c++ primer 学习杂记3【标准IO库】
第8章 标准IO库
发现书中一个错误,中文版p248
流状态的查询和控制,举了一个代码例子:
int ival; // read cin and test only for EOF; loop is executed even if there are other IO failures while (cin >> ival, !cin.eof()) { if (cin.bad()) // input stream is corrupted; bail out throw runtime_error("IO stream corrupted"); if (cin.fail()) { // bad input cerr<< "bad data, try again"; // warn the user cin.clear(istream::failbit); // reset the stream continue; // get next input } // ok to process ival }
但是我运行之后发现,如果输入的字符非int类型,则会产生死循环,不会有再次输入的提示符。
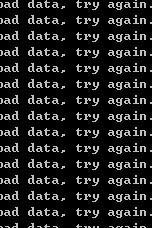
百度,参考如下几篇文章:
http://blog.csdn.net/daineng/article/details/2252730
http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/240034587
http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/100051638
解决方法总结如下:
while(cin>>ival, !cin.eof()) { if (cin.bad()) throw runtime_error("IO stream corrupted"); if (cin.fail()) { cerr<<"bad data, try again."<<endl; cin.clear(); cin.ignore(10000,'\n'); continue; } }
或者,用如下语句代替cin.clear();
cin.clear(istream::failbit ^ cin.rdstate());
结果如下:
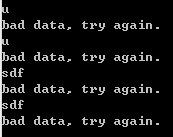
注意,这里要弄明白clear函数并不是我们表面上以为的那种功能。
s.clear()将流s中的所有状态值都重设为有效状态。相当于s.clear(goodbit);
s.clear(flag)将流s中的某个指定条件状态设置为有效。包括两个步骤:清除所有标志;设置标志为flag.
msdn中的解释:
basic_ios::clear
Clears all error flags.
void clear( iostate _State=goodbit, bool _Reraise = false ); void clear( io_state _State );
_State (optional)