从零开始构建自己的数字货币(初学简易版,Java实现)
参考b站up主 是落拓呀 数字货币教程,略有改动。
SHA256
参考比特币的模式,比特币挖矿本质就是在做逆哈希运算,找到一个哈希值符合要求的源字符串。比特币的哈希算法是SHA256(Secure Hash Algorithm)
哈希函数把消息或数据压缩成摘要,并将数据的格式固定下来。将数据打乱混合,重新创建一个叫做散列值(或哈希值)的指纹。哈希值通常用一个短的随机字母和数字组成的字符串来代表。
对于任意长度的消息,SHA256都会产生一个256bit长的哈希值,称作消息摘要,通常用一个长度为64的十六进制字符串来表示。
哈希函数最重要的特点有二:
1.即使输入只有微小的不同,得到的哈希值也会天差地别
2.只要有同样的输入,经过哈希函数的结果必定也会相同
那么我们要创建一个独特的数字货币,首先需要的也是哈希算法。此处用到了网上找到的SHA256的java实现。
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
public class SHA256 {
/**
* 利用java原生的类实现SHA256加密
* @param str 加密后的报文
* @return
*/
public static String getSHA256(String str){
MessageDigest messageDigest;
String encodestr = "";
try {
messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
messageDigest.update(str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
encodestr = byte2Hex(messageDigest.digest());
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return encodestr;
}
/**
* 将byte转为16进制
* @param bytes
* @return
*/
private static String byte2Hex(byte[] bytes){
StringBuilder stringBuffer = new StringBuilder();
String temp = null;
for (byte aByte : bytes) {
temp = Integer.toHexString(aByte & 0xFF);
if (temp.length() == 1) {
//1得到一位的进行补0操作
stringBuffer.append("0");
}
stringBuffer.append(temp);
}
return stringBuffer.toString();
}
}
调用getSHA256()方法,即可得到一个字符串的哈希值。
区块链结构
区块链是一种安全性极高的“数据库”,它的安全性是由它的结构与哈希函数的特性一起实现的。
所谓区块链,其实就是把一个一个的区块通过链条连接起来,结构上类似于链表,而且除自己包含的信息之外,还储存了上一个区块的哈希值和本区块的哈希值(其中本区块哈希值是通过自己的信息和上一区块哈希值共同计算得出的)
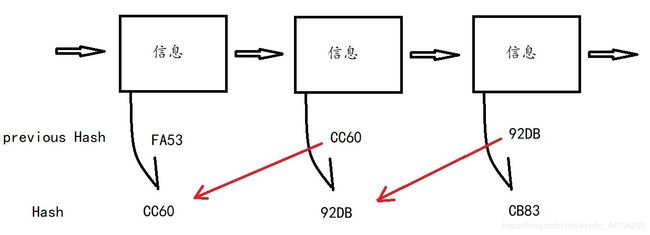
如图所示,假设这是一条很长的区块链的一部分,当我想改这里第二个区块的信息,那么算出来的哈希值就和当时打包时算出来的哈希值不同,与下一个区块的previous Hash不符,这时就出现了链条断裂,就可以检测到数据被篡改。如果我想使得整个链重新变得合法,就不得不从该区块开始,一路把后面所有的区块的Hash重新计算一遍。
如果我们的区块链像数字货币一样使用了分布式存储,即每个用户本地都有一份完整的区块链备份,那么就不得不把所有人本地的区块完全修改掉。对于数字货币等应用来说,在此时还不断地有区块生成,要进行这样的改动简直是难如登天,以此来保证安全性。
对于比特币来说,还有工作量证明机制(Proof Of Work)来实现动态调整哈希计算的难度,使得对区块进行哈希运算的时间与生成新区块的时间都是10分钟。当你修改好了上一个区块,下一个区块又生成了,那么即使有再大的算力,也难以修改区块链上的数据了。
比特币核心在于区块链,区块链就是比特币的“账本”,对于普通支付软件来讲,每个人的账户里记录了自己的资产多少,但即使防范措施再周密,总不免会有疏漏。而我们上述分布式存储+区块链的方式是从结构上使得篡改变得不可能,也就是完全可以信任。所以比特币并不记录每个账户上的资产,而是通过从第一条交易开始进行推算,直到上一个区块为止,由其中某用户进行的所有交易行为来推断该用户的当前资产。挖矿的奖励发放也是通过交易来进行的。
那么区块链,肯定有区块,也有链条
package BlockChain;
import static BlockChain.SHA256.getSHA256;
import java.sql.Timestamp;
import java.util.List;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
// Block类实现
public class Block {
List<Transaction> transactions; // 交易记录
String previousHash; // 上一个区块的hash
String hash; // 自己的hash
String data; // 初始字符串
int nonce = 0; // 初始nonce
Timestamp time; // block生成的时间
/*
* Constructor
* */
Block(List<Transaction> transactions, String previousHash, String data) {
this.transactions = transactions;
this.previousHash = previousHash;
this.data = data;
}
// 计算区块的hash
// transactions need stringify
String computeHash() {
return getSHA256(JSON.toJSONString(this.transactions) +
this.previousHash + this.data + this.nonce);
}
// 得到由difficulty个0组成的字符串
String getAnswer(int difficulty) {
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < difficulty; i++) {
ans.append("0");
}
return ans.toString();
}
// 计算符合区块链设置要求的hash
void mine(int difficulty) {
String ans = getAnswer(difficulty);
this.hash = this.computeHash();
while (!this.hash.substring(0, difficulty).equals(ans)) {
this.nonce++;
this.hash = this.computeHash();
}
}
// 覆写toString()方法打印区块信息
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder ret = new StringBuilder();
ret.append("\tTransactions:\n");
if (transactions != null) {
for (Transaction t : this.transactions) {
ret.append(t.toString());
}
}
ret.append("\tpreviousHash:").append(this.previousHash).append("\n");
ret.append("\thash:").append(this.hash).append("\n");
ret.append("\tdata:").append(this.data).append("\n");
ret.append("\tnonce:").append(this.nonce).append("\n");
ret.append("\ttime:").append(this.time).append("\n");
return ret.toString();
}
}
