OpenStack------环境配置
OpenStack 环境配置
- 一、虚拟机资源信息
-
- 1.1 控制节点ct
- 1.2 计算节点c1
- 1.3 计算节点c2
- 二、部署思路
- 三、部署环境
-
- 3.1 基础环境配置
-
- 1、主机名
- 2、防火墙、核心防护
- 3、控制节点配置(ct)
- 4、配置Hosts
- 5、免交互
- 6、配置DNS
- 7、安装基础环境依赖包
- 8、时间同步+周期性计划任务
- 3.2 系统环境配置
-
- 3.2.1 安装、配置MariaDB
- 3.2.2 开机自启动、开启服务
- 3.2.3 执行MariaDB 安全配置脚本
- 3.3 安装RabbitMQ
- 3.4 安装memcached
-
- 3.4.1 安装Memcached
- 3.4.2 修改Memcached配置文件
- 3.4.3 安装etcd
- 3.4.4 修改etcd配置文件
一、虚拟机资源信息
1.1 控制节点ct
| CPU | 双核双线程-CPU虚拟化开启 | |
|---|---|---|
| 内存 | 6G | |
| 硬盘 | 300G+1024G(CEPH块存储) | |
| 双网卡 | VM1-(局域网)192.168.86.11 | NAT-192.168.238.11 |
| 操作系统 | Centos 7.6(1810)-最小化安装 |
1.2 计算节点c1
| CPU | 双核双线程-CPU虚拟化开启 | |
|---|---|---|
| 内存 | 8G | |
| 硬盘 | 300G+1024G(CEPH块存储) | |
| 双网卡 | VM1-(局域网)192.168.86.12 | NAT-192.168.238.12 |
| 操作系统 | Centos 7.6(1810)-最小化安装 |
1.3 计算节点c2
| CPU | 双核双线程-CPU虚拟化开启 | |
|---|---|---|
| 内存 | 8G | |
| 硬盘 | 300G+1024G(CEPH块存储) | |
| 双网卡 | VM1-(局域网)192.168.86.13 | NAT-192.168.238.13 |
| 操作系统 | Centos 7.6(1810)-最小化安装 |
二、部署思路
1、配置操作系统+OpenStack运行环境
2、配置OpenStack平台基础服务(rabbitmq、mariadb、memcache、Apache)
3、配置OpenStack keystone组件
4、配置OpenStack Glance组件
5、配置placement服务
6、配置OpenStack Nova组件
7、配置OpenStack Neutron组件
8、配置OpenStack dashboard组件
9、配置OpenStack Cinder组件
10、常用云主机操作
三、部署环境
3.1 基础环境配置
配置项(所有节点)
1、主机名
hostnamectl set-hostname ct
su
2、防火墙、核心防护
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
setenforce 0
vim /etc/sysconfig/selinux
SELINUX=disabled
3、控制节点配置(ct)
c1、c2配置步骤差不多,自己修改
#局域网设置主机模式VMnet1
cp /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens36
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens36
#记得修改设备名称,UUID
BOOTPROTO=static
ONBOOT=yes
IPADDR=192.168.86.11
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
#GATEWAY=192.168.86.2
#网络为NAT模式
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
BOOTPROTO=static
IPV4_ROUTE_METRIC=90 ###调由优先级,NAT网卡优先
ONBOOT=yes
IPADDR=192.168.238.11
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
GATEWAY=192.168.238.2
systemctl restart network #重启网卡
4、配置Hosts
所有节点一样
vi /etc/hosts
192.168.86.11 ct
192.168.86.12 c1
192.168.86.13 c2
#以上为局域网IP
5、免交互
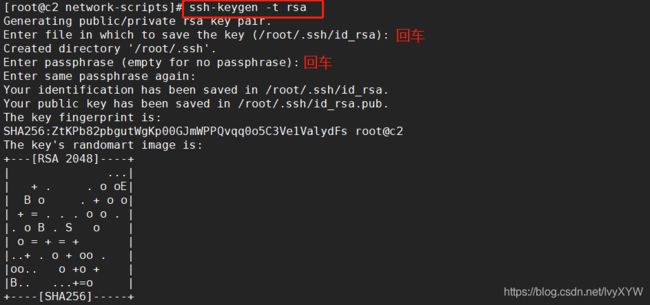
三台节点做免交互
非对称密钥
ssh-keygen -t rsa
ssh-copy-id ct
ssh-copy-id c1
ssh-copy-id c2
6、配置DNS
(所有节点)
vim /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 114.114.114.114
7、安装基础环境依赖包
yum -y install net-tools bash-completion vim gcc gcc-c++ make pcre pcre-devel expat-devel cmake bzip2 lrzsz
#EXPAT C语言发开库
yum -y install centos-release-openstack-train python-openstackclient openstack-selinux openstack-utils
#OpenStack 的 train 版本仓库源安装 包,同时安装 OpenStack 客户端和 openstack-selinux 安装包
8、时间同步+周期性计划任务
通过控制节点ct时间同步配置
ct ->同步阿里云时钟服务器
c1、c2 -> 同步ct
节点ct
yum install chrony -y
vim /etc/chrony.conf
systemctl enable chronyd
systemctl restart chronyd
vi /etc/chrony.conf
server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst #注释掉
server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst #注释掉
server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst #注释掉
server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst #注释掉
server ntp6.aliyun.com iburst #配置阿里云时钟服务器源
allow 192.168.86.0/24 #允许192.168.86.0/24网段的主机来同步时钟服务
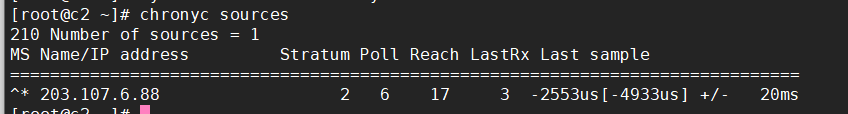
[root@ct ~]# chronyc sources #使用 chronyc sources 命令查询时间同步信息
210 Number of sources = 1
MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample
===============================================================================
^* 203.107.6.88 2 6 17 3 -2553us[-4933us] +/- 20ms
#控制节点c1、c2时间同步配置
[root@c1 ~]# vi /etc/chrony.conf
server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst #注释掉
server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst #注释掉
server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst #注释掉
server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst #注释掉
server ct iburst #配置阿里云时钟服务器源
[root@c1 ~]# systemctl enable chronyd.service #永久开启时间同步服务器
[root@c1 ~]# systemctl restart chronyd.service #重启时间同步服务器
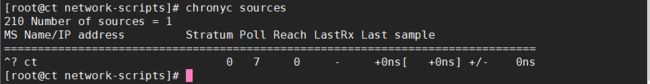
[root@c2 ~]# chronyc sources
210 Number of sources = 1
MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample
===============================================================================
^? ct 0 7 0 - +0ns[ +0ns] +/- 0ns
#设置周期性任务
[root@c1 ~]# crontab -e #配置计划任务,每隔2分钟同步一次
*/2 * * * * /usr/bin/chronyc sources >> /var/log/chronyc.log
no crontab for root - using an empty one
crontab: installing new crontab
3.2 系统环境配置
控制节点ct
3.2.1 安装、配置MariaDB
