Mybatis源码分析(一)
mybatis源码
- 1、回顾JDBC
-
- 1.1 jdbc执行流程
- 1.2 SqlSessionFactory & SqlSession
-
- 1.2.1 获取SqlSession
-
- 1.2.1.1 源码解析
- 1.3 MapperProxy
- 1.4 Excutor
-
- 1.4.1 执行流程
- 1.4.2 MapperProxy
- 下期详细讲解Mybatis中用到的设计模式,以及具体实现
- 交流群 867157531
1、回顾JDBC
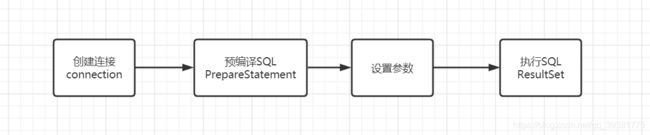
1.1 jdbc执行流程
/*第一步,获取连接*/
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(JDBC.URL,JDBC.USER,JDBC.PASSWORD);
/*第二步,预编译SQL*/
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatment("SELECT * FROM USER");
/*第三步,执行SQL*/
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(statement);
/*第四步,获取结果集*/
readResultSet(resultSet);
1.2 SqlSessionFactory & SqlSession
1.2.1 获取SqlSession
1.2.1.1 源码解析
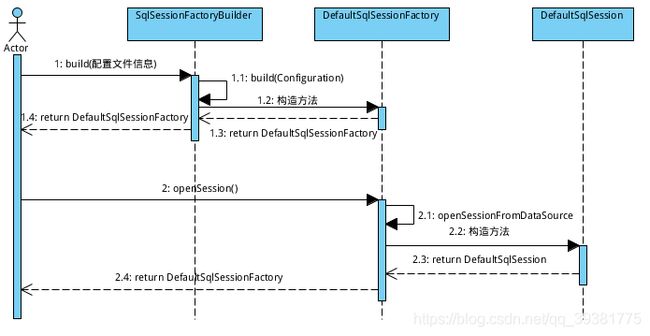
- SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build();
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader) {
/**调用内部build方法*/
return build(reader, null, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment) {
return build(reader, environment, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, Properties properties) {
return build(reader, null, properties);
}
}
- SqlSessionFactoryBuilder内部build()一个DefaultSqlSessionFactory
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
/**解析XML解析器*/
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
/**parser.parse() 获取Configuration,build一个DefaultSqlSessionFactory*/
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
}
- 获取到SqlSessionFactory后通过SqlSessionFactory获取SqlSession对象
/**SqlSessionFactory对象中的openSession方法最终都会调用openSessionFromDataSource方法*/
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
//通过Configuration获取mybatis的配置信息
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
//结合JDBC的执行流程来看 与数据库相互是statement对象,实际上executor是对于statement的封装,也就是说executor是statement的一个执行器
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
// 重点!! 创建了一个DefaultSqlSession对象
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
- 通过以上步骤,我们已经获取到了一个SqlSession,按照JDBC的步骤来说我们应该去执行sql了,结合以下Demo理解
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactory();
String resource = "classpath:mybatis-config.xml"
try{
//SqlSessionFactoryBuilder读取配置文件
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource));
} catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//获取sqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()
1.3 MapperProxy
- 到目前为止我们写的.mapper文件还没有使用!!!,下面介绍 MapperPorxy
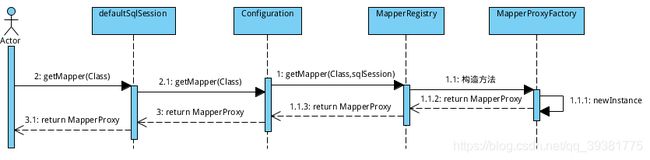
在mybatis中我的写的dao层的接口其实是MapperProxy在代理,也就是说我们在执行dao层中的方法是,其实是在执行MapperProxy - 我们通过SqlSession从Configuration中找到一个getMapper方法
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
// mapperRegistry是什么?见名知意 应该是mapper注册机之类的东西,接着往下走看看这个mapperRegister是什么
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
- 我们看下MapperRegistry是什么
// MapperRegistry实际上就是一个注册机用来调用MapperProxyFactory工厂的
public class MapperRegistry {
private final Configuration config;
//
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();
public MapperRegistry(Configuration config) {
this.config = config;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 这里定了一个MapperProxyFactory的工厂
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
//代理工厂的实例 返回了一个mapper的代理对象工厂的实例,这是不是就是我们想要的dao层对象呢?我们继续往下看MapperProxyFactory
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
- MapperProxyFactory的作用是什么
/**部分代码*/
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
//!!!重点来了 这里代理到了我们写的Dao层接口
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] {
mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
通过以上的动态代理就可以获取到我们的Dao层
//获取Dao对象
TestDao dao = sqlSession.getMapper(TestDao.class);
有个疑问,我们定义的Dao是接口(Interface),按理说接口是不能实例对象的,那我们这个对象是怎么得到的呢?
答:建议补习java的动态代理,划重点–>Proxy.newProxyInstance() AOP也是基于动态代理实现的!
1.4 Excutor
1.4.1 执行流程
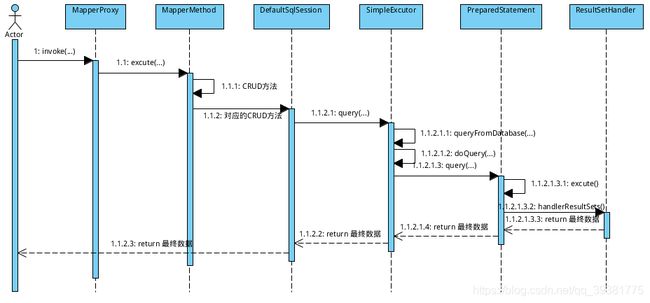
到这里我们获取到了SqlSession 和 我们的mapper接口,那接下来应该做什么呢? 没错! 执行SQL ,我们去看下真正的SQL执行流程
1.4.2 MapperProxy
上面提到 我们通过MapperProxyFactory拿到了MapperProxy,我们都知道每一个MapperProxy都是对应的我们的dao层接口
//MapperProxy在执行的时候会触发此方法
interface MapperMethodInvoker {
Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable;
}
private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
private final MapperMethod mapperMethod;
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
// 这里交给mapperMethod去处理
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}
//这里是对数据库操作类型的判断,最终还是返回了SqlSession,那我们去看看SqlSession的CRUD方法
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
我们进入到SqlSession的实现类DefaultSqlSession随便找一个方法我们进行查看 我这里选择了SelectOne
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
// 我们点击selectList方法一直点 我们最终可以发现
List<T> list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
// 粗心的小伙伴一定见过这段异常
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
我们随着this.selectList()方法一直查看最终我们会在SimpleExecutor这个类看到这块内容
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
@Override
protected <E> Cursor<E> doQueryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, null, boundSql);
Statement stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
Cursor<E> cursor = handler.queryCursor(stmt);
stmt.closeOnCompletion();
return cursor;
}
@Override
public List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
//有没有发现这里很熟悉?,这就是我们创建连接获取Statement的操作!这下就这真相大白了!
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}