libtorch学习笔记(8)- 自己实现图片到张量
自己实现的意义
本系列笔记主要用C/C++来实现神经网络模型,所以用原生的C/C++自己动手实现图片到张量的转换,更助于了解张量的含义和用途,以及其如何组织。
为了便于理解输出结果,制作了一张Red, Green和Blue的图片(10x10):
![]()
Pytorch来实现
假设图片放在I:\
import torch
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
loader1 = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor()])
unloader = transforms.ToPILImage()
image = Image.open('I:\\RGB.png').convert('RGB')
image = loader1(image).unsqueeze(0)
print(image)
loader2 = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
image = Image.open('I:\\RGB.png').convert('RGB')
image = loader2(image).unsqueeze(0)
print(image)
输出结果如下:

第一个tensor,1代表原始颜色通道中255,0还是代表0;第二个tensor是经过转换后的图像tensor, 1还是代表原始图像颜色通道中的255, -1则是代表0。在神经网络中多用第二种tensor中数据组织方式,1.0最大值,-1.0最小值。
在第一个输出tensor的第一个Channel,是红色Channel,可以看到左上方有个3x2的红色长方形红色区块,都是填重1.0, 也就是红色(R: 255),右下方也有一个5x5的红色方块,5x5区域都是1.0(R: 255),没有红色的区域都是0(R:0), 在上图中用橘红色表示出来了对应的区域。
在第一个输出tensor的第二个Channel,是绿色Channel,同样的填充方式;第三个Channel,是蓝色Channel,也是同样的填充方式。
Native C++来实现
图片解码
图片解码用Windows系统标准的Windows Image Component接口,首先创建WICImaging Factory,用来解码和颜色空间转换;然后创建D2D1 Factory, 用来对对象做缩放:
HRESULT hr = S_OK;
// Create D2D1 factory to create the related render target and D2D1 objects
D2D1_FACTORY_OPTIONS options;
ZeroMemory(&options, sizeof(D2D1_FACTORY_OPTIONS));
#if defined(_DEBUG)
// If the project is in a debug build, enable Direct2D debugging via SDK Layers.
options.debugLevel = D2D1_DEBUG_LEVEL_INFORMATION;
#endif
if (FAILED(hr = D2D1CreateFactory(D2D1_FACTORY_TYPE_MULTI_THREADED,
__uuidof(ID2D1Factory2), &options, &m_spD2D1Factory)))
printf("Failed to create D2D1 factory {hr: 0X%X}.\n", hr);
// Create the image factory
if (FAILED(hr = CoCreateInstance(CLSID_WICImagingFactory,
nullptr, CLSCTX_INPROC_SERVER, IID_IWICImagingFactory, (LPVOID*)&m_spWICImageFactory)))
printf("Failed to create WICImaging Factory {hr: 0X%X}.\n", hr);
如何所有的图像都需要转化为相同尺寸的图片张量,送入网络进行处理,需要提前Init一下,以便创建一个固定大小的Render Target,把图片按照原来比例缩放填入这个Render Target上,当然上下,或者左右会被padding成一个统一颜色,比如黑色。这样能重用内存和Render Target,对性能有好处。m_pBGRABuf是用来存放接出来的BGRA buffer,每像素占4个byte,在内存中存放的方式是Blue Channel Byte, Green Channel Byte,Red Channel Byte和Alpha Channel Byte,后面会基于这个buffer转化为pytorch的tensor。
HRESULT ImageProcess::Init(UINT outWidth, UINT outHeight)
{
HRESULT hr = S_OK;
if (outWidth == 0 || outHeight == 0)
{
// Use the original image width and height as the output width and height
m_outWidth = outWidth;
m_outHeight = outHeight;
return hr;
}
// 创建一个Pre-multiplexed BGRA的224x224的WICBitmap
if (SUCCEEDED(hr = m_spWICImageFactory->CreateBitmap(outWidth, outHeight, GUID_WICPixelFormat32bppPBGRA,
WICBitmapCacheOnDemand, &m_spNetInputBitmap)))
{
// 在此WICBitmap上创建D2D1 Render Target
D2D1_RENDER_TARGET_PROPERTIES props = D2D1::RenderTargetProperties(D2D1_RENDER_TARGET_TYPE_DEFAULT,
