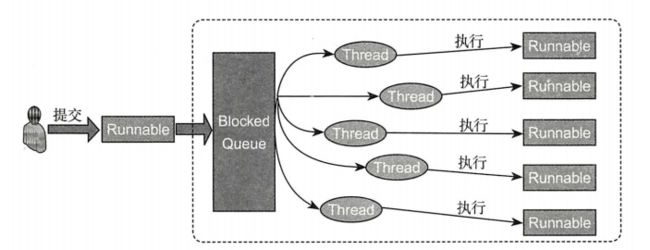
1.线程池简介
线程池的主要目的是重复利用线程,减少Thread创建、启动、销毁时的资源消耗,提高系统效率,系统性能往往和线程数量是一个抛物线的关系,因此要控制线程数量。
线程池里面存放在一定量的已经创建好的线程,当有任务提交给线程池时,线程池中的某个线程主动执行该任务,如果线程池中的线程数量不够,则需要自动扩充新的线程到线程池,但扩充的数量有限,受最大的线程数量限制,当任务比较少的时候,线程池能够自动回收、释放资源,为了能够异步提交任务和缓存未被处理的任务,需要一个队列。
完整的线程池应具备的要素:
1)任务队列,用于缓存提交的任务
2)线程数量管理功能,通常有三个参数来实现,线程初始数量init,线程池自动扩充最大数量max,线程空闲时维护一定的活跃数量或核心数量core,通常init<=core<=max
3)线程拒绝策略,如果线程数量已经达到上限且任务队列已满,则需要相应的拒绝策略来通知任务提交者
4)线程工厂,用于定制线程,如设置是否守护、线程名称
5)QueueSize:任务队列主要存放提交的Runnable,为了防止内存溢出,需要有limit数量对其进行控制
6)KeepDalive时间:该时间主要决定线程各个重要参数自动维护的时间间隔
线程池原理图:
2.线程池实现
2.1线程池类图
2.2线程池接口定义:
1)ThreadPool接口
/** * ThreadPool 主要定义一个线程池的基本操作和方法 */ public interface ThreadPool { //提交任务到线程池 void execute(Runnable runnable); //关闭线程池 void shutdown(); //获取初始线程数量 int getInitSize(); //获取最大线程数量 int getMaxSize(); //获取线程池核心线程数量 int getCoreSize(); //获取队列中缓存的任务数量 int getQueueSize(); //获取活跃的线程数量 int getActiveCount(); //查看线线程是否关闭 boolean isShutDown(); }
2)RunnableQueue接口
/** * RunnableQueue用于提交Runnable,是一个BlockedQueue,且有limit限制 */ public interface RunnableQueue { //提交新的Runnable void offer(Runnable runnable); //获取Runnable Runnable take() throws InterruptedException; //获取当前RunnableQueue里面Runnable数量 int size(); }
3)ThreadFactory接口
/** *ThreadFactory用于创建线程 */ public interface ThreadFactory { Thread createThread(Runnable ruanRunnable); }
4)DenyPolicy接口
/** * DenyPolicy拥有当任务到达max limit上限时决定采用何种策略通知提交者 */ public interface DenyPolicy { void reject(Runnable runnable,ThreadPool threadPool); //丢弃策略,当任务到达上限时直接丢弃任务 class DiscardDenyPolicy implements DenyPolicy{ @Override public void reject(Runnable runnable, ThreadPool threadPool) { //do nothing } } //异常策略,当任务到达上限时抛出异常 class AbortDenyPolicy implements DenyPolicy{ @Override public void reject(Runnable runnable, ThreadPool threadPool) { throw new RunnableDenyException("The Runnable " + runnable + " is abort."); } } //当前线程执行策略,当任务到达上限时由当前线程执行任务 class CurrentThreadRunDenyPolic implements DenyPolicy{ @Override public void reject(Runnable runnable, ThreadPool threadPool) { if(!threadPool.isShutDown()) { runnable.run(); } } } }
2.3辅助类
1)RunnableDenyException
/** * RunnableDenyException是RuntimeException子类,主要用于通知提交者任务队列无法再接收新的任务 */ public class RunnableDenyException extends RuntimeException{ public RunnableDenyException(String msg){ super(msg); } }
2)InternalTask
/** * InternalTask是Runnable的一个实现,主要用于ThreadPool内部, * 该类会用到RunnableQueue,不断从queue中取出Runnable并执行run方法 */ public class InternalTask implements Runnable { private final RunnableQueue runQueue; private volatile boolean running = true; public InternalTask(RunnableQueue runQueue) { this.runQueue = runQueue; } @Override public void run() { while(running && !Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { try { Runnable task = runQueue.take(); task.run(); } catch (Exception e) { running = false; break; } } } //停止当前线程 public void stop() { this.running = false; } }
2.4线程的实现
1)RunnableQueue的实现
