Scikit-learn机器学习实战之Kmeans
摘要
上篇博客谈到了如何安装Python中强大的机器学习库
scikit-learn
:
Windos环境安装scikit-learn函数库流程
,本篇主要是对其Kmeans示例进行学习。
有关Kmeans的介绍可以参见这篇博客:
K均值聚类算法及Matlab函数使用
Kmeans算法的缺陷
- 聚类中心的个数K 需要事先给定,但在实际中这个 K 值的选定是非常难以估计的,很多时候,事先并不知道给定的数据集应该分成多少个类别才最合适
- Kmeans需要人为地确定初始聚类中心,不同的初始聚类中心可能导致完全不同的聚类结果。
(1)第一种缺陷通常人为解决,例如假设有K=10(根据先验知识,尽量大些),进行第一次聚类,如果结果显示某一类中的样本过少,则K=K-1,重新进行聚类。
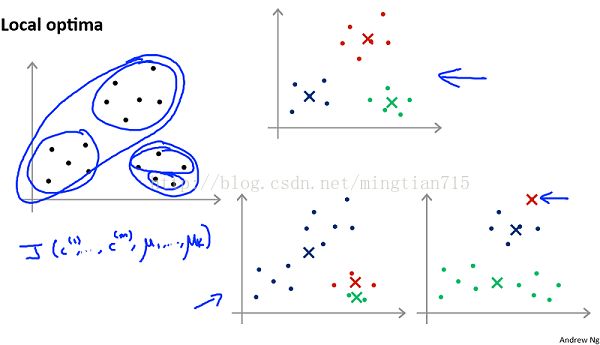
(2)第二种缺陷如下图所示,随机初始化的聚类中心在更新过程中可能陷入局部极小值,造成聚类效果不佳,常用的方法是多次初始化聚类中心,找到使得代价函数最小的初始化中心。
从上图可以看出,如果初始聚类中心间的距离尽可能远的话,聚类的效果可能会更好,因此初始化时应使得聚类中心距离尽可能远(即
Kmeans++
算法)
Scikit-learn示例
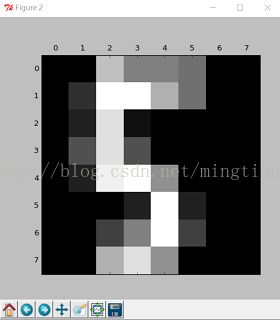
该例为手写识别(数字0~9)数据(8*8图像)的聚类,主要是对Kmeans、kmeans++、以及(Pca+Kmean)做了算法性能比较,并且使用了Pca进行数据可视化。
(1)数据样本
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
digits = load_digits()
print(digits.data.shape)
(1797, 64) #1797个数据,每个数据64维
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.gray()
plt.matshow(digits.images[0])
plt.show()
(2)算法性能比较
from time import time
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from sklearn.preprocessing import scale
np.random.seed(42) #随机种子,用于初始化聚类中心
digits = load_digits() #载入数据
data = scale(digits.data) #中心标准化数据
n_samples, n_features = data.shape #1797,64
n_digits = len(np.unique(digits.target)) #10
labels = digits.target #数据真实标签
sample_size = 300
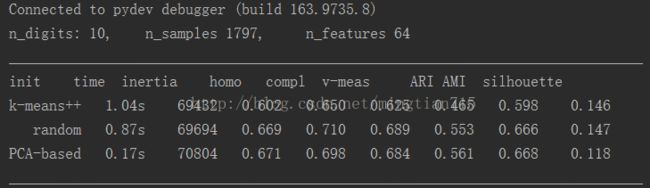
print("n_digits: %d, \t n_samples %d, \t n_features %d"
% (n_digits, n_samples, n_features))
print(79 * '_')
print('% 9s' % 'init'
' time inertia homo compl v-meas ARI AMI silhouette')
#算法评估函数,包括处理时间、最终代价函数值、以及不同的聚类评价指标
def bench_k_means(estimator, name, data):
t0 = time()
estimator.fit(data)
print('% 9s %.2fs %i %.3f %.3f %.3f %.3f %.3f %.3f'
% (name, (time() - t0), estimator.inertia_,
metrics.homogeneity_score(labels, estimator.labels_),
metrics.completeness_score(labels, estimator.labels_),
metrics.v_measure_score(labels, estimator.labels_),
metrics.adjusted_rand_score(labels, estimator.labels_),
metrics.adjusted_mutual_info_score(labels, estimator.labels_),
metrics.silhouette_score(data, estimator.labels_,
metric='euclidean',
sample_size=sample_size)))
#Kmeans++,随机初始化10次
bench_k_means(KMeans(init='k-means++', n_clusters=n_digits, n_init=10),
name="k-means++", data=data)
#Kmeans,随机初始化10次
bench_k_means(KMeans(init='random', n_clusters=n_digits, n_init=10),
name="random", data=data)
#Pca+kmeans,采用如下调用方式聚类中心是确定的,因此只初始化一次
pca = PCA(n_components=n_digits).fit(data) #fit函数表示拟合数据
bench_k_means(KMeans(init=pca.components_, n_clusters=n_digits, n_init=1),
name="PCA-based",
data=data)
print(79 * '_')
处理结果:
性能上:Kmeans++>random Kmeans>Pca Kmeans,但差别不大。
时间上:Pca Kmeans处理时间远快于另两种算法。并且降维度越低,处理速度越快,但代价函数会逐渐上升,因此寻找一个合适的处理的维度是关键。
PS:这些函数的介绍在 Scikit-learn官网都有介绍;PCA函数也可以参看这篇博客: Scikit-learn中PCA的用法
(3)可视化聚类结果
在(2)中,是将数据从64降维10,再进行Kmeans聚类;在(3)中,为方便可视化,将数据降到2维,进行聚类,可视化。
reduced_data =PCA(n_components=2).fit_transform(data)
#fit_transform得到是用降维度处理后的数据
kmeans = KMeans(init='k-means++', n_clusters=n_digits, n_init=10)
kmeans.fit(reduced_data)
#fit表示用括号数据“训练”模型,返回一个kmeans对象
#定义网格步长
# Step size of the mesh. Decrease to increase the quality of the VQ.
h = .02 # point in the mesh [x_min, x_max]x[y_min, y_max].
#定义边界坐标,定义网格坐标
# Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each
x_min, x_max = reduced_data[:, 0].min() - 1, reduced_data[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = reduced_data[:, 1].min() - 1, reduced_data[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
#用训练模型获得网格预测每一点的类值
# Obtain labels for each point in mesh. Use last trained model.
Z = kmeans.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
#绘制函数
# Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure(1)
plt.clf()
plt.imshow(Z, interpolation='nearest',
extent=(xx.min(), xx.max(), yy.min(), yy.max()),
cmap=plt.cm.Paired,
aspect='auto', origin='lower')
plt.plot(reduced_data[:, 0], reduced_data[:, 1], 'k.', markersize=2)
# Plot the centroids as a white X
centroids = kmeans.cluster_centers_
plt.scatter(centroids[:, 0], centroids[:, 1],
marker='x', s=169, linewidths=3,
color='w', zorder=10)
plt.title('K-means clustering on the digits dataset (PCA-reduced data)\n'
'Centroids are marked with white cross')
plt.xlim(x_min, x_max)
plt.ylim(y_min, y_max)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
绘制结果: