Java零碎知识点总结
- 标准代码——JavaBean
JavaBean 是 Java语言编写类的一种标准规范。符合 JavaBean 的类,要求类必须是具体的和公共的,并且具有无参数的构造方法,提供用来操作成员变量的 set 和 get 方法。
格式
public class ClassName{
成员变量
构造方法
无参构造方法【必须】
有参构造方法【建议】
成员方法
getXxx()
setXxx()
}
举例
public class Student {
//成员变量
private String name;
private int age;
//构造方法
public Student() {}
public Student(String name,int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//成员方法
publicvoid setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
publicvoid setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
publicint getAge() {
return age;
}
}- ArrayList对象不能存储基本类型,只能存储引用类型的数据:Integer、Character等
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
public boolean add(E e) :将指定的元素添加到此集合的尾部。
public E remove(int index) :移除此集合中指定位置上的元素。返回被删除的元素。
public E get(int index) :返回此集合中指定位置上的元素。返回获取的元素。
public int size() :返回此集合中的元素数。遍历集合时,可以控制索引范围,防止越界。 - static 关键字,可以修饰变量、方法和代码块。在使用的过程中,其主要目的还是想在不创建对象的情况下,去调用方法。
- 当 static 修饰成员变量时,该变量称为类变量。该类的每个对象都共享同一个类变量的值。任何对象都可以更改该类变量的值,但也可以在不创建该类的对象的情况下对类变量进行操作。
- 当 static 修饰成员方法时,该方法称为类方法 。静态方法在声明中有 static ,建议使用类名来调用,而不需要创建类的对象。调用方式非常简单。
Arrays和Maths类的所有方法均为静态方法,调用起来非常简单。
String s = Arrays.toString(arr);
Arrays.sort(arr);
double d1 = Math.abs(‐5); - 方法重写(Override) :子类中出现与父类一模一样的方法时(返回值类型,方法名和参数列表都相同),会出现覆盖效果,也称为重写或者复写。声明不变,重新实现。
- 抽象类中,不一定包含抽象方法,但是有抽象方法的类必定是抽象类。
- 抽象类的子类,必须重写抽象父类中所有的抽象方法,否则,编译无法通过而报错。除非该子类也是抽象类。
- 接口,是Java语言中一种引用类型,是方法的集合,内部主要就是封装了方法,包含抽象方法(JDK 7及以前),默认方法和静态方法(JDK 8),私有方法(JDK 9)。
接口格式
public interface 接口名称 {
// 抽象方法
public abstract void method();
// 默认方法
public default void method() {
执行语句
}
// 静态方法
public static void method2() {
执行语句
}
// 私有方法
private void method() {
执行语句
}
}
接口实现
1.抽象方法必须全部实现。
2.默认方法可以继承,可以重写,二选一,但是只能通过实现类的对象来调用。
3.静态方法只能使用接口名调用,不可以通过实现类的类名或者实现类的对象调用。
4.私有方法:只有默认方法可以调用。
5.私有静态方法:默认方法和静态方法可以调用。- 一个类是可以实现多个接口的,这叫做接口的多实现。并且,一个类能继承一个父类,同时实现多个接口。
class 类名 [extends 父类名] implements 接口名1,接口名2,接口名3... {
重写接口中抽象方法【必须】
重写接口中默认方法【不重名时可选】
}- 多态 : 是指同一行为,具有多个不同表现形式。当使用多态方式调用方法时,首先检查父类中是否有该方法,如果没有,则编译错误;如果有,执行的是子类重写后的方法。
父类类型 变量名 = new 子类对象;
变量名.方法名();
Fu f = new Zi();
f.method();
为避免ClassCastException的发生,Java提供了 instanceof 关键字,给引用变量做类型的校验,格式如下:
变量名 instanceof 数据类型
如果变量属于该数据类型,返回true。
如果变量不属于该数据类型,返回false。- 匿名内部类 :是内部类的简化写法。它的本质是一个 带具体实现的 父类或者父接口的 匿名的 子类对象。
定义接口:
public abstract class FlyAble{
public abstract void fly();
}
创建匿名内部类,并调用:
public class InnerDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
创建匿名内部类,直接传递给showFly(FlyAble f)
*/
showFly( new FlyAble(){
public void fly() {
System.out.println("我飞了~~~");
}
});
}
public static void showFly(FlyAble f) {
f.fly();
}
}- public String format(Date date) :将Date对象格式化为字符串。
/*
把Date对象转换成String
*/
public class Demo03DateFormatMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date = new Date();
// 创建日期格式化对象,在获取格式化对象时可以指定风格
DateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日");
String str = df.format(date);
System.out.println(str); // 2008年1月23日
}
}- public Date parse(String source) :将字符串解析为Date对象。
/*
把String转换成Date对象
*/
public class Demo04DateFormatMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
DateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日");
String str = "2018年12月11日";
Date date = df.parse(str);
System.out.println(date); // Tue Dec 11 00:00:00 CST 2018
}
}- java.util.Calendar 是日历类,就是方便获取各个时间属性的。
public class CalendarUtil {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建Calendar对象
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
// 设置年
int year = cal.get(Calendar.YEAR);
// 设置月
int month = cal.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1;
// 设置日
int dayOfMonth = cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.print(year + "年" + month + "月" + dayOfMonth + "日");
}
}- public static long currentTimeMillis() :返回以毫秒为单位的当前时间。
验证for循环打印数字1-9999所需要使用的时间(毫秒)
public class SystemTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("共耗时毫秒:" + (end ‐ start));
}
}- public static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length) :将数组中指定的数据拷贝到另一个数组中。
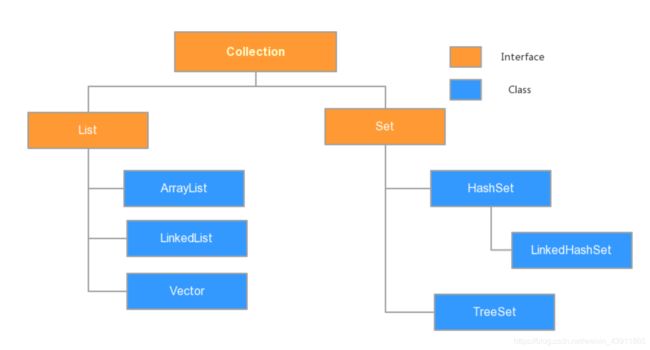
- Collection是所有单列集合的父接口,因此在Collection中定义了单列集合(List和Set)通用的一些方法,这些方法可用于操作所有的单列集合。方法如下:
public boolean add(E e) : 把给定的对象添加到当前集合中 。
public void clear() :清空集合中所有的元素。
public boolean remove(E e) : 把给定的对象在当前集合中删除。
public boolean contains(E e) : 判断当前集合中是否包含给定的对象。
public boolean isEmpty() : 判断当前集合是否为空。
public int size() : 返回集合中元素的个数。
public Object[] toArray() : 把集合中的元素,存储到数组中。- Iterator 迭代器
public class IteratorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用多态方式 创建对象
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
// 添加元素到集合
coll.add("串串星人");
coll.add("吐槽星人");
coll.add("汪星人");
//遍历
//使用迭代器 遍历 每个集合对象都有自己的迭代器
Iterator it = coll.iterator();
// 泛型指的是 迭代出 元素的数据类型
while(it.hasNext()){ //判断是否有迭代元素
String s = it.next();//获取迭代出的元素
System.out.println(s);
}
}
} - 增强for
for(元素的数据类型 变量 : Collection集合or数组){
写操作代码
}
for(int a : arr){//a代表数组中的每个元素
System.out.println(a);
} - List接口:元素存取有序、带有索引、可以有重复的元素。
public void add(int index, E element) : 将指定的元素,添加到该集合中的指定位置上。
public E get(int index) :返回集合中指定位置的元素。
public E remove(int index) : 移除列表中指定位置的元素, 返回的是被移除的元素。
public E set(int index, E element) :用指定元素替换集合中指定位置的元素,返回值的更新前的元素- List接口的子类:ArrayList类和LinkedList类。
LinkedList特有方法:
public void addFirst(E e) :将指定元素插入此列表的开头。
public void addLast(E e) :将指定元素添加到此列表的结尾。
public E getFirst() :返回此列表的第一个元素。
public E getLast() :返回此列表的最后一个元素。
public E removeFirst() :移除并返回此列表的第一个元素。
public E removeLast() :移除并返回此列表的最后一个元素。
public E pop() :从此列表所表示的堆栈处弹出一个元素。
public void push(E e) :将元素推入此列表所表示的堆栈。
public boolean isEmpty() :如果列表不包含元素,则返回true。- Set接口:元素存取无序、不可以有重复的元素。