这里的哈希值计算,是找出某个哈希值是以若干个’0’开头的字符串,修改difficulty参数可以调整哈希值计算的难度。
package BlockChain;
import java.sql.Timestamp;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.List;
// Chain类实现
public class Chain {
Deque<Block> blockChain; // 区块链
List<Transaction> transactionPool; // 交易池
int minerReward = 50; // 矿工奖赏
int difficulty = 5; // 挖矿难度
static User system;
// Constructor
Chain() {
// 区块队列
this.blockChain = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 添加祖先区块
this.blockChain.addLast(this.generateGenesisBlock());
// 交易队列
this.transactionPool = new ArrayList<>();
system = new User("");
}
// 生成祖先区块
private Block generateGenesisBlock() {
Block genesisBlock = new Block(null, "", "GenesisBlock");
genesisBlock.hash = genesisBlock.computeHash();
genesisBlock.time = new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
return genesisBlock;
}
// 添加Transaction到transactionPool
public void transaction2Pool(User from, User to, int amount) throws Exception {
Transaction t = new Transaction(from, to, amount);
if (t.isValid()) {
this.transactionPool.add(t);
}
}
// 挖矿并发放矿工奖励
public void mineTransaction(User address, String data) throws Exception {
this.validateTransactions();
assert this.blockChain.peekLast() != null;
Block newBlock = new Block(transactionPool, this.blockChain.peekLast().hash, data);
newBlock.mine(this.difficulty);
Transaction minerReward = new Transaction(system, address, this.minerReward);
if (minerReward.isValid()) {
this.transactionPool.add(minerReward);
}
pack(newBlock);
}
// 打包之前验证每个交易的合法性
private void validateTransactions() throws Exception {
for (Transaction t : transactionPool) {
if (!t.isValid()) {
transactionPool.remove(t);
}
}
}
// 验证区块链合法性
// 重新计算每个区块的hash并对比是否一致
// 检查每个区块的previousHash与其上一区块的hash是否一致
private boolean validateChain() {
String previousHash = "";
for (Block block : this.blockChain) {
if (!block.hash.equals(block.computeHash())) {
System.out.println("数据被篡改");
return false;
}
if (!block.previousHash.equals(previousHash)) {
System.out.println("区块链接断裂");
return false;
}
previousHash = block.hash;
}
return true;
}
// block打包
private void pack(Block newBlock) {
newBlock.time = new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
newBlock.hash = newBlock.computeHash();
this.blockChain.addLast(newBlock);
if (!validateChain()) {
blockChain.pollLast();
}
this.transactionPool = new ArrayList<>();
}
// 覆写toString()方法打印区块链
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder ret = new StringBuilder("BlockChain:\n");
for (Block block : this.blockChain) {
ret.append(block.toString()).append("\n");
}
return ret.toString();
}
}
这里的Transaction类和User类分别是描述交易和用户的类。
对于每个在打包间隔产生的交易,验证后先暂存到交易池中,这里的验证方法是数字签名,在后面会提到。
当区块要打包,并发放该时段的矿工奖励时,我们首先对所有交易进行重新验证、对该区块链的合法性、区块链间的连接合法性做验证。如果均通过,我们就可以将区块加入区块链中。
数字签名
在实际的发起、确认交易时,数据在传输过程中可能被篡改。为了防止这种情况,我们需要添加验证的手段,这里采用RSA加密算法。
RSA加密算法为每位用户提供一对钥匙,一个叫公钥,另一个叫私钥。基本原理是用一个钥匙加密的数据可以用另一个钥匙解密。所有人可以把公钥给任何人,但必须保护好自己的私钥。如果别人拿到了私钥,就可以仿造你的签名,以你的身份发送信息。
我们选择私钥加密数据,加密过的数据可以视为我对信息签了名。只要对方有我的公钥,就可以解密数据。如果解密失败则证明数据在传输过程中遭到了篡改。
以下给出RSA算法实现,可以用main来测试
package BlockChain;
import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder;
import sun.misc.BASE64Encoder;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.security.*;
import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec;
import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RSAUtils {
private static final String KEY_ALGORITHM = "RSA";
private static final String PUBLIC_KEY = "RSAPublicKey";
private static final String PRIVATE_KEY = "RSAPrivateKey";
private static final int KEY_SIZE = 1024;
/**
* 得到密钥字符串(经过base64编码)
* @return
*/
public static String getKeyString(Key key) throws Exception {
byte[] keyBytes = key.getEncoded();
return (new BASE64Encoder()).encode(keyBytes);
}
/**
* 公钥加密
* @param content 明文
* @param publicKeyString 公钥字符串(经过base64编码)
* @throws Exception
*/
