linux内核数据结构之双向循环链表struct list_head
linux内核数据结构之双向循环链表struct list_head
链表对每位写过程序的同学都再熟悉不过了,无非是对链表的创建、初始化、插入、删除、遍历等操作。但您是否想过如果针对每一种数据结构都实现一套对链表操作的服务原语是否太浪费时间和精力了,实际上在linux内核2.4以后内核开发者对链表的结构实现了一个统一的接口,可以利用这些接口实现链表而不用去考虑数据结构的差异。您的兴趣是否来了.....那就让我们一睹为快吧。
--------------------------------原理篇-------------------------------------
链表数据结构的定义很简单(节选自[include/linux/list.h],以下所有代码,除非加以说明,其余均取自该文件):
struct list_head {
struct list_head *prev;
struct list_head *next;
};
list_head结构包含两个指向list_head结构的指针prev和next,乍一看这定义,似乎很普通,其实伟大常常孕育在平凡之中。
我是初学者时会这样构造数据:
struct list_node {
TYPE data; //代表链表中的数据域 TYPE为你要定义存放数据的类型
struct list_node *prev;
strcut list_node *next;
};
这样我们把数据嵌入到链表节点中示意图:
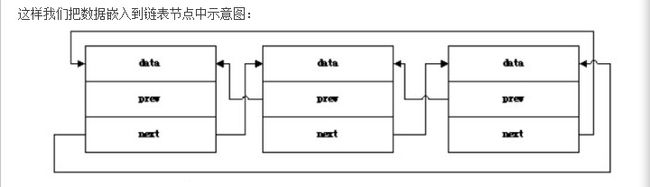
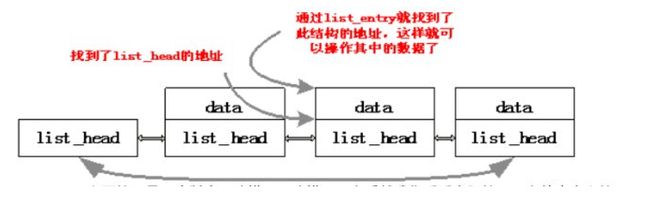
而内核的数据结却是将链表的节点嵌入到数据结构中:
struct list_node{
TYPE data;
struct list_head list; //定义一个list_head的节点
};

链表的操作是通过访问每一个list_head来操作的。
在这种链表中,所有的链表基本操作都是针对list_head数据结构进行,而不是针对包含list_head的数据结构,所以无论什么数据,链表操作都得到了统一。那么,现在碰到一个问题,因为所有链表操作涉及到的指针都是指向list_head数据结构的,而不是包含的数据结构,那么怎样从list_head的地址得到包含其的数据结构的地址呢?我们来看linux内核中的list_entry(ptr,type,member)这个宏:
有两个定义可供参考:
(1)参考定义
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
( (type *)((char *)(ptr)-(unsigned long)(&((type *)0)->member)) )
(unsigned long)(&(type *)0)->member) )定义为把0地址转化为type类型的指针,然后获取该结构中member成员的指针,并将其强制转换为unsigned long类型。看上去不知所云,我们细细的来分析一下:
在应用中:
ptr是指向list_head类型链表的指针
type为一个包含list_head结构的结构类型
member为结构中类型为list_head的域

如果data现在在0地址上,那么&(type *)0->member就是从0地址到list_head的偏移量(相对长度),说白了就是数据域data在 此结构中的占多长的空间。这样如果我们有一个绝对的地址ptr(list_head类型)那么:
绝对地址 - 相对地址 = 包含list_head结构的绝对地址
Very good!!!
试想如果我们知道链表中的list_head的地址(以为list_head为链表的节点我们当然可以知道它的地址)就可以找到包含这个节点的数据结构的地址,找到这个数据结构的地址顺理成章的就可以访问这个结构中的每个元素了。
2)上面的只是一个版本,略懂。。略懂。。之后然我们看看实际的list.h文件中定义的list_entry()。
实际定义
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
container_of(ptr, type, member)
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \
const typeof( ((type*)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \
(type *)( (char*)__mptr - offsetof(type, member) ); \
})
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER)
上面的定义是GNU风格的C语言,实际上是和(1)是一个道理的,请您简要分析。
--------------------------实践篇------------------------------------------------------------------
既然原理看懂了,那我们也的实际操作一下毕竟实践是验证真理的唯一标准。
操作前先来看看两个宏:
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) {&(name), &(name)}
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
我们来分析第二个宏,定义一个以name为名字的节点,并将节点初始化如图:
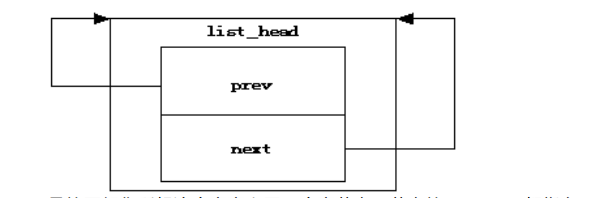
是的正如你所想这个宏定义了一个空节点,节点的next,prev都指向节点本身,相当于:
name->prev = &name;
name->next = &name;
list_add(new, head); //将new插入到head元素后面
list_add_tail(new, head); //额,跟上面的区别就不用解释了,不过这里的head是 真正的链表头
list_del(entry); //删除entry节点
list_empty(head); //检查是否为空链表
list_entry(ptr, type, member); //前面解释过了
list_for_each(pos, head); //遍历列表,每次循环是通过pos返回节点list_head指针
//下面这个最有用!
list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member); //同上,但通过pos返回的是container数据结 构的地址。
。。。。。。
还有其他的定义都可以在include/linux/list.h中找到
需要强调的是:
#define list_for_each(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member); \
prefetch(pos->member.next), &pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))
这里的prefetch()还没理清,将在后续文章中写出。
写个小例子说明用法:
#include
#include
#include "list.h" //因为我没有是从内核中copy过来的list.h放在本地文件夹下
//注意你用到哪个定义就copy那个定义
struct test_list{
int data;
struct list_head list;
};
int main()
{
LIST_HEAD(boy); //define and initialize a doubly linked of boy
int i;
struct test_list *ptr[10];
struct list_head *tmp = NULL;
struct test_list *node;
for(i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
ptr[i] = (struct test_list *)malloc(sizeof(struct test_list));
if(!ptr[i])
printf("error");
ptr[i]->data = i;
}
for(i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
list_add_tail(&ptr[i]->list, &boy);
}
printf("Traverse link:\n");
list_for_each(tmp, &boy) //boy为链表的头节
{ // tmp为list_head类型的指针用来暂时存放节点
node = list_entry(tmp, struct test_list, list); //node为包含list_head的结构这里类
//型为struct test_list 即如前面所讲
//知道了链表的节点(tmp)就可以找
//到包含节点结构的地址
printf("%d ", node->data);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
} 
为了方便我测试用的list.h在下边给出
#ifndef _LINUX_LIST_H
#define _LINUX_LIST_H
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER)
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \
const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \
(type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );})
struct list_head{
struct list_head *next;
struct list_head *prev;
};
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) {&(name), &(name)}
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
container_of(ptr, type, member)
#define list_for_each(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
static inline int list_empty(struct list_head *head)
{
return head->next == head;
}
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev,struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = new;
new->next = next;
new->prev = prev;
prev->next = new;
}
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head, head->next);
}
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head->prev, head);
}
static inline void __list_del(struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = prev;
prev->next = next;
}
static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
}
#endif参考资料:
Linux内核设计与实现(原书第三版第六章)
在线文档https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/kernel/l-chain/