Python 字符串详解总结(字符串基本特性,回文字符串的判断,字符串的内建函数,string字符串模块,随机验证码的生成,小学计算能力评估系统)
1.字符串的基本特性:
1-1: 字符串的输入:
单引号,双引号,三引号引起来的都是字符串 ;
转译字符:
\n 换行符
\t 制表符
1-2 : 连接和重复
连接操作符: + (只能同类型的数据类型拼接)
>>> name = "westos"
>>> print('hello ' + name)
hello westos
>>> print('hello ' + str(1))
hello 1
重复操作符: *
>>> print("*" * 30 + '学生管理系统' + '*' * 30)
******************************学生管理系统******************************
1-3: 成员操作符: in 返回bool值 ;
>>> s = 'hello westos'
>>> print('westos' in s)
True
>>> print('westos' not in s)
False
1-4: 正向索引和反向索引 :
索引:获取特定偏移的元素; 分为正向索引和反向索引 (表示只拿一个字符)
>>> s = 'WESTOS'
>>> print(s[0]) # W (正数第一个)
W
>>> print(s[3]) # T (正数第四个)
T
>>> print(s[-3]) # T (倒数第三个)
T
1-5: 切片 (拿多个字符):
s[start : end : step] 和range()类似 ,start索引开始,end-1索引结束,部长为step ;
s[:end] start没写默认从0 开始 ;
>>> s = "hello westos"
>>> print(s[1:3]) #从第一个索引开始,到3-1个索引结束 , # el ;
el
>>> print(s[:3]) #从头开始,到3-1个索引结束, # hel ;
hel
>>> print(s[1:]) #从第1个索引开始拿到最后 # ello westos
ello westos
>>> print(s[:]) #拷贝字符串
hello westos
常见切片表示的意义:
s[:n] 拿出前n个字符
s[n:] 拿出除了前n个元素
s[:] 从0个索引开始到结束
s[::-1] 倒序输出
2: 使用for循环遍历字符串:
>>> s = 'westos'
>>> count = 0
>>> for item in s:
... count += 1
... print(f"第{count}个字符{item}")
...
第1个字符w
第2个字符e
第3个字符s
第4个字符t
第5个字符o
第6个字符s
3.练习1:
需求:用户输入一个字符串,判断该字符串是否为回文字符串 (回文字符串:例如: aba , abba等);
法一:
s = input("请输入字符串:")
s1 = s[::-1]
if s1 == s :
print(f"{s}字符串是回文字符串")
else:
print(f"{s}字符串不是回文字符串")
法二:三元运算符:
s = input("请输入字符串:")
print("回文字符串" if s == s[::-1] else "不是回文字符串")
s = input("请输入字符串:")
result = ("回文字符串" if s == s[::-1] else "不是回文字符串")
print(s + result)
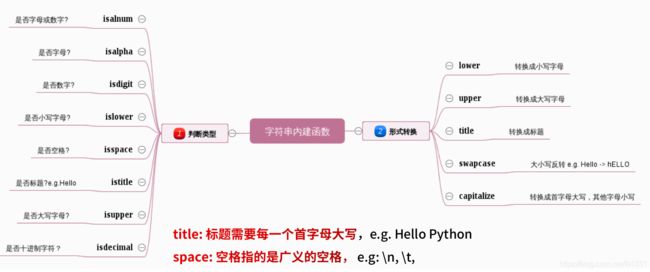
4.字符串的内建函数:
4-1: 判断类型(bool值)
s = 'HelloWESTOS'
print(s.isalnum()) # True (是数字或字母吗)
print(s.isdigit()) # Flase (是数字吗)
print(s.isupper()) # False (全是大写吗)
4-2: 形式转换 :
>>> s = 'Hello WESTOS'
>>> print('hello'.upper()) #HELLO
HELLO
>>> print('HellO'.lower()) #hello
hello
>>> print('HellO WOrld'.title()) #Hello World
Hello World
>>> print('HellO WOrld'.capitalize()) #Hello world
Hello world
>>> print('HellO WOrld'.swapcase()) #hELLo woRLD 大写变小写,小写变大写
hELLo woRLD
4-3: 字符串的开头和结尾匹配:
# startswith 以 ... 开头
url = 'http://www.baidu.com'
if url.startswith('http'):
# 具体实现爬虫,感兴趣的话可以看request模块。
print(f'{url}是一个正确的网址,可以爬取网站的代码')
# endswith: 以 ... 结尾
# 常用的场景: 判断文件的类型
filename = 'hello.png'
if filename.endswith('.png'):
print(f'{filename} 是图片文件')
elif filename.endswith('mp3'):
print(f'{filename}是音乐文件')
else:
print(f'{filename}是未知文件')
4-4: 字符串的数据清洗:
strip 删除空格(Tab ‘space’ 回车)
lstrip 删除字符串左边的空格 (Tab ‘space’ 回车)
rstrip 删除字符串右边的空格 (Tab ‘space’ 回车)
replace 替换函数,可用作删除,删除字符串中间的空格时,可以将空格替换成空 " hell o " .replace(" "."")