public class LinkedRunnableQueue implements RunnableQueue { //任务队列的最大容量 private final int limit; //任务队列满了时的拒绝策略 private final DenyPolicy denyPolicy; //存放任务的队列 private LinkedListlinkedList = new LinkedList (); private final ThreadPool threadPool; public LinkedRunnableQueue(int limit,DenyPolicy denyPolicy,ThreadPool threadPool) { this.limit = limit; this.denyPolicy = denyPolicy; this.threadPool = threadPool; } //offer是一个同步方法,当数量达到最大值时,执行拒绝策略的拒绝方法 @Override public void offer(Runnable runnable) { synchronized (linkedList) { if(linkedList.size() >= limit) { denyPolicy.reject(runnable, threadPool); }else { linkedList.addLast(runnable); linkedList.notifyAll(); } } } //take方法也是同步方法,当队列为空时,阻塞 //如果阻塞被中断,需要抛出异常给上游 @Override public Runnable take() throws InterruptedException { synchronized (linkedList) { while(linkedList.isEmpty()) { try { linkedList.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw e; } } return linkedList.removeFirst(); } } @Override public int size() { synchronized (linkedList) { return linkedList.size(); } } }
2)ThreadPool的实现
import java.util.ArrayDeque; import java.util.Queue; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; public class BasicThreadPool extends Thread implements ThreadPool{ //初始线程数量 private final int innitSize; //最大线程数量 private final int maxSize; //核心线程数量 private final int coreSize; //当前活跃线程数量 private int activeCount; //线程工厂 private final ThreadFactory threadFactory; //任务队列 private final RunnableQueue runnableQueue; private final long keepAliveTime; private final TimeUnit timeUnit; //是否已关闭 private volatile boolean isShutdown = false; //工作线程队列 private class ThreadTask{ public ThreadTask(Thread thread,InternalTask internalTask) { this.thread = thread; this.internalTask = internalTask; } InternalTask internalTask; Thread thread; } private final QueuethreadQueue = new ArrayDeque<>(); private final static DenyPolicy DEFAULT_DENYPOLICY = new DenyPolicy.CurrentThreadRunDenyPolic(); private final static ThreadFactory DEFAULT_THREADFACTORY = new DefaultThreadFactory(); private static class DefaultThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory{ private static final AtomicInteger GROUP_COUNTER = new AtomicInteger(1); private static final ThreadGroup group = new ThreadGroup("MyThreadGroup-"+GROUP_COUNTER.getAndDecrement()); private static final AtomicInteger COUNTER = new AtomicInteger(0); @Override public Thread createThread(Runnable ruanRunnable) { return new Thread(group, ruanRunnable, "Thread-Pool-"+COUNTER.getAndDecrement()); } } public BasicThreadPool(int innitSize,int maxSize,int coreSize, int queueSize) { this( innitSize, maxSize, coreSize, DEFAULT_THREADFACTORY, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, DEFAULT_DENYPOLICY, queueSize); } public BasicThreadPool(int innitSize,int maxSize,int coreSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory,long keepAliveTime,TimeUnit timeUnit, DenyPolicy denyPolicy,int queueSize) { this.innitSize = innitSize; this.maxSize = maxSize; this.coreSize = coreSize; this.threadFactory = threadFactory; this.keepAliveTime = keepAliveTime; this.timeUnit = timeUnit; this.runnableQueue = new LinkedRunnableQueue(queueSize, denyPolicy, this); this.init(); } //初始时创建初始线程 private void init() { start(); for(int i = 0;i < innitSize;i++) { newThread(); } } //线程自动维护 //创建线程 private void newThread() { InternalTask internalTask = new InternalTask(runnableQueue); Thread