Pytorch深度学习框架YOLOv3目标检测学习笔记(三)——网络的前向传播
定义网络
我们前面指出,用nn.Module类去搭建pytorch传统结构。让我们从我们的检测文件中定义网络
在darknet.py中,我们加入了如下类
class Darknet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, cfgfile):
super(Darknet, self).__init__()
self.blocks = parse_cfg(cfgfile)
self.net_info, self.module_list = create_modules(self.blocks)
继承了nn.Module类并命名为darknet初始化成员为member,blocks,net_info和module_list
网络的前向传播
前向传播通过重写nn.Module类中的forward函数实现
forward函数两个目的,1计算输出2以某种方式变化输出检测特征图以便后面处理
def forward(self, x, CUDA):
modules = self.blocks[1:]
outputs = {} #We cache the outputs for the route layer
forward有三个参数self,x,CUDA如果CUDA is True,用GPU加速前向传播
这里我们迭代self.blocks[1:]而不是self.blocks因为self.blocks的第一个元素是网络块而不是前向传播的部分
因为路线和段阶层需要前面层的输出特征,我们暂时将每一层的输出特征放到outputs这个目录中,关键字是层的索引,权值是特征图。像create_modules函数的例子,我们迭代含有网络的模块module_list,需要注意的是模块在配置文件中已经加入了一定的顺序,说明我们只需要运行我们的输入模块来获得输出
write = 0 #This is explained a bit later
for i, module in enumerate(modules):
module_type = (module["type"])
卷积和上采样层
遇到卷积或者上采样模块,就该使用前向传播
if module_type == "convolutional" or module_type == "upsample":
x = self.module_list[i](x)
路线层和短接层
如果看到路线层的代码,我们必须想到两种情况,如果我们要链接两个特征图,我们用到torch.cat函数第二个参数为1,因为我们想沿着深度方向链接特征图
elif module_type == "route":
layers = module["layers"]
layers = [int(a) for a in layers]
if (layers[0]) > 0:
layers[0] = layers[0] - i
if len(layers) == 1:
x = outputs[i + (layers[0])]
else:
if (layers[1]) > 0:
layers[1] = layers[1] - i
map1 = outputs[i + layers[0]]
map2 = outputs[i + layers[1]]
x = torch.cat((map1, map2), 1)
elif module_type == "shortcut":
from_ = int(module["from"])
x = outputs[i-1] + outputs[i+from_]
YOLO (检测层)
YOLO检测层的输出是包含着特征图深度方向的属性的锚框的卷积层,相邻的网格所预测锚框的属性。
另外一个问题是因为检测在三中尺度下进行,预测图的维度也不同,尽管三种特征图的维度不同,但输出处理方式是一致的,将在一个向量中操作而不是三个分开的向量。
转换输出
在util.py中提供了predict_transform函数,当我们使用Darknet类中的forward函数时我们会引入predict_transform这个函数
在util.py中添加导入的模块
from __future__ import division
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
import numpy as np
import cv2
predict_transform函数有五个参数:prediction (our output), inp_dim (input image dimension), anchors, num_classes, and an optional CUDA flag
def predict_transform(prediction, inp_dim, anchors, num_classes, CUDA = True):
predict_transform函数读取检测特征图并将其转化成2-D向量,每一行的向量对应着锚框的权值
如下是前面转化的代码
batch_size = prediction.size(0)
stride = inp_dim // prediction.size(2)
grid_size = inp_dim // stride
bbox_attrs = 5 + num_classes
num_anchors = len(anchors)
prediction = prediction.view(batch_size, bbox_attrs*num_anchors, grid_size*grid_size)
prediction = prediction.transpose(1,2).contiguous()
prediction = prediction.view(batch_size, grid_size*grid_size*num_anchors, bbox_attrs)
锚点的维度是根据net块的高和宽的属性确定的,这些属性描述了输入图像的维度,比检测图要大,所以,我们必须根据检测特征图的步长来划分锚框