>>> " hello ".strip()
'hello' #去掉空格
>>> " hello ".lstrip()
'hello ' #去掉左边的空格
>>> " hello ".rstrip()
' hello' #去掉右边的空格
>>> " hel lo ".replace(" ", "")
'hello' #将空格替换为“”(可以用来删除中间的空格)
4-5: 字符串的位置调整 :
>>> "学生管理系统".center(50)
' 学生管理系统 '
>>> "学生管理系统".center(50, "*")
'**********************学生管理系统**********************'
>>> "学生管理系统".center(50, "-")
'----------------------学生管理系统----------------------'
>>> "学生管理系统".ljust(50, "-")
'学生管理系统--------------------------------------------'
>>> "学生管理系统".rjust(50, "-")
'--------------------------------------------学生管理系统'
>>>
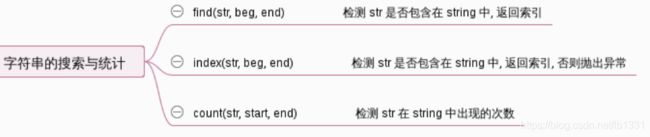
4-6: 字符串的搜索和统计:
s = "hello westos"
s.find("llo") #2(索引)
s.index("llo") #2
s.find(“xx”) # -1
s.index("xx") #报错(抛出异常)
s.count("l") # 2 (出现两次)
s.count("xx") # 0 出现0次
>>> s = "hello westos"
>>> s.find("llo")
2
>>> s.index("llo")
2
>>> s.find("xxx")
-1
>>> s.index("xxx")
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "" , line 1, in <module>
ValueError: substring not found
>>> # find如果找到子串, 则返回子串开始的索引位置。 否则返回-1
>>> # index如果找到子串,则返回子串开始的索引位置。否则报错(抛出异常).
>>>
>>> s.count("xxx")
0
>>> s.count("l")
2
>>> s.count("o")
2
4-7: 字符串的分离和拼接:
法一:分割再拼接
IP = '172.25.254.100'
items = IP.split('.') # ['172', '25', '254', '100']
"-".join(items) # 172-25-254-100
法二:数据清洗replace
IP = input("please input ip:")
print(IP.replace(".", "-"))
字符串的分离和拼接:
>>> ip = "172.25.254.100"
>>> # 需求:IP地址的合法性-将ip的每一位数字拿出, 判断每位数字是否在0-255之间。
>>> ip.split('.')
['172', '25', '254', '100']
>>> items = ip.split('.')
>>> items
['172', '25', '254', '100']
>>> # 拼接
>>> items
['172', '25', '254', '100']
>>> # 需求: 将四个数字用'-'拼接起来
>>> "-".join(items)
'172-25-254-100'
练习:需求:将ip中的每一位数字拿出判断每位数字是否在0~255之间 (判断ip地址的合法性):
IP = input("please input ip:")
items = IP.split('.')
