谈谈Epoll是如何工作的?
epoll相关视频解析:
支撑亿级io的底层基石 epoll实战揭秘
linux多线程之epoll原理剖析与reactor原理及应用
epoll的网络模型,从redis、memcached到nginx,一起搞定
epoll 是Linux平台下的一种特有的多路复用IO实现方式,与传统的 select 相比,epoll 在性能上有很大的提升。
epoll 的创建
要使用 epoll 首先需要调用 epoll_create() 函数创建一个 epoll 的句柄,epoll_create() 函数定义如下:
int epoll_create(int size);
参数 size 是由于历史原因遗留下来的,现在不起作用。当用户调用 epoll_create() 函数时,会进入到内核空间,并且调用 sys_epoll_create() 内核函数来创建 epoll 句柄,sys_epoll_create() 函数代码如下:
asmlinkage long sys_epoll_create(int size)
{
int error, fd = -1;
struct eventpoll *ep;
error = -EINVAL;
if (size <= 0 || (error = ep_alloc(&ep)) < 0) {
fd = error;
goto error_return;
}
fd = anon_inode_getfd("[eventpoll]", &eventpoll_fops, ep);
if (fd < 0)
ep_free(ep);
error_return:
return fd;
}
sys_epoll_create() 主要做两件事情:
- 调用 ep_alloc() 函数创建并初始化一个 eventpoll 对象。
- 调用 anon_inode_getfd() 函数把 eventpoll 对象映射到一个文件句柄,并返回这个文件句柄。
我们先来看看 eventpoll 这个对象,eventpoll 对象用于管理 epoll 监听的文件列表,其定义如下:
struct eventpoll {
...
wait_queue_head_t wq;
...
struct list_head rdllist;
struct rb_root rbr;
...
};
先来说明一下 eventpoll 对象各个成员的作用:
- wq: 等待队列,当调用 epoll_wait(fd) 时会把进程添加到 eventpoll 对象的 wq 等待队列中。
- rdllist: 保存已经就绪的文件列表。
- rbr: 使用红黑树来管理所有被监听的文件。
下图展示了 eventpoll 对象与被监听的文件关系:
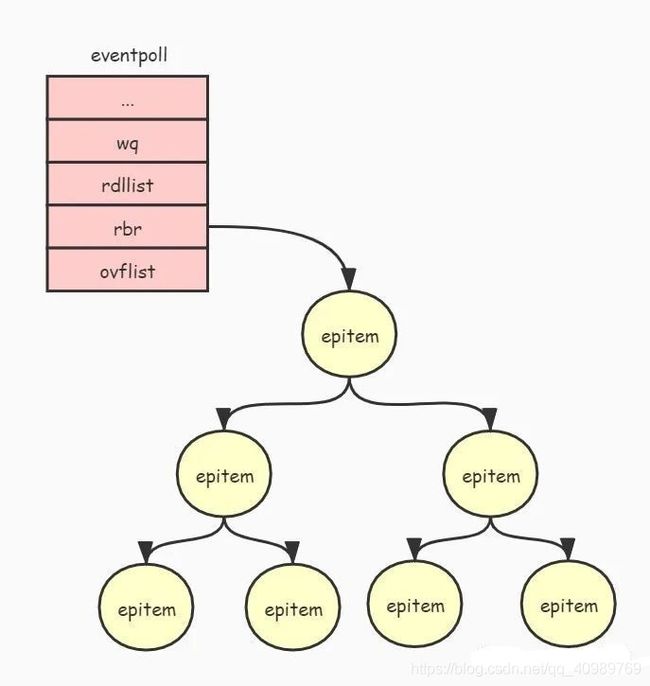
由于被监听的文件是通过 epitem 对象来管理的,所以上图中的节点都是以 epitem 对象的形式存在的。为什么要使用红黑树来管理被监听的文件呢?这是为了能够通过文件句柄快速查找到其对应的 epitem 对象。红黑树是一种平衡二叉树,如果对其不了解可以查阅相关的文档。
向 epoll 添加文件句柄
前面介绍了怎么创建 epoll,接下来介绍一下怎么向 epoll 添加要监听的文件。
通过调用 epoll_ctl() 函数可以向 epoll 添加要监听的文件,其原型如下:
long epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd,struct epoll_event *event);
下面说明一下各个参数的作用:
1、epfd: 通过调用 epoll_create() 函数返回的文件句柄。
2、op: 要进行的操作,有3个选项:
- EPOLL_CTL_ADD:表示要进行添加操作。
- EPOLL_CTL_DEL:表示要进行删除操作。
- EPOLL_CTL_MOD:表示要进行修改操作
3、fd: 要监听的文件句柄。
4、event: 告诉内核需要监听什么事。其定义如下:
struct epoll_event {
__uint32_t events; /* Epoll events */
epoll_data_t data; /* User data variable */
};
events 可以是以下几个宏的集合:
- EPOLLIN :表示对应的文件句柄可以读(包括对端SOCKET正常关闭);
- EPOLLOUT:表示对应的文件句柄可以写;
- EPOLLPRI:表示对应的文件句柄有紧急的数据可读;
- EPOLLERR:表示对应的文件句柄发生错误;
- EPOLLHUP:表示对应的文件句柄被挂断;
- EPOLLET:将EPOLL设为边缘触发(Edge Triggered)模式,这是相对于水平触发(Level Triggered)来说的。
- EPOLLONESHOT:只监听一次事件,当监听完这次事件之后,如果还需要继续监听这个socket的话,需要再次把这个socket加入到EPOLL队列里。
【文章福利】需要C/C++ Linux服务器架构师学习资料加群812855908(资料包括C/C++,Linux,golang技术,Nginx,ZeroMQ,MySQL,Redis,fastdfs,MongoDB,ZK,流媒体,CDN,P2P,K8S,Docker,TCP/IP,协程,DPDK,ffmpeg等)
data 用来保存用户自定义数据。