anchors = [(a[0]/stride, a[1]/stride) for a in anchors]
我们需要根据第一部分的公式来转换我们的输出
用sigmoid函数处理XY坐标和目标得分
#Sigmoid the centre_X, centre_Y. and object confidencce
prediction[:,:,0] = torch.sigmoid(prediction[:,:,0])
prediction[:,:,1] = torch.sigmoid(prediction[:,:,1])
prediction[:,:,4] = torch.sigmoid(prediction[:,:,4])
给中心预测坐标加入网格偏置
#Add the center offsets
grid = np.arange(grid_size)
a,b = np.meshgrid(grid, grid)
x_offset = torch.FloatTensor(a).view(-1,1)
y_offset = torch.FloatTensor(b).view(-1,1)
if CUDA:
x_offset = x_offset.cuda()
y_offset = y_offset.cuda()
x_y_offset = torch.cat((x_offset, y_offset), 1).repeat(1,num_anchors).view(-1,2).unsqueeze(0)
prediction[:,:,:2] += x_y_offset
将锚点添加到锚框的维度上去
#log space transform height and the width
anchors = torch.FloatTensor(anchors)
if CUDA:
anchors = anchors.cuda()
anchors = anchors.repeat(grid_size*grid_size, 1).unsqueeze(0)
prediction[:,:,2:4] = torch.exp(prediction[:,:,2:4])*anchors
将sigmoid激活函数应用到类的得分中
prediction[:,:,5: 5 + num_classes] = torch.sigmoid((prediction[:,:, 5 : 5 + num_classes]))
最后我们想做的是将预测图转换成输入图像一样大小,锚框的大小属性根据特征图(13*13),如果输入416×416,我们在这个属性乘步长,将stride设置成variable
prediction[:,:,:4] *= stride
包含循环体
在函数末尾返回预测值
return prediction
重新访问检测层
将输出向量转换后,我们就能连接三个不同尺度的检测图成为一个大的向量,
现在我们使用predict_transform函数,我们在forward函数中写调整检测特征图的代码:
在darknet.py文件中
加入如下导入包
from util import *
然后在forward函数中
elif module_type == 'yolo':
anchors = self.module_list[i][0].anchors
#Get the input dimensions
inp_dim = int (self.net_info["height"])
#Get the number of classes
num_classes = int (module["classes"])
#Transform
x = x.data
x = predict_transform(x, inp_dim, anchors, num_classes, CUDA)
if not write: #if no collector has been intialised.
detections = x
write = 1
else:
detections = torch.cat((detections, x), 1)
outputs[i] = x
返回检测值
return detections
测试前向传播
现在一个创建虚拟输入的函数,将这个输入传输到网络中,在写这函数之前,将图片保存到工作目录中去,如果是在linux系统中输入
wget https://github.com/ayooshkathuria/pytorch-yolo-v3/raw/master/dog-cycle-car.png
然后,在darknet.py文件开始定义函数
def get_test_input():
img = cv2.imread("dog-cycle-car.png")
img = cv2.resize(img, (416,416)) #Resize to the input dimension
img_ = img[:,:,::-1].transpose((2,0,1)) # BGR -> RGB | H X W C -> C X H X W
img_ = img_[np.newaxis,:,:,:]/255.0 #Add a channel at 0 (for batch) | Normalise
img_ = torch.from_numpy(img_).float() #Convert to float
img_ = Variable(img_) # Convert to Variable
return img_
然后输入如下代码
model = Darknet("cfg/yolov3.cfg")
inp = get_test_input()
pred = model(inp, torch.cuda.is_available())
print (pred)
就可以看到输出文件了
( 0 ,.,.) =
16.0962 17.0541 91.5104 ... 0.4336 0.4692 0.5279
15.1363 15.2568 166.0840 ... 0.5561 0.5414 0.5318
14.4763 18.5405 409.4371 ... 0.5908 0.5353 0.4979
⋱ ...
