第四周------spring整合mybatis框架
spring框架整合mybatis
让我们一起来感受框架的强大,和spring配置地狱的疯狂吧
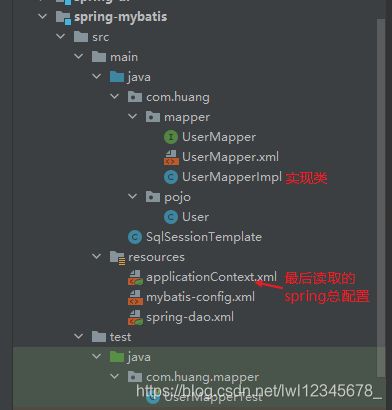
项目文件目录
配置文件
spring的核心配置 /spring-dao.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<!-- DataSource:使用Spring的数据源替换Mybatis的配置-->
<!-- 这里使用spring提供的jdbc-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<!-- 绑定mybatis配置文件-->
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"/>
<!-- 绑定mybatis配置文件中的Mapper接口的xml文件-->
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:com/huang/mapper/*.xml"/>
</bean>
<bean id="sqlSession" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate">
<!-- 只能使用构造器注入sqlSessionFactory,因为它没有set方法-->
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
</beans>
mybatis核心配置 /mybatis-config.xml
该文件中通常都只留下设置和别名,其余可以在spring配置文件配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- <properties resource="db.properties"/>-->
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true" />
</settings>
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.huang.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
</configuration>
最终读取的配置文件 /applicationContext.xml 将控制层的业务放在此文件,同时整合/spring-dao.xml文件中数据源和sqlSession等的配置,最后CPX中读取该文件即可,实现了配置文件的分工
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<import resource="spring-dao.xml"/>
<bean id="userMapper" class="com.huang.mapper.UserMapperImpl">
<property name="sqlSession" ref="sqlSession"/>
</bean>
</beans>
提示:在实现了以上三个配置文件的分层,spring的核心配置 /spring-dao.xml基本可以写死,可以作为默认文件保存为模板,以后直接使用即可,简化了我们的操作
pojo类
lombok配置在上篇博客已经有说明
package com.huang.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String pwd;
}
Mapper接口和接口xml和实现类
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> getUserList(int id);
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.huang.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="getUserList" resultType="user">
select * from mybatis.user where id = #{
id};
</select>
</mapper>
关键是实现mapper接口类的代码(注意理解各个文件之间的逻辑)
package com.huang.mapper;
import com.huang.pojo.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import java.util.List;
public class UserMapperImpl implements UserMapper{
private SqlSession sqlSession;
public void setSqlSession(SqlSession sqlSession) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
}
@Override
public List<User> getUserList(int id) {
return sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class).getUserList(id);
}
}
我们不必再通过new来得到sqlSession了,而是使用spring的set注入来获得sqlSession对象。
业务逻辑的接口都在application.xml中使用bean来配置 此处一定要理解各个文件之间的逻辑与联系。
<bean id="userMapper" class="com.huang.mapper.UserMapperImpl">
<property name="sqlSession" ref="sqlSession"/>
</bean>
测试类
public class UserMapperTest {
@Test
public void test1() throws IOException {
//原来没整合前的代码
// String resources = "mybatis-config.xml";
// InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resources);
// SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
// UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// List userList = mapper.getUserList();
// for (User user : userList) {
// System.out.println(user);
// }
// sqlSession.close();
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserMapper userMapper = context.getBean("userMapper", UserMapper.class);
for (User user : userMapper.getUserList(1)) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
}
整合易错点:
org.springframework.core.ResolvableType org.springframework.beans.factory.co
spring-framework 核心包版本必须保持一致