public static byte[] publicEncrypt(byte[] content, String publicKeyString) throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
PublicKey publicKey = getPublicKey(publicKeyString);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
return rsaSplitCodec(cipher, Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, content);
}
/**
* 公钥解密
* @param content 密码
* @param publicKeyString 公钥字符串(经过base64编码)
* @throws Exception
*/
public static byte[] publicDecrypt(byte[] content, String publicKeyString) throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
PublicKey publicKey = getPublicKey(publicKeyString);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
return rsaSplitCodec(cipher, Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, content);
}
/**
* 私钥加密
* @param content 明文
* @param privateKeyString 私钥字符串(经过base64编码)
* @throws Exception
*/
public static byte[] privateEncrypt(byte[] content, String privateKeyString) throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
PrivateKey privateKey = getPrivateKey(privateKeyString);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
return rsaSplitCodec(cipher, Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, content);
}
/**
* 私钥解密
* @param content 密码
* @param privateKeyString 私钥字符串(经过base64编码)
* @throws Exception
*/
public static byte[] privateDecrypt(byte[] content, String privateKeyString) throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
PrivateKey privateKey = getPrivateKey(privateKeyString);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
return rsaSplitCodec(cipher, Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, content);
}
/**
* 得到公钥
* @param key 密钥字符串(经过base64编码)
* @throws Exception
*/
public static PublicKey getPublicKey(String key) throws Exception {
byte[]keyBytes;
keyBytes = (new BASE64Decoder()).decodeBuffer(key);
X509EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(keyBytes);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
return keyFactory.generatePublic(keySpec);
}
/**
* 得到私钥
* @param key 密钥字符串(经过base64编码)
* @throws Exception
*/
public static PrivateKey getPrivateKey(String key) throws Exception {
byte[]keyBytes;
keyBytes = (new BASE64Decoder()).decodeBuffer(key);
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(keyBytes);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
return keyFactory.generatePrivate(keySpec);
}
// 初始化秘钥
public static Map<String, String> initKey() {
try {
// 生成公钥和私钥对,基于RSA算法生成对象
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGen = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
// 初始化秘钥对生成器
keyPairGen.initialize(KEY_SIZE);
// 生成一个密钥对,保存在keyPair中
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGen.generateKeyPair();
PublicKey publicKey = keyPair.getPublic(); // 得到公钥
PrivateKey privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate(); // 得到私钥
Map<String, String> keyMap = new HashMap<>(2);
keyMap.put(PUBLIC_KEY, getKeyString(publicKey));
keyMap.put(PRIVATE_KEY, getKeyString(privateKey));
return keyMap;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
// 分段加密解密
private static byte[] rsaSplitCodec(Cipher cipher, int opmode, byte[] datas) throws Exception {
int maxBlock = 0;
if (opmode == Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE){
maxBlock = KEY_SIZE / 8;
} else {
maxBlock = KEY_SIZE / 8 - 11;
}
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int offSet = 0;
byte[] buff;
int i = 0;
while(datas.length > offSet){
if (datas.length - offSet > maxBlock){
buff = cipher.doFinal(datas, offSet, maxBlock);
} else {
buff = cipher.doFinal(datas, offSet, datas.length-offSet);
}
out.write(buff, 0, buff.length);
i++;
offSet = i * maxBlock;
}
return out.toByteArray();
}
/**
* 字节数组转16进制
* @param bytes 需要转换的byte数组
* @return 转换后的Hex字符串
*/