thread = this.threadFactory.createThread(internalTask); ThreadTask threadTask = new ThreadTask(thread, internalTask); threadQueue.offer(threadTask); this.activeCount++; thread.start(); } //移除线程 private void removeThread() { ThreadTask threadTask = threadQueue.remove(); threadTask.internalTask.stop(); this.activeCount--; } //run方法继承自Thread,主要用于维护线程数量,如扩容、回收 @Override public void run() { while(!isShutdown && !isInterrupted()) { try { timeUnit.sleep(keepAliveTime); } catch (InterruptedException e) { isShutdown = true; break; } synchronized (this) { if(isShutdown) break; //如果队列中有任务未执行, activeCount < coreSize 则进行扩容 if(runnableQueue.size()>0 && activeCount < coreSize) { for(int i = activeCount;i < coreSize && i < runnableQueue.size();i++) { newThread(); } //continue防止一次扩充到最大数量 continue; } //如果队列中有任务未执行, activeCount < maxSize 则继续进行扩容 if(runnableQueue.size()>0 && activeCount < maxSize) { for(int i = activeCount;i < maxSize && i < runnableQueue.size();i++) { newThread(); } } //如果队列中没有任务,则进行回收,回收至core数量即可 if(runnableQueue.size() == 0 && activeCount > coreSize) { /*for(int i = activeCount;i > coreSize ;i++) { removeThread(); }*/ //下面写法较上面写法可以避免一次性直接将线程数量减少到coreSize for(int i = coreSize;i < activeCount;i++) { removeThread(); } } } } } @Override public void execute(Runnable runnable) { if(isShutdown) throw new IllegalStateException("the ThreadPool has destory."); this.runnableQueue.offer(runnable); } @Override public void shutdown() { synchronized (this) { if(isShutdown) return; isShutdown = true; threadQueue.forEach(threadTask->{ threadTask.internalTask.stop(); threadTask.thread.interrupt(); }); System.out.println("》》》》》》shutdown:"+getName()); this.interrupt(); } } @Override public int getInitSize() { if(isShutdown) throw new IllegalStateException("the ThreadPool has destory."); return this.innitSize; } @Override public int getMaxSize() { if(isShutdown) throw new IllegalStateException("the ThreadPool has destory."); return this.maxSize; } @Override public int getCoreSize() { if(isShutdown) throw new IllegalStateException("the ThreadPool has destory."); return this.coreSize; } @Override public int getActiveCount() { if(isShutdown) throw new IllegalStateException("the ThreadPool has destory."); return this.activeCount; } @Override public int getQueueSize() { if(isShutdown) throw new IllegalStateException("the ThreadPool has destory."); return this.runnableQueue.size(); } @Override public boolean isShutDown() { return isShutdown; } }
2.5使用线程池
1)动态扩展功能:
public class ThreadPoolTest { public static void main(String[] args) { final ThreadPool tp = new BasicThreadPool(2,6,4,1000); for(int i = 0;i < 20;i ++) { int j = i; tp.execute(()->{ try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("任务"+j+"由Thread:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"完成执行。"); }); } while(true) { try { System.out.println("tp.getActiveCount() :"+tp.getActiveCount()); System.out.println("tp.getCoreSize() :"+tp.getCoreSize()); System.out.println("tp.getInitSize() :"+tp.getInitSize()); System.out.println("tp.getMaxSize() :"+tp.getMaxSize()); System.out.println("tp.getQueueSize() :"+tp.getQueueSize()); System.out.println("======================================="); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("==============================E"); e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