D2D1::PixelFormat(DXGI_FORMAT_B8G8R8A8_UNORM, D2D1_ALPHA_MODE_PREMULTIPLIED), 96, 96);
if (SUCCEEDED(hr = m_spD2D1Factory->CreateWicBitmapRenderTarget(
m_spNetInputBitmap.Get(), props, &m_spRenderTarget)))
{
hr = m_spRenderTarget->CreateSolidColorBrush(
D2D1::ColorF(D2D1::ColorF::Black, 1.0f), &m_spBGBrush);
}
}
// Create a buffer to be used for converting ARGB to tensor
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
if (m_pBGRABuf != NULL)
delete[] m_pBGRABuf;
m_pBGRABuf = new unsigned char[outWidth*outHeight * 4];
m_outWidth = outWidth;
m_outHeight = outHeight;
}
return hr;
}
然后检查文件是否存在,并将UTF8转化为UNICODE
if (cszImageFile == NULL || _taccess(cszImageFile, 0) != 0)
return E_INVALIDARG;
wchar_t* wszInputFile = NULL;
size_t cbFileName = _tcslen(cszImageFile);
#ifndef _UNICODE
wszInputFile = new wchar_t[cbFileName + 1];
if (MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, cszCatImageFile, -1, wszInputFile, cbFileName + 1) == 0)
{
delete[] wszInputFile;
return -1;
}
#else
wszInputFile = (wchar_t*)cszImageFile;
#endif
开始创建图片解码对象,并获取图片信息,比如长,宽,像素格式,多少帧图片,如果不是转化为固定的长宽的tensor,outWidth/outHeight为0,这时候会将它们赋值为图片本身的长宽,同时还需要在后面创建输出buffer, pBGRABuf用于接受输出。
// 加载图片, 并为其创建图像解码器
if (FAILED(m_spWICImageFactory->CreateDecoderFromFilename(wszInputFile, NULL,
GENERIC_READ, WICDecodeMetadataCacheOnDemand, &spDecoder)))
goto done;
// 得到多少帧图像在图片文件中,如果无可解帧,结束程序
if (FAILED(hr = spDecoder->GetFrameCount(&uiFrameCount)) || uiFrameCount == 0)
goto done;
// 得到第一帧图片
if (FAILED(hr = hr = spDecoder->GetFrame(0, &spBitmapFrameDecode)))
goto done;
// 得到图片大小
if (FAILED(hr = spBitmapFrameDecode->GetSize(&uiWidth, &uiHeight)))
goto done;
// 调整转换和输出
if (outWidth == 0)
{
outWidth = uiWidth;
dst_rect.right = uiWidth;
rect.Width = uiWidth;
bDynamic = TRUE;
}
if (outHeight == 0)
{
outHeight = uiHeight;
dst_rect.bottom = uiHeight;
rect.Height = uiHeight;
bDynamic = TRUE;
}
// Create a buffer to be used for converting ARGB to tensor
if (bDynamic)
pBGRABuf = new unsigned char[outWidth*outHeight * 4];
得到图像像素格式,如果不是BGRA的格式,就将其转化为BGRA 32bit的格式,这个主要是为了用D2D1 Render Target可以对其进行缩放,当然也存在一些优化空间,比如如果是RGB格式,并且不需要进行缩放,就没必要做这一步:
// 得到图片像素格式
if (FAILED(hr = spBitmapFrameDecode->GetPixelFormat(&pixelFormat)))
goto done;
// 如果图片不是Pre-multiplexed BGRA格式,转化成这个格式,以便用D2D硬件处理图形转换
if (!IsEqualGUID(pixelFormat, GUID_WICPixelFormat32bppPBGRA))
{
if (FAILED(hr = WICConvertBitmapSource(GUID_WICPixelFormat32bppPBGRA,
spBitmapFrameDecode.Get(), &spConverter)))
goto done;
}
else
spConverter = spBitmapFrameDecode;
图像缩放
最后就是进行缩放,然后将缩放结果取出来用于转化为tensor
// If the width and height are not matched with the image width and height, scale the image
if (!bDynamic && (outWidth != uiWidth || outHeight != uiHeight))
{
// 转化为Pre-multiplexed BGRA格式的WICBitmap
if (FAILED(hr = m_spWICImageFactory->CreateBitmapFromSource(
spConverter.Get(), WICBitmapCacheOnDemand, &spHandWrittenBitmap)))
goto done;
// 将转化为Pre-multiplexed BGRA格式的WICBitmap的原始图片转换到D2D1Bitmap对象中来,以便后面的缩放处理
if (FAILED(hr = spRenderTarget->CreateBitmapFromWicBitmap(spHandWrittenBitmap.Get(), &spD2D1Bitmap)))
goto done;
// 将图片进行缩放处理,转化为224x224的图片
spRenderTarget->BeginDraw();
spRenderTarget->FillRectangle(dst_rect, spBGBrush.Get());
if (GetImageDrawRect(outWidth, outHeight, uiWidth, uiHeight, dst_rect))
spRenderTarget->DrawBitmap(spD2D1Bitmap.Get(), &dst_rect);
spRenderTarget->EndDraw();
//ImageProcess::SaveAs(spNetInputBitmap, L"I:\\test.png");
// 并将图像每个channel中数据转化为[-1.0, 1.0]的raw data
hr = spNetInputBitmap->CopyPixels(&rect, outWidth * 4, 4 * outWidth * outHeight, pBGRABuf);
}
else
hr = spConverter->CopyPixels(&rect, outWidth * 4, 4 * outWidth * outHeight, pBGRABuf);
Tensor转换
最后就是转化为tensor的blob,然后用torch::from_blob转化为tensor,res_data可以理解成一个三维数组tensor_blob[number_of_channel][number_of_rows][number_of_columns],torch::from_blob中可以指定内存释放函数,以避免内存泄漏。med是用户进行转换的平均值,std是用于转换值,对应的公式是:
c h a n n e l t r a n s f o r m = ( c h a n n e l o r i g i n a l / 255.0 f − m e d ) / s t d channel_{transform} = (channel_{original} /255.0f - med)/std channeltransform=(channeloriginal/255.0f−med)/std
一般来讲网上查到的资料,根据ImageNet的统计数据, RGB channel转换的均值和方差不是采用[0.5, 0.5, 0.5], [0.5,0.5,0.5]而是
m e a n s R , G , B = [ 0.485 f , 0.456 f , 0.406 f ] s t d s R , G , B = [ 0.229 f , 0.224 f , 0.225 f ] t e n s o r R , G , B = ( R G B o r i g i n a l / 255.0 f − m e a n s R , G , B ) / s t d s R , G , B means_{R,G,B} = [0.485f, 0.456f, 0.406f] \\stds_{R,G,B} = [0.229f, 0.224f, 0.225f] \\tensor_{R,G,B} = (RGB_{original} /255.0f - means_{R,G,B})/stds_{R,G,B} meansR,G,B=[0.485f,0.456f,0.406f]stdsR,G,B=[0.229f,0.224f,0.225f]tensorR,G,B=(RGBoriginal/255.0f−meansR,G,B)/stdsR,G,B
float* res_data = (float*)malloc(3 * outWidth * outHeight * sizeof(float));
for (int c = 0; c < 3; c++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < outHeight; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < outWidth; j++)
{
int pos = c * outWidth*outHeight + i * outWidth + j;
res_data[pos] = ((pBGRABuf[i * outWidth * 4 + j * 4 + 2 - c]) / 255.0f - med) / std;
}
}
}
tensor = torch::from_blob(res_data, {
1, 3, outWidth, outHeight }, FreeBlob);
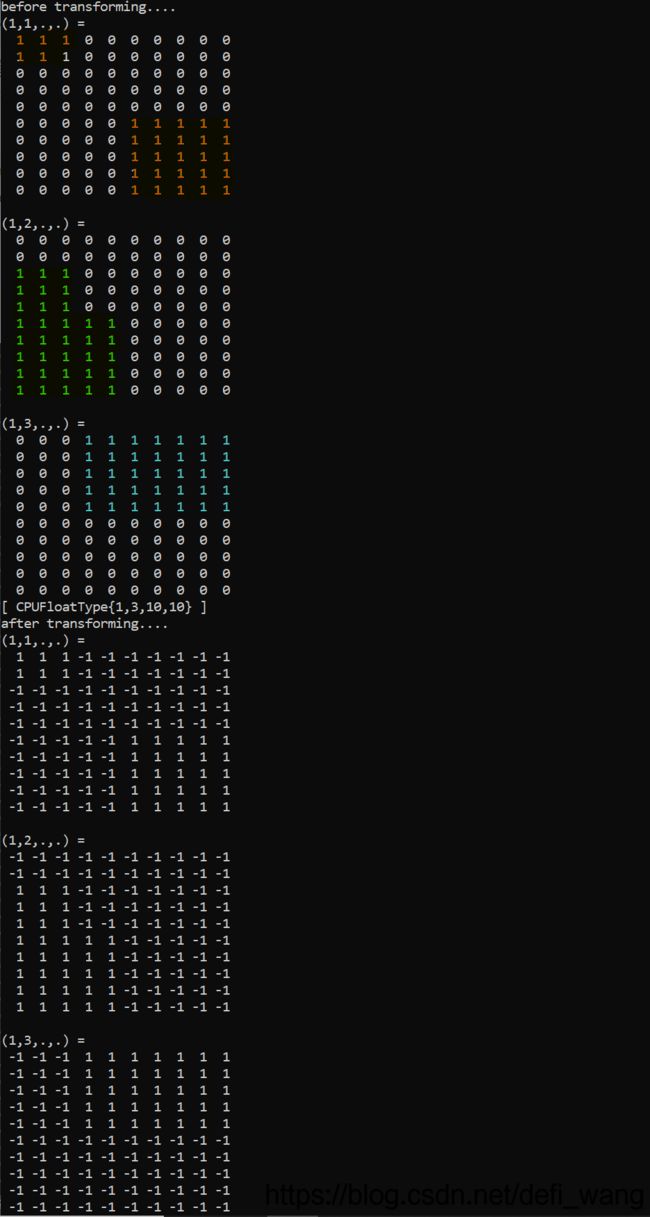
测试结果
这是对应的测试代码,我也把代码上传到GitHub:
ImageProcess imageprocessor;
if (SUCCEEDED(imageprocessor.Init(10, 10)))
{
torch::Tensor tensor;
if (SUCCEEDED(imageprocessor.ToTensor(_T("I:\\RGB.png"), tensor)))
{
printf("before transforming....\n");
std::cout << tensor << '\n';
}
if (SUCCEEDED(imageprocessor.ToTensor(_T("I:\\RGB.png"), tensor, 0.5f, 0.5f)))
{
printf("after transforming....\n");
std::cout << tensor << '\n';
}
}