使用 express 构建简单 GraphQL 接口
使用 express 构建简单 GraphQL 接口
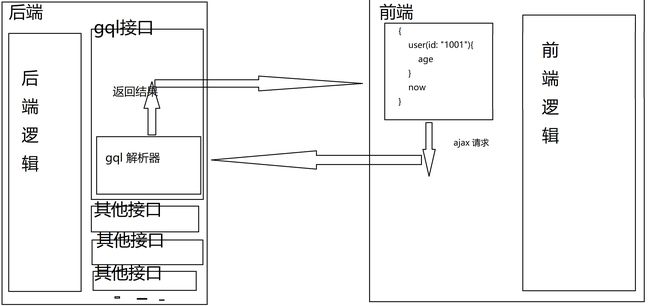
GQL
GQL(Graph Query Language) 是一种查询语言。用来设计出较 Restful api 更易于扩展和升级的接口,可以理解为 Restful api 的替代品。
GQL 服务可以开放在 Restful api 下,不过其逻辑并不依赖任何平台。
在后端,可以使用 GQL 直接描述数据模型,或使用 GraphQL.js 提供的其他接口来描述数据模型。
在前端,使用 GQL 直接描述我们需要的数据结构,然后就可以拿到不多不少、结构相似的数据。
例如我们请求,
{
user {
name
}
}
返回,
{
"data": {
"user": {
"name": "高厉害"
}
}
}
使用GraphQL.js
GraphQL.js泛指使用 JavaScript 实现的 GraphQL 库,我们在 node.js 平台学习开发 GQL 接口可以称之为 —— 学习GraphQL.js。
GraphQL.js的核心是一个解析器,用来解析 GQL 文本,实现“定义 GQL 数据模型”,和“增删改查数据”,本文仅描述 GQL 的查询接口。
初始化
初始化并安装依赖,
npm init -y
npm i express graphql
在graphql中,我们暂时仅关心两个接口:graphql和buildSchema,前者是 GQL 的解析器,后者用于构造一个GraphQLSchema类型的对象。
来看看解析器都需要什么参数,下面给出一个调用实例:
graphql.graphql(schema, query, root).then((gqlRes) => {
console.log(gqlRes);
});
-
schema 是查询接口的模型(
GraphQLSchema类型) -
query 是 GQL 的查询文本,例如
{ user { name } } -
root 是查询接口模型涉及到的每个字段的函数(GQL 对不同层次函数调用是广度优先的)
使用 graphql 开发查询接口只需要三步,第一步是描述数据模型和查询接口模型(对应 schema),第二步是针对每个字段提供函数(对应 root),第三步是将数据送往解析器并将结果返回给请求端。
数据模型
在GraphQL.js里,查询接口模型的类型是GraphQLSchema,我们可以使用buildSchema来构造。
下面开始设计一个对用户开放的接口
假设我们在这个接口可能需要获得两个东西:
- 根据 id 查询用户信息
- 当前时间
| 字段 | 类型 |
|---|---|
| user | UserType |
| now | string |
使用 GQL 描述为:
type Query {
user(id: String!): UserType
now: String
}
user 字段括号里是参数,通过 id 唯一确定一个用户,参数末尾的 ! 表示该字段必须提供。
Query 的位置是自定义类型名,但接口模型的类型固定为 Query。
同样地,UserType 也是一种自定义类型,考虑下面这个用户模型,id 为主键:
| 字段 | 类型 |
|---|---|
| id | string |
| username | string |
| age | int |
使用 GQL 描述为:
type UserType {
id: String
username: String
age: Int
}
调用buildSchema,将返回一个GraphQLSchema对象,实现如下:
const schema = graphql.buildSchema(`
type UserType {
id: String
username: String
age: Int
}
type Query {
user(id: String!): UserType
}
`);
这样一来我们就搞定了解析器的第一个参数 schema。
字段函数
我们有了数据模型,下面就要确定数据来源,这里简单手动提供一些数据和接口:
'./db.js'
const data = {
'1001': {
username: '高厉害', age: 21 },
'1002': {
username: '列队猫', age: 90 },
'1003': {
username: '小明', age: 15 },
'1004': {
username: '小红', age: 16 },
}
module.exports = {
findById(id) {
if (id in data) {
return data[id];
}
return null;
}
}
然后提供 root 参数,root 是一个对象,描述了 Query 即接口模型各个字段的来源:
let root = {
user: (args, context, info) => {
return db.findById(args.id);
},
now: (args, context, info) => {
return new Date().toLocaleString();
}
};
对象深层的字段也可以特别指定:
但这样做似乎就无法为外层的 user 提供函数了,所以传入解析器的 root 参数的功能非常局限,一般仅提供根字段的函数。
此外,若不提供深层字段的函数,则默认提供外层对象的对应值,就像上面那个例子那样。
let root = {
user: {
username: (args, context, info) => {
return ...;
},
age: (args, context, info) => {
return ...;
},
},
now: (args, context, info) => {
return new Date().toLocaleString();
},
};
提供服务
参数都准备好了。
写一个查询:
let query = `
{
user(id: "1001"){
age
}
now
}
`;
调用解析器:
graphql.graphql(schema, query, root).then((result) => {
console.log(result);
});
输出:
{
"data": {
"user": {
"age": 21
},
"now": "2021-1-25 16:19:03"
}
}
下面引入express,在某个路由提供 GQL 服务:
const graphql = require('graphql');
const express = require('express');
const db = require('./db.js');
const app = express();
// 数据模型和查询接口模型
let schema = graphql.buildSchema(`
type UserType {
id: String
username: String
age: Int
}
type Query {
user(id: String!): UserType
