2019暑假牛客多校第五场B.generator 1(十进制矩阵快速幂)
B.generator 1
传送门
You are given four positive integers x 0 , x 1 , a , b x_0, x_1, a, b x0,x1,a,b. And you know x i = a ⋅ x i − 1 + b ⋅ x i − 2 x_i = a \cdot x_{i-1} + b \cdot x_{i-2} xi=a⋅xi−1+b⋅xi−2 for all i ≥ 2 i \ge 2 i≥2.
Given two positive integers n, and MOD, please calculate x n x_n xn modulo MOD.
Does the problem look simple? Surprise! The value of n may have many many digits!
输入描述:
The input contains two lines.
The first line contains four integers x 0 , x 1 , a , b x_0, x_1, a, b x0,x1,a,b,a,b ( 1 ≤ x 0 , x 1 , a , b ≤ 1 0 9 1 \le x_0, x_1, a, b \le 10^9 1≤x0,x1,a,b≤109 ).
The second line contains two integers n, MOD ( 41 ≤ n < 1 0 ( 1 0 6 ) 41 \le n < 10^{(10^6)} 41≤n<10(106), 1 0 9 < M O D ≤ 2 × 1 0 9 10^9 < MOD \le 2 \times 10^9 109<MOD≤2×109, n has no leading zero).
输出描述:
Print one integer representing the answer.
示例1
输入
1 1 1 1
10 1000000001
输出
89
说明
The resulting sequence x is Fibonacci sequence. The 11-th item is 89.
示例2
输入
1315 521 20185 5452831
9999999999999999999999999999999999999 1000000007
输出
914730061
题意
给你 x 0 x_0 x0、 x 1 x_1 x1、a、b、b、mod,根据 x i = a ∗ x i − 1 + b ∗ x i − 2 x_i=a∗x_{i−1}+b∗x_{i−2} xi=a∗xi−1+b∗xi−2求出 x n x_n xn
思路
一般看到这种题就会想到矩阵快速幂,但是这次的n太大了,所以要用十进制倍增来算,(第一种做法)。同时还可以用二进制快速幂优化它(第二种做法)。
- 矩阵快速幂的通项式
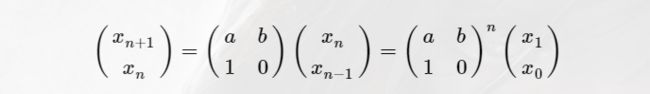
- 用十进制
设 ( a b 1 0 ) \tbinom{a \ \ \ b}{1\ \ \ 0} (1 0a b)为res
则可得 a n s = r e s n [ i ] − ′ 0 ′ ans=res^{n[i]-'0'} ans=resn[i]−′0′(n[i]用字符串储存n)
我们再设res = r e s 10 ( i − 1 ) res^{10(i-1)} res10(i−1);
就是分解n为每一位,再去相乘。
如
r e s 298 = r e s 1 ∗ 8 ∗ r e s 10 ∗ 9 ∗ r e s 100 ∗ 2 res^{298}=res^{1*8}*res^{10*9}*res^{100*2} res298=res1∗8∗res10∗9∗res100∗2
计算每一位即可。
所以最后就是
len(n)→1
ans=ans*cul(res,n[i]-‘0’);
res=pow(res,10);
ac代码(1512ms):
#include 另一种写法(1800ms):
#include