public static String bytesToHex(byte[] bytes) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (byte aByte : bytes) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(aByte & 0xFF);
if (hex.length() < 2) {
sb.append(0);
}
sb.append(hex);
}
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* Hex字符串转byte
* @param inHex 待转换的Hex字符串
* @return 转换后的byte
*/
public static byte hexToByte(String inHex){
return (byte)Integer.parseInt(inHex,16);
}
/**
* hex字符串转byte数组
* @param inHex 待转换的Hex字符串
* @return 转换后的byte数组结果
*/
public static byte[] hexToByteArray(String inHex){
int hexlen = inHex.length();
byte[] result;
if (hexlen % 2 == 1){
hexlen++;
result = new byte[(hexlen / 2)];
inHex = "0" + inHex;
} else {
result = new byte[(hexlen / 2)];
}
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < hexlen; i+=2){
result[j] = hexToByte(inHex.substring(i, i+2));
j++;
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[]args) throws Exception {
Map<String, String> keyMap = initKey();
assert keyMap != null;
String privateKeyString = keyMap.get(PRIVATE_KEY);
String publicKeyString = keyMap.get(PUBLIC_KEY);
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("mode:0->encode 1->decode 2->close");
int mode = in.nextInt();
in.nextLine();
if (mode == 0) {
String content = in.nextLine();
System.out.println(bytesToHex(publicEncrypt(content.getBytes(), publicKeyString)));
} else if (mode == 1){
String encodeString = in.nextLine();
System.out.println(new String(privateDecrypt(hexToByteArray(encodeString), privateKeyString)));
} else {
break;
}
}
in.close();
}
}
剩下两个简单的库:Transaction和User,就没什么好说的了
package BlockChain;
import static BlockChain.RSAUtils.*;
import static BlockChain.SHA256.getSHA256;
import java.util.Arrays;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation.JSONField;
// Transaction类实现
public class Transaction {
// 交易发送方
@JSONField(ordinal = 0)
User from;
// 交易接收方
@JSONField(ordinal = 1)
User to;
// 交易数额
@JSONField(ordinal = 2)
int amount;
// 数字签名
byte[] signature;
// Constructor
Transaction(User from, User to, int amount) throws Exception {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.amount = amount;
this.sign();
}
public String getFrom() {
return this.from.name;
}
public String getTo() {
return this.to.name;
}
public int getAmount() {
return this.amount;
}
public String computeHash() {
return getSHA256(this.from.name + this.to.name + this.amount);
}
// 签名
public void sign() throws Exception {
this.signature = privateEncrypt(this.computeHash().getBytes(), this.to.getPublicKey());
}
// 验证交易是否合法
public boolean isValid() throws Exception {
return Arrays.equals(publicDecrypt(this.signature, this.to.getPrivateKey()), this.computeHash().getBytes());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "\t\tfrom:" + this.from +
"\t\tto:" + this.to +
"\t\tamount:" + this.amount + "\n";
}
}
package BlockChain;
import static BlockChain.RSAUtils.initKey;
import java.util.Map;
// User类实现
public class User {
public final String name; // 用户名
private final String publicKey; // 私钥
private final String privateKey; // 公钥
private static final String PUBLIC_KEY = "RSAPublicKey";
private static final String PRIVATE_KEY = "RSAPrivateKey";
// Constructor
public User(String userName) {
this.name = userName;
// 生成密钥对
Map<String, String> keyMap = initKey();
assert keyMap != null;
this.publicKey = keyMap.get(PUBLIC_KEY);
this.privateKey = keyMap.get(PRIVATE_KEY);
}
public String getPublicKey() {
return publicKey;
}
public String getPrivateKey() {
return privateKey;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.name;
}
}
以下为测试代码
package BlockChain;
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// register
Chain chain = new Chain();
User u1 = new User("a");
User u2 = new User("b");
User u3 = new User("c");
// transactions
chain.mineTransaction(u1, "miner1");
chain.transaction2Pool(u1, u2, 5);
chain.mineTransaction(u3, "miner2");
System.out.println(chain);
}
}