now: String
}
`);
// 所有字段的解析方法
let root = {
user: (args, context, info) => {
return db.findById(args.id);
},
now: (args, context, info) => {
return new Date().toLocaleString();
}
};
// 路由
app.use('/graphqlAPI', (req, res) => {
let reqJson = '';
req.on('data', (data) => reqJson += data);
req.on('end', () => {
reqJson = JSON.parse(reqJson);
graphql.graphql(schema, reqJson.query, root).then((result) => {
res.send(result);
});
})
});
app.listen(80, () => {
console.log('listen on 80.'); });
创建模型的推荐方法
刚才我们已经完成了一个简单的 GQL 接口,
- 通过 GQL 文本描述了数据模型和接口模型
- 提供了根字段的函数
- 对外提供 GQL 服务
在给定字段的函数时,我们无法对每个字段精确控制,root 参数仅允许对根字段(或深层的根字段)提供函数。
而文档中给出的字段的函数原型是这样的:
他有四个参数,而我们在 root 参数中提供的函数仅有三个参数
// See below about resolver functions.
type GraphQLFieldResolveFn = (
source?: any,
args?: {
[argName: string]: any},
context?: any,
info?: GraphQLResolveInfo
) => any
缺失的 source 参数是让接口模型的开发更加灵活的关键,该参数是当前字段外层对象的查询结果,例如 username 字段函数的 source 参数指代的是 user 的查询结果:
user {
id,
username,
age,
}
这样,我们可以在外层查询结束后(广度优先的),对内层进行更加精确的控制。
这种转变需要改动前两步,描述接口模型和提供字段函数,或者说,这两步在下面要介绍的推荐方法中是耦合的。
接下来我们需要关注两个类型,GraphQLSchema和GraphQLObjectType,前者是我们熟悉的 schema,而后者则是模型类型,虽然是一个 js 对象,但却用来描述一个 GQL 类型,例如 UserType(很有趣,因为 GQL.js 是 JavaScript 平台下的一个抽象,所以出现了从 js 类型中构造出另一个抽象类型的情况)。
GraphQLSchema对象用来直接提供给解析器,其构造接受一个 option,其中包含模型类型 query,我们现在仅关注 query 即可,其他的是用来实现增删改数据等操作的。
const schema = new GraphQLSchema({
query: new GraphQLObjectType({
...}),
});
现在需要从 GraphQL 提供的 DDL 转化为对 GraphQLObjectType 对象的实例化:
type UserType {
id: String
username: String
age: Int
}
等价于:
下面的代码中,每个字段都拥有一个 resolve 函数,他就是当前字段的(解析)函数。
注意,下面这些 resolve 都是默认实现。
const UserType = new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'UserType',
fields: {
id: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString,
resolve: (source, args, context, info) => {
return source.id;
},
},
username: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString,
resolve: (source, args, context, info) => {
return source.username;
}
},
age: {
type: graphql.GraphQLInt,
resolve: (source, args, context, info) => {
return source.age;
}
},
}
});
这就是一个 GQL 的模型类型,可以直接填充到GraphQLSchema对象的实例化操作中:
const schema = new GraphQLSchema({
query: UserType,
});
此时的 schema 等价于:
type Query {
id: String
username: String
age: Int
}
现在我们利用 UserType 来实现以下 DLL:
type UserType {
id: String
username: String
age: Int
}
type Query {
user(id: String!): UserType
}
上述代码等价于:
注意看下面代码是如何定义参数的
const schema = new graphql.GraphQLSchema({
query: new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'queryType',
fields: {
user: {
type: UserType,
args: {
id: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString,
defaultValue: '1001'
},
},
resolve: (source, args, context, info) => {
console.log(source, args, context, info);
return db.findById(args.id);
}
},
now: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString,
resolve: (source, args, context, info) => {
return new Date().toLocaleString();
}
}
}
}),
});
通过这种方法,我们将前两步合到了一起,且提供了更灵活的解析函数结构。
完整代码:
虽然形式上更加复杂了,但功能更加强大。
另外,注意,我没有为解析器提供 root 参数,因为没有必要,解析函数的结构已经体现在了接口模型的创建过程中,当然我们可以提供 root,不过 GQL.js 不会优先使用它。
const graphql = require('graphql');