- Set接口的子类:HashSet类和LinkedHashSet类(有序)。
注意:给HashSet中存放自定义类型元素时,需要重写对象中的hashCode和equals方法,建立自己的比较方式,才能保证HashSet集合中的对象唯一。
- java.utils.Collections 是集合工具类,用来对集合进行操作。
public static boolean addAll(Collection c, T... elements) :往集合中添加一些元素。
public static void shuffle(List list) 打乱顺序 :打乱集合顺序。
public static void sort(List list) :将集合中元素按照默认规则排序。
public static void sort(List list,Comparator ) :将集合中元素按照指定规则排序。
例:ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
Collections.addAll(list, 5, 222, 1,2);
Collections.sort(list);//默认规则排序
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator() { //使用Comparator比较器
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
return o2.charAt(0) ‐ o1.charAt(0);
}
}); - Collection 中的集合称为单列集合, Map 中的集合称为双列集合。需要注意的是, Map 中的集合不能包含重复的键,值可以重复;每个键只能对应一个值。
- Map 常用子类:HashMap和LinkedHashMap(有序)。
public V put(K key, V value) : 把指定的键与指定的值添加到Map集合中。
public V remove(Object key) : 把指定的键 所对应的键值对元素 在Map集合中删除,返回被删除元素的
值。
public V get(Object key) 根据指定的键,在Map集合中获取对应的值。
public Set keySet() : 获取Map集合中所有的键,存储到Set集合中。
public Set> entrySet() : 获取到Map集合中所有的键值对对象的集合(Set集合)。 throw用在方法内,用来抛出一个异常对象,将这个异常对象传递到调用者处,并结束当前方法的执行。
throw new 异常类名(参数);
关键字throws运用于方法声明之上,用于表示当前方法不处理异常,而是提醒该方法的调用者来处理异常(抛出异常).
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数) throws 异常类名1,异常类名2…{ }
try{
编写可能会出现异常的代码
}catch(异常类型 e){
处理异常的代码
//记录日志/打印异常信息/继续抛出异常
}
finally:有一些特定的代码无论异常是否发生,都需要执行。- 并发:指两个或多个事件在同一个时间段内发生。
- 并行:指两个或多个事件在同一时刻发生(同时发生)。
- 进程:是指一个内存中运行的应用程序,每个进程都有一个独立的内存空间,一个应用程序可以同时运行多个进程;进程也是程序的一次执行过程,是系统运行程序的基本单位;系统运行一个程序即是一个进程从创建、运行到消亡的过程。
- 线程:线程是进程中的一个执行单元,负责当前进程中程序的执行,一个进程中至少有一个线程。一个进程中是可以有多个线程的,这个应用程序也可以称之为多线程程序。
- 简而言之:一个程序运行后至少有一个进程,一个进程中可以包含多个线程。
- Java使用的线程调度为抢占式调度:优先让优先级高的线程使用 CPU,如果线程的优先级相同,那么会随机选择一个(线程随机性)。
- Thread 类
public Thread() :分配一个新的线程对象。
public Thread(String name) :分配一个指定名字的新的线程对象。
public Thread(Runnable target) :分配一个带有指定目标新的线程对象。
public Thread(Runnable target,String name) :分配一个带有指定目标新的线程对象并指定名字。
常用方法:
public String getName() :获取当前线程名称。
public void start() :导致此线程开始执行; Java虚拟机调用此线程的run方法。
public void run() :此线程要执行的任务在此处定义代码。
public static void sleep(long millis) :使当前正在执行的线程以指定的毫秒数暂停(暂时停止执行)。
public static Thread currentThread() :返回对当前正在执行的线程对象的引用。- 同步锁:对象的同步锁只是一个概念,可以想象为在对象上标记了一个锁.
1. 锁对象 可以是任意类型。
2. 多个线程对象 要使用同一把锁。
synchronized(同步锁){
需要同步操作的代码
}- 同步方法 :使用synchronized修饰的方法,就叫做同步方法,保证A线程执行该方法的时候,其他线程只能在方法外等着。
public synchronized void method(){
可能会产生线程安全问题的代码
}- Lock锁也称同步锁,加锁与释放锁方法化了,如下:
public void lock() :加同步锁。
public void unlock() :释放同步锁。
- wait:线程不再活动,不再参与调度,进入 wait set 中,因此不会浪费 CPU 资源,也不会去竞争锁了,这时的线程状态即是WAITING。它还要等着别的线程执行一个特别的动作,也即是“通知(notify)”在这个对象上等待的线程从wait set 中释放出来,重新进入到调度队列(ready queue)中。
- notify:则选取所通知对象的 wait set 中的一个线程释放;例如,餐馆有空位置后,等候就餐最久的顾客最先入座。
- notifyAll:则释放所通知对象的 wait set 上的全部线程。
- 线程池:其实就是一个容纳多个线程的容器,其中的线程可以反复使用,省去了频繁创建线程对象的操作,无需反复创建线程而消耗过多资源。