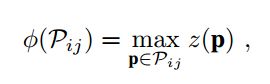ScanContext 论文详解 - 用途:Lidar SLAM 回环检测、空间描述符
ScanContext 论文阅读笔记
- 1. 浅读文章
- 2. 提出的方法
- 3. 算法流程
-
- 3.1 Scan Context的创建
-
- (1) 与Shape Context的渊源
- (2) 为什么选择Maximum height?
- (3) Partition a 3D scan
- (4) 给每个Bin进行赋值:Bin Encoding
- (5) Scan Context Matrix
- 3.2 Similarity Score的计算
- 3.3 Two-phase Search Algorithm
-
- (1) Ring Key
- (2) KD-Tree
- 4. Scan Context算法延伸
-
- 4.1 ICP Initial Value中的应用
- 4.2 Future Works
- 参考文献
1. 浅读文章
Scan Context,从英文字面理解就是“扫描 上下文”。类比于我们阅读的时候,需要理解上下文,才能明白其意,LidarSLAM在进行回环检测的时候,也需要将“上下文” (之前的数据)进行比较,方才知道我们是不是又走到了之前的同一个地方(回环)。
Scan Context这篇文章由韩国KAIST大学的Giseop Kim和Ayoung Kim所写,它的主要特点是提出了Scan Context这个非直方图的全局描述符,来帮助我们对“上下文”(当前/之前的数据)进行更快速、有效地搜索。典型的应用就是在LiDAR SLAM中进行回环检测和Place Recognition。
2. 提出的方法
- The representation that preserves absolute location information of a point cloud in each bin (如图2所示)
- Efficient bin encoding function
- Two-step search algorithm
3. 算法流程
3.1 Scan Context的创建
(1) 与Shape Context的渊源
Scan Context这个算法其实一开始是由Shape Context [2] 所启发的,而Shape Context是把点云的 local Keypoint 附近的点云形状 encode 进一个图像中。Scan Context的不同在于,它不仅仅是count the number of points,而是采用了maximum height of points in each bin。
(2) 为什么选择Maximum height?
- The reason for using the height is to efficiently summarize the vertical shape of surrounding structures.
- In addition, the maximum height says which part of the surrounding structures is visible from the sensor.
- This egocentric visibility has been a well-known concept in the urban design literature for analyzing an identity of a place
(3) Partition a 3D scan
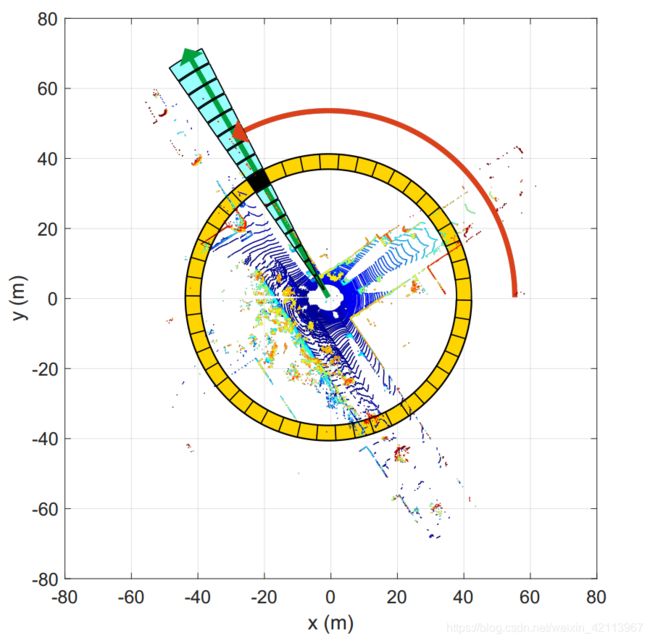
首先,对每一次Scan进行分割:
- Nr: number of rings (黄色圈圈)
- Ns: number of sectors (浅蓝色/绿色?的格子)
- Lmax: 雷达每一个射线的最远距离
- Radial Gap between rings = L m a x N r \frac{L_{max}}{N_r} NrLmax
- Sector弧度 = 2 π N s \frac{2\pi}{N_s} Ns2π
- 文章中: Nr=20, Ns=60
其次,分割后的 P i j P_{ij} Pij就是指the set of points belonging to the bin where the ith ring and jth sector overlapped。
(4) 给每个Bin进行赋值:Bin Encoding
- z ( ⋅ ) z(\cdot ) z(⋅) 是指point P 的Z坐标。
- 直接使用最大z坐标值 z ( p ) z(p) z(p),作为这个bin的value。
(5) Scan Context Matrix
A scan context I is finally represented as a Nr × Ns matrix as:
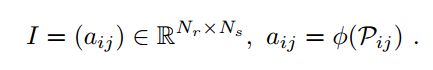
3.2 Similarity Score的计算
假设我们得到了一对Scan Context的矩阵,我们要计算他们俩( I p , I c I_p, I_c Ip,Ic)之间的相似度,文章中采用了columnwise (按列) 的距离计算。
- I q I_q Iq: Query Point Cloud (简言之,我们当前用来query的点云)
- I c I_c Ic: Candidate Point Cloud (咱们的“数据库”中储存的用来匹配的candidate点云)
- c j q c^{q}_{j} cjq: Column j of Query Point Cloud (列向量)
- c j c c^{c}_{j} cjc: Column j of Candidate Point Cloud (列向量)
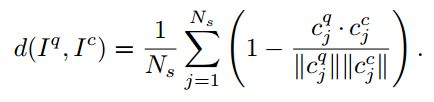
小红薯:且慢,大师兄!
