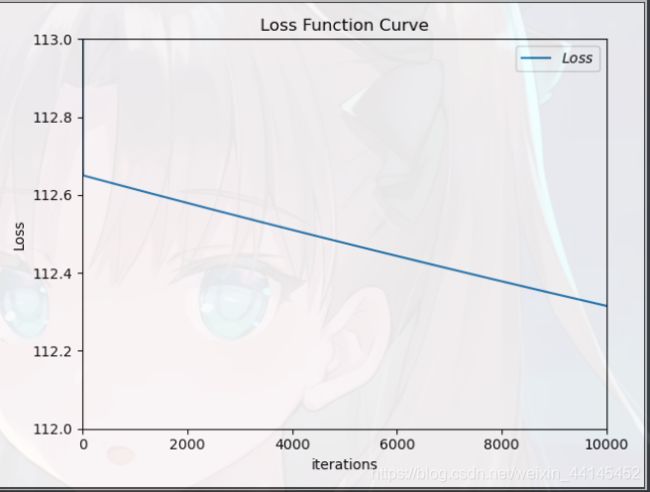
plt.title('Loss Function Curve') # 图片标题
plt.xlabel('iterations') # x轴变量名称
plt.ylabel('Loss') # y轴变量名称
plt.axis([0, 10000, 112, 113])
plt.plot(train_loss_results, label="$Loss$") # 逐点画出trian_loss_results值并连线,连线图标是Loss
plt.legend() # 画出曲线图标
plt.show() # 画出图像
return [b, w]
def run():
points = np.genfromtxt('l3_data.csv', delimiter = ',')
lr = 0.0001
initial_b = 0
initial_w = 0
iterations = 10000
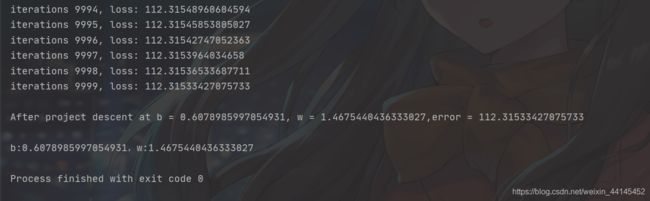
print(f"Starting project descent at b = {initial_b}, w = {initial_w}, error = {compute_error_for_line_given_points(initial_b,initial_w,points)}")
print('\nRunning...')
[b, w] = gradient_descent_runner(points, initial_b, initial_w, lr, iterations)
print(f"\nAfter project descent at b = {b}, w = {w},error = {compute_error_for_line_given_points(b,w,points)}")
print('\nb:{},w:{}'.format(b, w))
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()
里面用了三个函数:
第一个函数:compute_error_for_line_given_points(b, w, points):是用来就是来计算loss均值的
第二个函数:step_gradient(b, w, points, lr): 计算 b 和 w的梯度值
第三个函数:gradient_descent_runner(points, b, w, lr, iterations):运行10000次,不断迭代b和w,批量梯度下降,优化参数
运行结果:
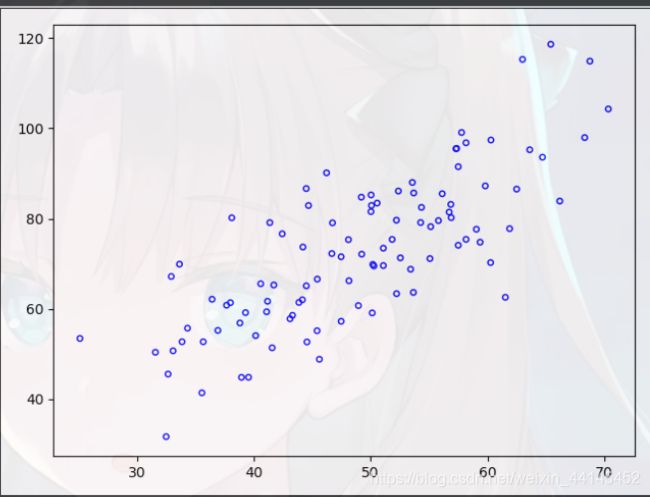
x-y散点图