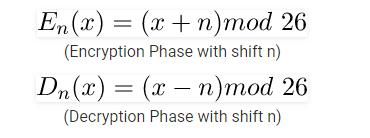Python零基础编程——09密码学实战篇-古典加密算法加密解密破解
摘要
书接前文:
1-《零基础编程——Python基础》
2-《零基础编程——密码学基础理论篇》
前面我们分享了密码学的基础理论篇,从摩斯密码切入,逐个分析了凯撒加密法、换位加密法、数乘加密法、仿射加密、简单替代、多表替代、对称加密、非对称加密RSA加密法等等。本篇继续分享实际使用实战。针对古典加密算法进行加密解密,学会对明文进行Python编程加密、解密,以及破解密码实战。
内容
1-凯撒加密法 编程实战
2-反转加密法 编程实战
3-换位加密法 编程实战
4-数乘加密法 编程实战
0-Python cryptography 库安装
针对密码学的基础加密算法,其实自己写也可以,不过为了不浪费时间,充分利用现有的资源,站在巨人的肩膀上学习。
我们使用cryptographic、pycipher等库
#源码参考
https://github.com/pyca/cryptography/tree/master/src/cryptography
https://github.com/jameslyons/pycipher
#安装使用
pip install cryptography
pip install pycipher
#不懂使用的童鞋,请参考我们的-Python基础篇章
0-Python cryptography 库安装
针对密码学的基础加密算法,其实自己写也可以,不过为了不浪费时间,充分利用现有的资源,站在巨人的肩膀上学习。
我们使用cryptographic、pycipher等库
#源码参考
https://github.com/pyca/cryptography/tree/master/src/cryptography
https://github.com/jameslyons/pycipher
#安装使用
pip install cryptography
pip install pycipher
#不懂使用的童鞋,请参考我们的-Python基础篇章
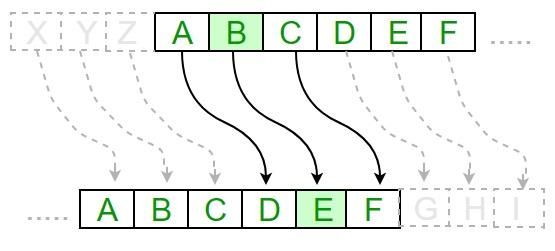
1-凯撒加密法 编程实战
- 原理:(具体参考我们上一篇密码学基础理论篇)
- 实战:
def encode(string, shift):
cipher = ''
for char in string:
if char == ' ':
cipher = cipher + char
elif char.isupper():
cipher = cipher + chr((ord(char) + shift - ord('A')) % 26 + ord('A'))
else:
cipher = cipher + chr((ord(char) + shift - ord('a')) % 26 + ord('a'))
return cipher
def decode(text, s):
result = ""
for x in text:
if(x == ' '):
result += " "
elif(ord(x)-ord('A')-s < 0):
result += chr(ord(x)-s+26)
else:
result += chr(ord(x)-s)
return result
text = 'Hello FreoStudio Welcome U '
print('明文:'+text)
text = encode(text, 4) # 加密
print('密文:'+text)
decode(text, 4)
当我们不知道密钥Key=4的情况下爆破:
for key in range(0, 26):
print('Key='+str(key))
text = decode('Lipps JvisWxyhms Aipgsqi Y', key)
print(text)
#运行结果:
Key=0
Lipps JvisWxyhms Aipgsqi Y
Key=1
Khoor IuhrVwxglr Zhofrph X
Key=2
Jgnnq HtgqUvwfkq Ygneqog W
Key=3
Ifmmp GsfpTuvejp Xfmdpnf V
Key=4
Hello FreoStudio Welcome U
Key=5
Gdkkn EqdnRstchn Vdkbnld T
Key=6
Fcjjm DpcmQrsbgm Ucjamkc S
Key=7
Ebiil CoblPqrafl Tbi`ljb R
Key=8
Dahhk BnakOpq`ek Sah_kia Q
Key=9
C`ggj Am`jNop_dj R`g^jh` P
Key=10
B_ffi Zl_iMno^ci Q_f]ig_ O
Key=11
A^eeh Yk^hLmn]bh P^e\hf^ N
Key=12
Z]ddg Xj]gKlm\ag O]d[ge] M
Key=13
Y\ccf Wi\fJkl[`f N\cZfd\ L
Key=14
X[bbe Vh[eIjkZ_e M[bYec[ K
Key=15
WZaad UgZdHijY^d LZaXdbZ J
Key=16
VY``c TfYcGhiX]c KY`WcaY I
Key=17
UX__b SeXbFghW\b JX_Vb`X H
Key=18
TW^^a RdWaEfgV[a IW^Ua_W G
Key=19
SV]]` QcV`DefUZ` HV]T`^V F
Key=20
RU\\_ PbU_CdeTY_ GU\S_]U E
Key=21
QT[[^ OaT^BcdSX^ FT[R^\T D
Key=22
PSZZ] N`S]AbcRW] ESZQ][S C
Key=23
ORYY\ M_R\ZabQV\ DRYP\ZR B
Key=24
NQXX[ L^Q[Y`aPU[ CQXO[YQ A
Key=25
MPWWZ K]PZX_`OTZ BPWNZXP Z一般情况下,我们明文字符集不止25个,像我们汉字常用的就有3千多个,那我们就需要进行爆破3千多个Key,但是爆破完了,我们怎么知道哪一个是我们想要的Key?一个个看也不现实。
可以用字典进行检测单词有效性,Python可以使用enchant或者nltk库来判断单词是否有效英语单词,我们也可以自己下载一本英文单词书(words.txt),进行逐个匹对:
def is_english_word(word):
with open("./files/words.txt") as word_file:
english_words = set(word.strip().lower() for word in word_file)
return word.lower() in english_words
is_english_word('hellX')
#运行结果:False
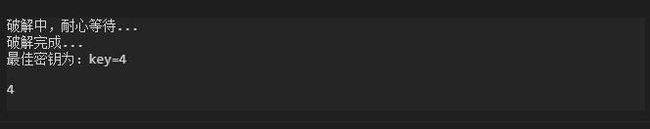
- 爆破,获取最佳密钥Key
import tools
#爆破凯撒加密的密文
def caesar_cracking(msg,len):
relKey =0
relCount =0
print('破解中,耐心等待...')