const express = require('express');
const db = require('./db.js');
const app = express();
// 数据模型和查询接口模型
let UserType = new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'UserType',
fields: {
id: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString,
resolve: (source, args, context, info) => {
return source.id;
},
},
username: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString,
resolve: (source, args, context, info) => {
return source.username;
}
},
age: {
type: graphql.GraphQLInt,
resolve: (source, args, context, info) => {
return source.age;
}
},
}
});
let schema = new graphql.GraphQLSchema({
query: new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'queryType',
fields: {
user: {
type: UserType,
args: {
id: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString,
defaultValue: '1001'
},
},
resolve: (source, args, context, info) => {
console.log(source, args, context, info);
return db.findById(args.id);
}
},
now: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString,
resolve: (source, args, context, info) => {
return new Date().toLocaleString();
}
}
}
}),
});
// 路由
app.use('/graphqlAPI', (req, res) => {
let reqJson = '';
req.on('data', (data) => reqJson += data);
req.on('end', () => {
reqJson = JSON.parse(reqJson);
graphql.graphql(schema, reqJson.query).then((result) => {
res.send(result);
});
})
});
app.listen(80, () => {
console.log('listen on 80.'); });
GraphQLObjectType的 option 结构
完整结构见 https://graphql.org/graphql-js/type/#graphqlobjecttype
new GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'string',
fields: {
fieldName: {
type: GraphQLOutputType,
args: {
argName: {
type: GraphQLInputType,
defaultValue: any,
description: 'string',
},
...
},
resolve: (source, args, context, info) => any,
deprecationReason: 'string',
description: 'string'
},
...
},
});
使用express-graphql
我们是如何让 GQL 与 express 交互的?
从 express 的一个路由拿到数据,然后交给 graphql 解析并查询,最后返回解析的结果。
接下来我们使用express-graphql来完成这个中间操作,express-graphql为express和graphql提供了一个薄薄的中间层,这个中间层以graphqlHTTP中间件形式实现。
安装
npm i express-graphql
从express-graphql解构出中间件graphqlHTTP,然后开放在某个路由,
const express = require('express');
const {
graphqlHTTP: graphqlMiddleware } = require('express-graphql');
const graphql = require('graphql');
const app = express();
// 描述接口模型
const schema = ...;
// 路由
app.use('/graphqlAPI', graphqlMiddleware({
// 接口模型
schema,
// 传递给 graphql 函数
rootValue,
context,
// 将 web 调试应用开放在该路由,配置为 true 后访浏览器问该路由即可
graphiql: true,
}));
app.listen(80, () => {
console.log('listen on 80.'); });
context
刚才我们一直忽略了一个参数 context,他是 graphql 解析器的一个实参,也是字段解析函数的一个形参,用于不同解析函数间的通信,或是解析器过程需要使用到的一些参数,可以通过 context 从外部向解析器传入。
例如,想要在每个字段解析函数中拿到 req, res,我们可以向外包一层 lambda 用来接收参数,随后使用参数创建一个新的中间件并触发他:
app.use('/graphqlAPI', (req, res) => graphqlMiddleware({
schema: schema,
context: {
req, res },
graphiql: true,
})(req, res));
variables
一般一次 GQL 查询总包含两个东西,一个是 queryString,一个是 variables,我们刚才一直忽略了后者,
无伤大雅,我们只需要在前两个实现中接收并传入解析器即可,
解析器的完整参数:
graphql(
schema: GraphQLSchema,
requestString: string,
rootValue?: ?any,
contextValue?: ?any,
variableValues?: ?{
[key: string]: any},
operationName?: ?string
): Promise<GraphQLResult>