epoll_ctl() 函数会调用 sys_epoll_ctl() 内核函数,sys_epoll_ctl() 内核函数的实现如下:
asmlinkage long sys_epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op,
int fd, struct epoll_event __user *event)
{
...
file = fget(epfd);
tfile = fget(fd);
...
ep = file->private_data;
mutex_lock(&ep->mtx);
epi = ep_find(ep, tfile, fd);
error = -EINVAL;
switch (op) {
case EPOLL_CTL_ADD:
if (!epi) {
epds.events |= POLLERR | POLLHUP;
error = ep_insert(ep, &epds, tfile, fd);
} else
error = -EEXIST;
break;
...
}
mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);
...
return error;
}
sys_epoll_ctl() 函数会根据传入不同 op 的值来进行不同操作,比如传入 EPOLL_CTL_ADD 表示要进行添加操作,那么就调用 ep_insert() 函数来进行添加操作。
我们继续来分析添加操作 ep_insert() 函数的实现:
static int ep_insert(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event *event,
struct file *tfile, int fd)
{
...
error = -ENOMEM;
// 申请一个 epitem 对象
if (!(epi = kmem_cache_alloc(epi_cache, GFP_KERNEL)))
goto error_return;
// 初始化 epitem 对象
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->rdllink);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->fllink);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->pwqlist);
epi->ep = ep;
ep_set_ffd(&epi->ffd, tfile, fd);
epi->event = *event;
epi->nwait = 0;
epi->next = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR;
epq.epi = epi;
// 等价于: epq.pt->qproc = ep_ptable_queue_proc
init_poll_funcptr(&epq.pt, ep_ptable_queue_proc);
// 调用被监听文件的 poll 接口.
// 这个接口又各自文件系统实现, 如socket的话, 那么这个接口就是 tcp_poll().
revents = tfile->f_op->poll(tfile, &epq.pt);
...
ep_rbtree_insert(ep, epi); // 把 epitem 对象添加到epoll的红黑树中进行管理
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
// 如果被监听的文件已经可以进行对应的读写操作
// 那么就把文件添加到epoll的就绪队列 rdllink 中, 并且唤醒调用 epoll_wait() 的进程.
if ((revents & event->events) && !ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink)) {
list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq))
wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))
pwake++;
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
...
return 0;
...
}
被监听的文件是通过 epitem 对象进行管理的,也就是说被监听的文件会被封装成 epitem 对象,然后会被添加到 eventpoll 对象的红黑树中进行管理(如上述代码中的 ep_rbtree_insert(ep, epi))。
tfile->f_op->poll(tfile, &epq.pt) 这行代码的作用是调用被监听文件的 poll() 接口,如果被监听的文件是一个socket句柄,那么就会调用 tcp_poll(),我们来看看 tcp_poll() 做了什么操作:
unsigned int tcp_poll(struct file *file, struct socket *sock, poll_table *wait)
{
struct sock *sk = sock->sk;
...
poll_wait(file, sk->sk_sleep, wait);
...