411.2625 412.0660 9.0127 ... 0.5054 0.4662 0.5043
412.1762 412.4936 16.0449 ... 0.4815 0.4979 0.4582
412.1629 411.4338 34.9027 ... 0.4306 0.5462 0.4138
[torch.FloatTensor of size 1x10647x85]
向量的形状是11064785,第一个维度是批的大小,因为我们只用了一张图片所以是1,对于一批中的每张图片,我们有10647*85表,表的每一行代表锚框
在这一点上,网络有随机权值,并且不会产生正确输出,我们需要在网络中加载权值文件,所以我们使用了官方的权值文件
下载预训练权重
将权值文件下载到工作目录
wget https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3.weights
理解权重文件
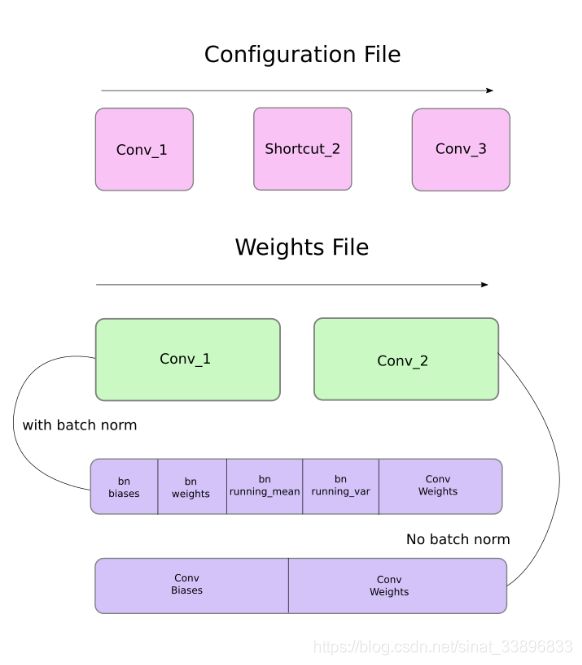
官方权值文件是包含权重的二进制文件。
首先,权重只属于两种层,批处理层或者卷积层
这些层的权重像配置文件中存储的那样。所以,如果卷积层紧接着是短接层,短接层和另一个卷积块成块,我们会期望文件包含先前卷积块的权值,紧接着后面的块。
当卷积块中出现批量归一化,就没有偏置,但是当没有批量归一化层,权重的偏置必须从文件中得到。
下图总结权重怎么储存
载入权重
写一个载入权重函数,是Darknet类的成员函数,会取一个参数作为权重文件的路径
def load_weights(self, weightfile):
权重文件的前160字节存储5个int32值构成文件的开头
#Open the weights file
fp = open(weightfile, "rb")
#The first 5 values are header information
# 1. Major version number
# 2. Minor Version Number
# 3. Subversion number
# 4,5. Images seen by the network (during training)
header = np.fromfile(fp, dtype = np.int32, count = 5)
self.header = torch.from_numpy(header)
self.seen = self.header[3]
剩下的位代表权值,权重保存在float32,用np.adarray加载剩下的权重
weights = np.fromfile(fp, dtype = np.float32)
使用了权值文件,权值加载进了网络的模块中去
ptr = 0
for i in range(len(self.module_list)):
module_type = self.blocks[i + 1]["type"]
#If module_type is convolutional load weights
#Otherwise ignore.
在循环中,我们首先检查卷积块是否含有批量归一化,基于这个,我们载入权重
if module_type == "convolutional":
model = self.module_list[i]
try:
batch_normalize = int(self.blocks[i+1]["batch_normalize"])
except:
batch_normalize = 0
conv = model[0]
设置ptr变量来跟踪我们在权值阵列的位置,如果批量归一化是True,按下面的方式加载权重
if (batch_normalize):
bn = model[1]
#Get the number of weights of Batch Norm Layer
num_bn_biases = bn.bias.numel()
#Load the weights
bn_biases = torch.from_numpy(weights[ptr:ptr + num_bn_biases])
ptr += num_bn_biases
bn_weights = torch.from_numpy(weights[ptr: ptr + num_bn_biases])
ptr += num_bn_biases
bn_running_mean = torch.from_numpy(weights[ptr: ptr + num_bn_biases])
ptr += num_bn_biases
bn_running_var = torch.from_numpy(weights[ptr: ptr + num_bn_biases])
ptr += num_bn_biases
#Cast the loaded weights into dims of model weights.
bn_biases = bn_biases.view_as(bn.bias.data)
bn_weights = bn_weights.view_as(bn.weight.data)
bn_running_mean = bn_running_mean.view_as(bn.running_mean)
bn_running_var = bn_running_var.view_as(bn.running_var)
#Copy the data to model
bn.bias.data.copy_(bn_biases)
bn.weight.data.copy_(bn_weights)
bn.running_mean.copy_(bn_running_mean)
bn.running_var.copy_(bn_running_var)
如果批量归一化不为真,从卷积层加载偏置
else:
#Number of biases
num_biases = conv.bias.numel()
#Load the weights
conv_biases = torch.from_numpy(weights[ptr: ptr + num_biases])
ptr = ptr + num_biases
#reshape the loaded weights according to the dims of the model weights
conv_biases = conv_biases.view_as(conv.bias.data)
#Finally copy the data
conv.bias.data.copy_(conv_biases)
最后,加载卷积层的权重
#Let us load the weights for the Convolutional layers
num_weights = conv.weight.numel()
#Do the same as above for weights
conv_weights = torch.from_numpy(weights[ptr:ptr+num_weights])
ptr = ptr + num_weights
conv_weights = conv_weights.view_as(conv.weight.data)
conv.weight.data.copy_(conv_weights)
我们已经写完了函数,现在可以在darknet对象中调用load_weights函数将权重文件加载到Darknet对象中去
model = Darknet("cfg/yolov3.cfg")
model.load_weights("yolov3.weights")