输出:
tp.getActiveCount() :2
tp.getCoreSize() :4
tp.getInitSize() :2
tp.getMaxSize() :6
tp.getQueueSize() :18
=======================================
tp.getActiveCount() :2
tp.getCoreSize() :4
tp.getInitSize() :2
tp.getMaxSize() :6
tp.getQueueSize() :18
=======================================
任务1由Thread:Thread-Pool--1完成执行。
任务0由Thread:Thread-Pool-0完成执行。
tp.getActiveCount() :4
tp.getCoreSize() :4
tp.getInitSize() :2
tp.getMaxSize() :6
tp.getQueueSize() :14
=======================================
tp.getActiveCount() :4
tp.getCoreSize() :4
tp.getInitSize() :2
tp.getMaxSize() :6
tp.getQueueSize() :14
=======================================
任务2由Thread:Thread-Pool--3完成执行。
任务3由Thread:Thread-Pool--2完成执行。
任务4由Thread:Thread-Pool--1完成执行。
任务5由Thread:Thread-Pool-0完成执行。
tp.getActiveCount() :6
tp.getCoreSize() :4
tp.getInitSize() :2
tp.getMaxSize() :6
tp.getQueueSize() :8
=======================================
tp.getActiveCount() :6
tp.getCoreSize() :4
tp.getInitSize() :2
tp.getMaxSize() :6
tp.getQueueSize() :8
=======================================
任务7由Thread:Thread-Pool--2完成执行。
任务8由Thread:Thread-Pool--3完成执行。
任务6由Thread:Thread-Pool--4完成执行。
任务9由Thread:Thread-Pool--5完成执行。
任务10由Thread:Thread-Pool-0完成执行。
任务11由Thread:Thread-Pool--1完成执行。
tp.getActiveCount() :6
tp.getCoreSize() :4
tp.getInitSize() :2
tp.getMaxSize() :6
tp.getQueueSize() :2
=======================================
tp.getActiveCount() :6
tp.getCoreSize() :4
tp.getInitSize() :2
tp.getMaxSize() :6
tp.getQueueSize() :2
=======================================
任务12由Thread:Thread-Pool--2完成执行。
任务14由Thread:Thread-Pool--4完成执行。
任务13由Thread:Thread-Pool--3完成执行。
任务15由Thread:Thread-Pool--5完成执行。
任务17由Thread:Thread-Pool--1完成执行。
任务16由Thread:Thread-Pool-0完成执行。
tp.getActiveCount() :6
tp.getCoreSize() :4
tp.getInitSize() :2
tp.getMaxSize() :6
tp.getQueueSize() :0
=======================================
tp.getActiveCount() :6
tp.getCoreSize() :4
tp.getInitSize() :2
tp.getMaxSize() :6
tp.getQueueSize() :0
=======================================
任务18由Thread:Thread-Pool--2完成执行。
任务19由Thread:Thread-Pool--4完成执行。
tp.getActiveCount() :5
tp.getCoreSize() :4
tp.getInitSize() :2
tp.getMaxSize() :6
tp.getQueueSize() :0
=======================================
tp.getActiveCount() :5
tp.getCoreSize() :4
tp.getInitSize() :2
tp.getMaxSize() :6
tp.getQueueSize() :0
=======================================
tp.getActiveCount() :4
tp.getCoreSize() :4
tp.getInitSize() :2
tp.getMaxSize() :6
tp.getQueueSize() :0
=======================================
tp.getActiveCount() :4
tp.getCoreSize() :4
tp.getInitSize() :2
tp.getMaxSize() :6
tp.getQueueSize() :0
=======================================
tp.getActiveCount() :4
tp.getCoreSize() :4
tp.getInitSize() :2
tp.getMaxSize() :6
tp.getQueueSize() :0
=======================================
。。。。。
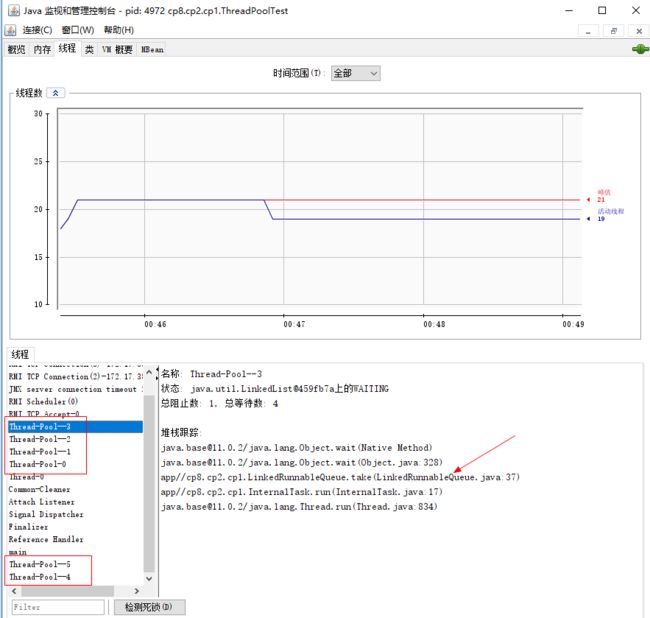
按照书上上面的线程数量应停止在core数量,看输出active的线程也确实如此,但是打开线程查看工具却发现线程数量仍旧保持在max,如下:
根据图中堆栈信息,可以发现线程都阻塞在获取任务的等待中了,如果长期没有任务提交,这些线程将长期保持,因此需要打断这些多余线程的循环等待。
遗留问题,请求支援:线程池停不下来