return mask;
}
每个 socket 对象都有个等待队列(waitqueue, 关于等待队列可以参考文章: 等待队列原理与实现),用于存放等待 socket 状态更改的进程。
从上述代码可以知道,tcp_poll() 调用了 poll_wait() 函数,而 poll_wait() 最终会调用 ep_ptable_queue_proc() 函数,ep_ptable_queue_proc() 函数实现如下:
static void ep_ptable_queue_proc(struct file *file,
wait_queue_head_t *whead, poll_table *pt)
{
struct epitem *epi = ep_item_from_epqueue(pt);
struct eppoll_entry *pwq;
if (epi->nwait >= 0 && (pwq = kmem_cache_alloc(pwq_cache, GFP_KERNEL))) {
init_waitqueue_func_entry(&pwq->wait, ep_poll_callback);
pwq->whead = whead;
pwq->base = epi;
add_wait_queue(whead, &pwq->wait);
list_add_tail(&pwq->llink, &epi->pwqlist);
epi->nwait++;
} else {
epi->nwait = -1;
}
}
ep_ptable_queue_proc() 函数主要工作是把当前 epitem 对象添加到 socket 对象的等待队列中,并且设置唤醒函数为 ep_poll_callback(),也就是说,当socket状态发生变化时,会触发调用 ep_poll_callback() 函数。ep_poll_callback() 函数实现如下:
static int ep_poll_callback(wait_queue_t *wait, unsigned mode, int sync, void *key)
{
...
// 把就绪的文件添加到就绪队列中
list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
is_linked:
// 唤醒调用 epoll_wait() 而被阻塞的进程
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq))
wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);
...
return 1;
}
ep_poll_callback() 函数的主要工作是把就绪的文件添加到 eventepoll 对象的就绪队列中,然后唤醒调用 epoll_wait() 被阻塞的进程。
等待被监听的文件状态发生改变
把被监听的文件句柄添加到epoll后,就可以通过调用 epoll_wait() 等待被监听的文件状态发生改变。
epoll_wait() 调用会阻塞当前进程,当被监听的文件状态发生改变时,epoll_wait() 调用便会返回。
epoll_wait() 系统调用的原型如下:
long epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events, int maxevents, int timeout);
各个参数的意义:
- epfd: 调用 epoll_create() 函数创建的epoll句柄。
- events: 用来存放就绪文件列表。
- maxevents: events 数组的大小。
- timeout: 设置等待的超时时间。
epoll_wait() 函数会调用 sys_epoll_wait() 内核函数,而 sys_epoll_wait() 函数最终会调用 ep_poll() 函数,我们来看看 ep_poll() 函数的实现:
static int ep_poll(struct eventpoll *ep,
struct epoll_event __user *events, int maxevents, long timeout)
{
...
// 如果就绪文件列表为空
if (list_empty(&ep->rdllist)) {
// 把当前进程添加到epoll的等待队列中
init_waitqueue_entry(&wait, current);
wait.flags |= WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE;
__add_wait_queue(&ep->wq, &wait);
for (;;) {
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE); // 把当前进程设置为睡眠状态
if (!list_empty(&ep->rdllist) || !jtimeout) // 如果有就绪文件或者超时, 退出循环
break;
if (signal_pending(current)) {
// 接收到信号也要退出
res = -EINTR;
break;
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
jtimeout = schedule_timeout(jtimeout); // 让出CPU, 切换到其他进程进行执行
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
}
// 有3种情况会执行到这里:
// 1. 被监听的文件集合中有就绪的文件
// 2. 设置了超时时间并且超时了
// 3. 接收到信号
__remove_wait_queue(&ep->wq, &wait);
set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
}
/* 是否有就绪的文件? */
eavail = !list_empty(&ep->rdllist);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
if (!res && eavail
&& !(res = ep_send_events(ep, events, maxevents)) && jtimeout)
goto retry;
return res;
}
ep_poll() 函数主要做以下几件事:
1、判断被监听的文件集合中是否有就绪的文件,如果有就返回。
2、如果没有就把当前进程添加到epoll的等待队列中,并且进入睡眠。
3、进程会一直睡眠直到有以下几种情况发生:
- 被监听的文件集合中有就绪的文件
- 设置了超时时间并且超时了
- 接收到信号
4、如果有就绪的文件,那么就调用 ep_send_events() 函数把就绪文件复制到 events 参数中。
5、返回就绪文件的个数。
下面通过文字来描述一下这个过程:
- 通过调用 epoll_create() 函数创建并初始化一个 eventpoll 对象。
- 通过调用 epoll_ctl() 函数把被监听的文件句柄 (如socket句柄) 封装成 epitem 对象并且添加到
eventpoll 对象的红黑树中进行管理。 - 通过调用 epoll_wait() 函数等待被监听的文件状态发生改变。
- 当被监听的文件状态发生改变时(如socket接收到数据),会把文件句柄对应 epitem 对象添加到 eventpoll 对象的就绪队列 rdllist 中。并且把就绪队列的文件列表复制到 epoll_wait() 函数的 events 参数中。
- 唤醒调用 epoll_wait() 函数被阻塞(睡眠)的进程。