小红薯:古希腊哲学家赫拉克利特说,“人不能两次踏进同一条河流”。
小红薯:这样来比较两个点云,而没考虑每次不可能在exactly同一个位置和角度观察,是不是too young, too simple了呢!
–
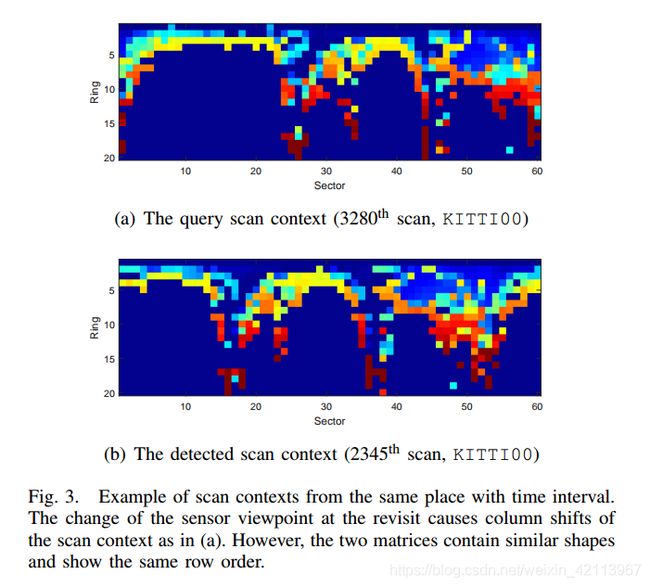
大师兄:恩,这是个好问题。假设咱们回到同一个地方,那有可能是沿着相反的方向回来的,那咱们的Viewpoint就发生了变化,这个Scan Context矩阵就会发生偏移!这样就会导致Column顺序发生变化。
大师兄:所幸的是,只要location是在同一个地方,不管你的方向朝着哪里,至少row order不会发生太大变化。咱们只需要关心column shift这个问题。
咱们可以看到在column方向发生了水平位移,但是竖着的row方向没有变化。
为了解决这个问题,文中采用了一个“地球人都能想到的方法”,那就是不断尝试各种角度的column shift。注意的是,旋转candidate point cloud有个resolution,那就是之前提到的 2 π N s \frac{2\pi}{N_s} Ns2π。
我们使用公式(7)进行最佳shift的选择,找到最好的 n ∗ n^{*} n∗后,用公式(6)进行distance计算。
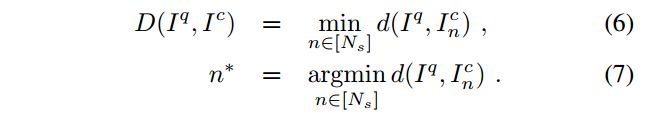
注意:这里咱们通过找最好的 n ∗ n^* n∗,还有一个意想不到的好处,那就是可以给ICP提供一个Good initial rotation value! (就是ICP代码中的predicted pose)
3.3 Two-phase Search Algorithm
文中提到,有三种主流的Place Recognition的Search Algorithm:
- Pairwise Similarity Scoring
- Nearest Neighbor Search搜索
- Sparse Optimization
本文中采用了pairwise scoring和nearest search来实现有效的Hierarchical Search。
(1) Ring Key
在3.2节中我们提到的公式(6)进行最短距离计算时,要先找到最佳旋转 n ∗ n^* n∗,计算量很大,所以在本文中提出了一种"Two-phase Search",并提出了Ring key这个Descriptor(描述子)来进行匹配搜索:
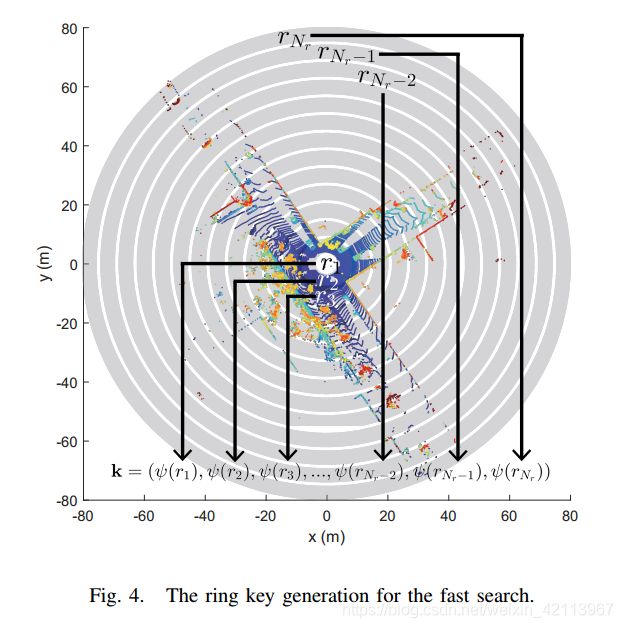
Ring key is a rotation-invariant descriptor, which is extracted from a scan context. Each row of a scan context, r, is encoded into a single real value via ring encoding function . The first element of the vector k is from the nearest circle from a sensor, and following elements are from the next rings in order as illustrated in Fig. 4
由内而外,一圈一圈的ring key通过对Scan Context Matrix的每一行row r r r进行 ψ ( ⋅ ) \psi(\cdot) ψ(⋅)的encoding就变成了一个 N r N_r Nr维度的Vector k \textbf{k} k:
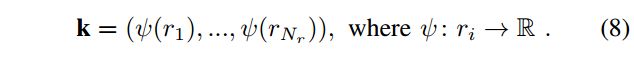
The ring encoding function ψ \psi ψ is a occupancy ratio using L 0 L_0 L0 norm:
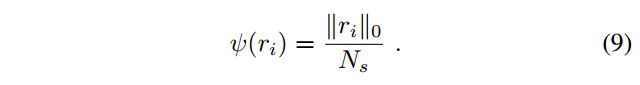
小红薯:大师兄,这里的 ∣ ∣ r i ∣ ∣ 0 ||r_i||_0 ∣∣ri∣∣0是什么意思呢?
大师兄:这是 L 0 L_0 L0 norm(范数)的意思,其实 L 0 L_0 L0 norm并不是一个真正的norm,它就是the total number of non-zero elements in a vector 。比如,(2,0,1,0,9)这个vector的 L 0 L_0 L0 norm就是3,因为有3个非零数。
大师兄: 这样一来,咱们统计每一圈的row中有多少个非零数值,那这就和rotation没啥关系啦(也就是原文中所说的rotation invariance)!这样就能够达到快速的search。
(2) KD-Tree
- 在得到ring key向量 k \textbf{k} k 之后,文章用了 k \textbf{k} k构建KD Tree。
- 用ring key of the query到这个KD Tree中搜索K个最相似的scan indexex(K是个heuristic number)
- 得到最相似的K个scan后,用上文中公式(6)进行Similarity Score计算
- 满足条件的最近的candidate c ∗ c^* c∗这个位置被选为revisited place,也就是loop的地方:
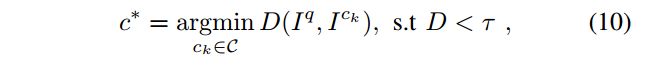
4. Scan Context算法延伸
4.1 ICP Initial Value中的应用
由上文3.2节的公式(7)需要找到一个 n ∗ n^* n∗旋转,使得两个点云之间的距离最小。这里其实也可以作为ICP的一个初始值,即predicted pose,来加快converge的过程。
文章的Experiment部分对此进行了试验,发现用Scan Context进行ICP初始化效果确实更好:
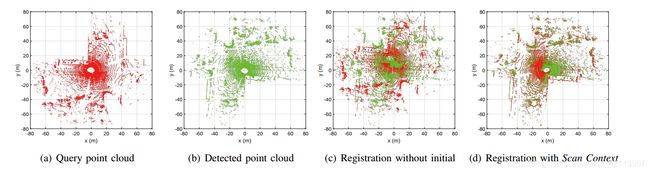
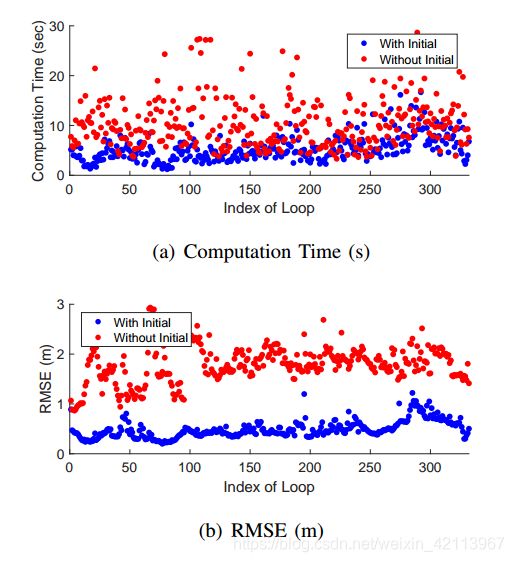
4.2 Future Works
在文章最后,作者提到可以使用更好的bin encoding function (eg., a bin’s segmantic information)来提升性能,目前咱们只是用了一个很简单的 m a x Z ( p ) max\ Z(p) max Z(p)来找Z轴高度上的最高点。
对于有梦想的读者,也期待你的贡献!
参考文献
[1] G. Kim and A. Kim, “Scan Context: Egocentric Spatial Descriptor for Place Recognition Within 3D Point Cloud Map,” 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, 2018, pp. 4802-4809, doi: 10.1109/IROS.2018.8593953.
[2] S. Belongie, J. Malik, and J. Puzicha, “Shape matching and object recognition using shape contexts,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intell., vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 509–522, 2002.