count = 0
for items_in in items:
if int(items_in) > 255 or int(items_in) < 0 :
count += 1
if count != 0:
print(f"{IP} is error ip")
exit()
else:
print(f"{IP} is right ip")
exit()
5. string 字符串模块:
详见 :https://www.cnblogs.com/lyy135146/p/11655105.html
需求:
生成100个验证码: 每个验证码由6个字符组成,2个数字和4个字母 :
random 模块:
>>> random.choice("0123456789")
'6'
>>> random.choice("0123456789") + random.choice('0123456789')
'84'
>>> random.choice("0123456789") + random.choice('0123456789') + random.choice('abcdef')
'16b'
从choice( ) 中进行随机选择
string 模块:
>>> string.digits
'0123456789'
>>> string.ascii_letters
'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
random.sample :
>>> random.sample(string.ascii_letters, 4)
['z', 'N', 'u', 't']
>>> random.sample(string.ascii_letters, 4)
['c', 'q', 'X', 'f']
>>> random.sample(string.ascii_letters, 4)
['D', 'b', 'e', 'A']
将随机的字符个数字拼接起来( 使用 “” ):
>>> "".join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters, 4))
'aMUF'
>>> "".join(random.sample(string.digits, 2)) + "".join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters, 4))
'95sGFj'
>>> "".join(random.sample(string.digits, 2)) + "".join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters, 4))
'17TlIb'
完成需求,生成100个验证码: 每个验证码由6个字符组成,2个数字和4个字母 :
import random
import string
for i in range(100):
print("".join(random.sample(string.digits,2)) + "".join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters,4)))
结果示例(部分):
37DFCp
82oeWC
06ciAI
46tpmU
91RJUh
50yHAh
98bdHG
04ZJfe
34wRfG
91qzIN
练习:小学计算能力评估系统:
需求:
"""
设计一个程序,用来实现帮助小学生进行算术运算练习,
它具有以下功能:
提供基本算术运算(加减乘)的题目,每道题中的操作数是随机产生的,
练习者根据显示的题目输入自己的答案,程序自动判断输入的答案是否正确
并显示出相应的信息。最后显示正确率。
"""
代码:
import random
level = str(input("please choice level(easy, normal, hard): "))
worknumber = int(input("please input number of work: "))
rightnum = 0
for i in range(worknumber):
if level == "easy":
num1 = random.randint(1,10)
num2 = random.randint(1,10)
symbol = random.choice(["+", "-", "*"])
print(f"queston{i+1}: {num1} {symbol} {num2}")
answer = eval(f"{num1}{symbol}{num2}")
useranswer = int(input("please input your answer: "))
if answer == useranswer:
rightnum += 1
print("Right")
else:
print("Error")
if level == "normal":
num1 = random.randint(10, 100)
num2 = random.randint(10, 100)
symbol = random.choice(["+", "-", "*"])
print(f"queston{i + 1}: {num1} {symbol} {num2}")
answer = eval(f"{num1}{symbol}{num2}")
useranswer = int(input("please input your answer: "))
if answer == useranswer:
rightnum += 1
print("Right")
else:
print("Error")
if level == "hard":
num1 = random.randint(100, 1000)
num2 = random.randint(100, 1000)
symbol = random.choice(["+", "-", "*"])
print(f"queston{i + 1}: {num1} {symbol} {num2}")
answer = eval(f"{num1}{symbol}{num2}")
useranswer = int(input("please input your answer: "))
if answer == useranswer:
rightnum += 1
print("Right")
else:
print("Error")
print("Right number:", rightnum)
print("Errot number:", worknumber - rightnum)
print("Right percent: %.2f%%" %(rightnum/worknumber*100))
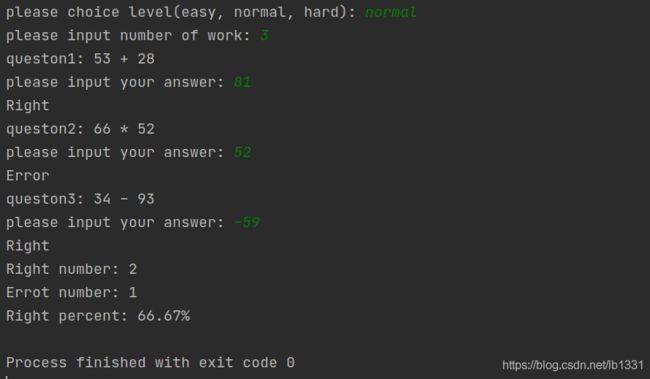
结果展示: