CPU利用率高的定位思路和方法
1. top命令
通过top命令,可以快速查看各cpu利用率,以及进程按利用率从高到底排列的列表。
输入top回车,然后按键盘数字1。
[root@cpe ~]# top
top - 10:55:00 up 2 days, 23:41, 5 users, load average: 1.03, 0.65, 0.31
Tasks: 120 total, 2 running, 118 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
%Cpu0 : 0.0 us, 0.3 sy, 0.0 ni, 99.7 id, 0.0 wa, 0.0 hi, 0.0 si, 0.0 st
%Cpu1 :100.0 us, 0.0 sy, 0.0 ni, 0.0 id, 0.0 wa, 0.0 hi, 0.0 si, 0.0 st
KiB Mem : 1909524 total, 94268 free, 1295204 used, 520052 buff/cache
KiB Swap: 2097148 total, 2069500 free, 27648 used. 379788 avail Mem
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
57231 root 20 0 4208 352 280 R 100.0 0.0 4:51.40 a.out
57286 root 20 0 162004 2260 1556 R 0.3 0.1 0:00.03 top
1 root 20 0 191052 2924 1696 S 0.0 0.2 0:24.82 systemd
2 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.13 kthreadd
3 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:33.62 ksoftirqd/0
7 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:01.80 migration/0
8 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 rcu_bh
9 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:09.73 rcu_sched
10 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:04.97 watchdog/0
11 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:05.33 watchdog/1
12 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.95 migration/1
13 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.91 ksoftirqd/1
17 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kdevtmpfs
18 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 netns
19 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.14 khungtaskd
20 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 writeback
21 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kintegrityd
22 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 bioset
23 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kblockd
24 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 md
30 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:06.64 kswapd0
31 root 25 5 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 ksmd
32 root 39 19 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:01.97 khugepaged 我们通过查看top结果,来初步进行问题判断。
1.1 kswapd0 进程占用cpu过高
如果是kswapd0占用cpu过高,大多数情况下是系统内存不足,于是kswapd0进程频繁操作swap分区与内存换页操作交换数据,导致CPU占用过高。
这种情况下我们需要查看内存占用情况,并做相应处理。内存占用下降后,cpu利用率自然就降下来了。
1.2 ksoftirqd 进程占用cpu过高
这种一般是软中断处理太多,在软中断中处理不了的部分,转由ksoftirqd来处理。
想要确认是那些中断处理占用cpu过高,需要perf工具进一步分析。
1.3 特定应用进程或者脚本占用cpu过高
这时需要分析进程或脚本是否存在异常逻辑,导致cpu占用过高。
如果从代码层面无法确认,则需要perf工具进一步分析。
例如我们top显示cpu1利用率100%,通过查看发现进程a.out占用了100%的cpu。这时就需要查看a.out相关代码,确认是否存在bug。
2. perf命令
perf是一款Linux性能分析工具,它的功能非常全面。我们主要使用它来做性能分析。
2.1 使用perf top对cpu进行性能分析
以下是对cpu0进行性能分析的展示,它能显示出各模块具体函数占用的cpu比例。
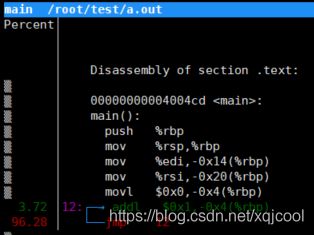
[root@localhost ~]# perf top -C 1 -e cpu-clock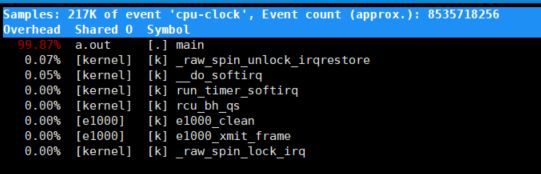
PS:
部分平台上perf会引起奇怪的crash。使用 -e cpu-clock 参数可以避免这个问题。
通过查看perf top可以看到那个具体函数的执行占用了最多的cpu利用率。然后分析该函数,确认是代码BUG还是性能瓶颈。
在Annotate中,我们可以看到函数中具体那些汇编指令占用的cpu比例最高。确定性能瓶颈,然后再考虑如何优化。
例如图片中显示a.out进程的main函数中,存在死循环,占用了95%以上的cpu处理时间。
2.2 使用perf 火焰图进行性能分析
perf 火焰图反映了一段时间内用户程序/内核模块在 CPU 上运行的热点,其绘制原理是对 Perf 采集到的 samples 进行解析,对函数调用栈进行归纳合并,以柱状图的形式呈现出来。
这里需要使用到FlameGraph辅助工具。下载地址:https://github.com/brendangregg/FlameGraph.git
生成火焰图需要分为两部分操作:
第一部分在问题设备上进行执行
//记录10s中cpu0的性能数据
[root@localhost ~]# perf record -C 1 -e cpu-clock -g sleep 10
[ perf record: Woken up 4 times to write data ]
[ perf record: Captured and wrote 1.124 MB perf.data (6321 samples) ]
//生成perf.folded
[root@localhost ~]# perf script -i perf.data > perf.folded第二部分在下载了FlameGraph的设备上执行
[root@localhost FlameGraph]# ./stackcollapse-perf.pl perf.folded > perf.unfold
[root@localhost FlameGraph]# ./flamegraph.pl perf.unfold > perf.svg这时就可以用浏览器直接打开perf.svg火焰图文件了。
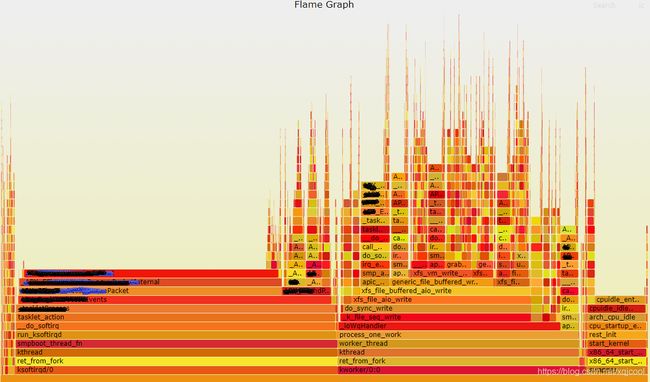
从火焰图上可以很直观的看到各函数占用cpu比例,以及栈的调用层级,配合perf top,可以更好的定位一些公共函数占用cpu高的问题,然后进行性能优化。
3. 中断亲和性调整
现网环境大多是多核设备,在实际应用中经常出现cpu利用率不均衡问题。
此时我们需要调整网卡中断亲和性,尽量使各cpu负载相对平均,避免部分cpu利用率很高,而其他cpu利用率空闲的情况。
3.1 关闭 irqbalance 服务
因为irqbalance会动态调整中断亲和性,可能会造成中断自动漂移,影响性能稳定,所以我们需要将其关闭。
//查看irqbalance进程
[root@localhost ~]#ps aux|grep irqbalance
root 663 0.0 0.0 21672 972 ? Ss Aug23 0:18 /usr/sbin/irqbalance --foreground
//停止irqbalance服务
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop irqbalance
//关闭irqbalance服务
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl disable irqbalance
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/irqbalance.service.3.2 查看中断分配/proc/interrupts
通过查看/proc/interrupts,我们可以知道网卡收发对应的中断号。
[root@localhost ~]# cat /proc/interrupts
CPU0 CPU1 CPU2 CPU3
0: 83 0 0 0 IO-APIC-edge timer
1: 2 0 0 0 IO-APIC-edge i8042
4: 7825 0 0 0 IO-APIC-edge serial
5: 0 0 0 0 IO-APIC-edge parport0
8: 0 0 0 0 IO-APIC-fasteoi rtc0
9: 0 0 0 0 IO-APIC-fasteoi acpi
12: 4 0 0 0 IO-APIC-edge i8042
23: 25 0 0 0 IO-APIC-fasteoi ehci_hcd:usb1
93: 512333 63029 1856 999 PCI-MSI-edge 0000:00:13.0
94: 176372 40901 17014 7926 PCI-MSI-edge i915
95: 0 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth0
96: 233336 40854 20950 12253 PCI-MSI-edge eth0-TxRx-0
97: 5 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth1
98: 3 0 1024153271 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth1-TxRx-0
99: 2 2 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth2
100: 37336 652758795 0 13437 PCI-MSI-edge eth2-TxRx-0
101: 0 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth3
102: 222837 51264 22140 11143 PCI-MSI-edge eth3-TxRx-0
103: 2 2 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth4
104: 13 0 0 597077157 PCI-MSI-edge eth4-TxRx-0
105: 0 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth5
106: 221078 53075 20830 12397 PCI-MSI-edge eth5-TxRx-0
NMI: 114857 22488 164694 144069 Non-maskable interrupts
LOC: 631617848 639672413 671254937 633416868 Local timer interrupts
SPU: 0 0 0 0 Spurious interrupts
PMI: 114857 22488 164694 144069 Performance monitoring interrupts
IWI: 2246140 2553778 1454384 1637762 IRQ work interrupts
RTR: 0 0 0 0 APIC ICR read retries
RES: 10967350 10867791 22446215 8787350 Rescheduling interrupts
CAL: 56889 31236 114202 176696 Function call interrupts
TLB: 711378 1799520 948549 1629026 TLB shootdowns
TRM: 0 0 0 0 Thermal event interrupts
THR: 0 0 0 0 Threshold APIC interrupts
DFR: 0 0 0 0 Deferred Error APIC interrupts
MCE: 0 0 0 0 Machine check exceptions
MCP: 2050 2050 2050 2050 Machine check polls
ERR: 0
MIS: 0
PIN: 0 0 0 0 Posted-interrupt notification event
PIW: 0 0 0 0 Posted-interrupt wakeup event间隔几秒再cat一下,通过对比,找到中断变化值比较高的中断。
3.3 调整中断亲和度
我们通过调整网卡中断亲和度,可以将网卡的硬中断绑定在指定的cpu上,从而达到调整cpu利用率的效果。
例如:
cpu0利用率较高,cpu3利用率较低,我们想把 eth0-TxRx-0(中断号96) 的绑定迁移到cpu3上。
cpu2利用率较高,cpu1利用率较低,我们想把 eth1-TxRx-0(中断号98) 的绑定迁移到cpu1上。
我们需要做的操作如下:
//8 (2^3)表示绑定到cpu3。如果绑定cpu2,则是 4 (2^2)
[root@cpe ~]# echo 8 > /proc/irq/96/smp_affinity
//2 (2^1)表示绑定到cpu1。如果绑定cpu0,则是 1 (2^0)
[root@cpe ~]# echo 2 > /proc/irq/98/smp_affinity通过对网卡中断亲和度的调整,我们可以使不通cpu的负载相对平均,更好地发挥设备性能。