for key in range(0, len):
print(key)
text = caesar_decode(msg, key)
count =0
for word in text.split(" "):
#print('====='+word)
if tools.is_english_word(word):
count+=1
if count > relCount:
relCount = count
relKey = key
if relKey >=100:#如果正确率达到100个,可以任务是得到了密钥
break
print('破解完成...')
print('最佳密钥为:key='+str(relKey))
return relKey
caesar_cracking('Lipps JvisWxyhms Aipgsqi Y',26)
#运行结果如下:
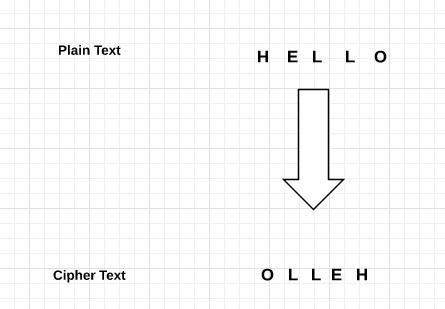
2-反转加密法 编程实战
- 原理:(具体参考我们上一篇密码学基础理论篇)
- 实战
# 反转加密法#加密算法与解密算法一致
def reverse_cipher(msg):
i = len(msg) - 1
result = '' # 存储加反转后的信息
while i >= 0:
result += msg[i]
i = i - 1
print("反转为:", result)
return result
message = 'This is program to explain reverse cipher.'
text = reverse_cipher(message)#反转加密
reverse_cipher(text)#反转再反转得到明文- 破解:反转即可,关键是你不知道别人的密文是不是其中一个环节用了反转
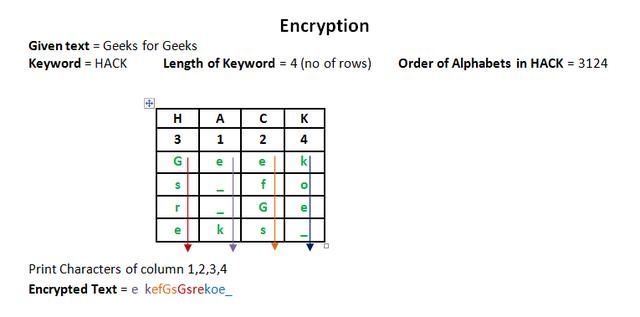
3-换位加密法 编程实战
- 原理:(具体参考我们上一篇密码学基础理论篇)
- 实战
# 换位加密法
from pycipher import ColTrans
#加密
def transposition_encode(key, msg):
return ColTrans(key).encipher(msg)
#解密
def transposition_decode(key, msg):
return ColTrans(key).decipher(msg)
text = transposition_encode("21334","Hello FreoStudio Welcome U")
transposition_decode("HELLO",text)
#pycipher ColTrans 换位加密具体算法源码
#我们站在巨人肩膀上,创新创造,不重复造轮子了
https://github.com/freostudio/pycipher/tree/master/pycipher/columnartransposition.py
- 密码分析
换位加密法通常称之为列转换加密法,行列转置密码,将明文按自定义列数换位。加密强度本身很弱,但通常和其他加密方法结合,例如替代加密法结合,ADFGVX密码就是用换位加密大大增强安全性的。
怎么破解呢,如果采用爆破去逐个尝试,基本不可能,因为首先换位的列数可以无数个,而且列进行排序组合也很多,得到结果后还得校验单词正确性。一般的计算机基本难于爆破。
逐个破解无望,可以使用字典攻击方法,通常加密Key是常用人名地名的,然后我们建立一个字典,逐个尝试,提高效率。
4-数乘加密法 编程实战
- 原理:(具体参考我们上一篇密码学基础理论篇)
- 实战
# 数乘加密
def multiplicative_encode(key,totol_num, text):
result = '' # 存储加反转后的信息
for x in text:
if(x == ' '):
result += " "
else:
offset = ord(x) - ord('A')
result +=chr(((key* offset ) % totol_num) + ord('A'))
return result
multiplicative_encode(7,26,"ABCDEFG")
##输出结果:
# 数乘加密...
'AHOVCJQ'
5-总结
我们针对古典加密算法的实战,实战是为了更好地掌握古典加密算法的思想。
上篇-
1-凯撒加密法 编程实战
2-反转加密法 编程实战
3-换位加密法 编程实战
4-数乘加密法 编程实战
下篇-
5-仿射加密法
6-简单替代加密法
7-维吉尼亚加密法——多表替代加密法
8-一次一密加密法 one time pad cipher