yum -y install mariadb mariadb-server python2-PyMySQL
#此包用于openstack的控制端连接mysql所需要的模块,如果不安装,则无法连接数据库;此包只安装在控制端
yum -y install libibverbs
● 添加MySQL子配置文件,增加如下内容
vim /etc/my.cnf.d/openstack.cnf
[mysqld]
bind-address = 192.168.86.11
default-storage-engine = innodb
innodb_file_per_table = on
max_connections = 4096
collation-server = utf8_general_ci
character-set-server = utf8
[mysqld]
bind-address = 192.168.86.11 #控制节点局域网地址
default-storage-engine = innodb #默认存储引擎
innodb_file_per_table = on #每张表独立表空间文件
max_connections = 4096 #最大连接数
collation-server = utf8_general_ci #默认字符集
character-set-server = utf8
3.2.2 开机自启动、开启服务
systemctl enable mariadb
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/mysql.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service.
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/mysqld.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service.
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mariadb.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service.
systemctl start mariadb
3.2.3 执行MariaDB 安全配置脚本
mysql_secure_installation
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none): #回车
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] Y
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] n #是否不允许root用户远程登陆
... skipping.
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y #是否删除test测试库
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
3.3 安装RabbitMQ
所有创建虚拟机的指令,控制端都会发送到rabbitmq,node节点监听rabbitmq
yum -y install rabbitmq-server
#配置服务,启动RabbitMQ服务,并设置其开机启动。
systemctl enable rabbitmq-server.service
systemctl start rabbitmq-server.service
#创建消息队列用户,用于controler和 计算节点连接rabbitmq的认证(关联)
rabbitmqctl add_user openstack RABBIT_PASS
Creating user "openstack"
#配置openstack用户的操作权限(正则,配置读写权限)
rabbitmqctl set_permissions openstack ".*" ".*" ".*"
Setting permissions for user "openstack" in vhost "/"
#可查看25672和5672 两个端口(5672是Rabbitmq默认端口,25672是Rabbit的测试工具CLI的端口)
● 选择配置:
#查看rabbitmq插件列表
[root@ct ~]# rabbitmq-plugins list
Configured: E = explicitly enabled; e = implicitly enabled
| Status: * = running on rabbit@c2
|/
[ ] amqp_client 3.6.16
[ ] cowboy 1.0.4
[ ] cowlib 1.0.2
[ ] rabbitmq_amqp1_0 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_auth_backend_ldap 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_auth_mechanism_ssl 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_consistent_hash_exchange 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_event_exchange 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_federation 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_federation_management 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_jms_topic_exchange 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_management 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_management_agent 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_management_visualiser 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_mqtt 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_random_exchange 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_recent_history_exchange 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_sharding 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_shovel 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_shovel_management 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_stomp 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_top 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_tracing 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_trust_store 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_web_dispatch 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_web_mqtt 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_web_mqtt_examples 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_web_stomp 3.6.16
[ ] rabbitmq_web_stomp_examples 3.6.16
[ ] sockjs 0.3.4
#开启rabbitmq的web管理界面的插件,端口为15672
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
The following plugins have been enabled:
amqp_client
cowlib
cowboy
rabbitmq_web_dispatch
rabbitmq_management_agent
rabbitmq_management
Applying plugin configuration to rabbit@c2... started 6 plugins.
#检查端口(25672 5672 15672)
ss -natp | grep 5672
LISTEN 0 128 *:25672 *:* users:(("beam.smp",pid=34623,fd=46))
LISTEN 0 128 *:15672 *:* users:(("beam.smp",pid=34623,fd=57))
TIME-WAIT 0 0 192.168.86.13:42078 192.168.86.13:25672
LISTEN 0 128 :::5672 :::* users:(("beam.smp",pid=34623,fd=55))
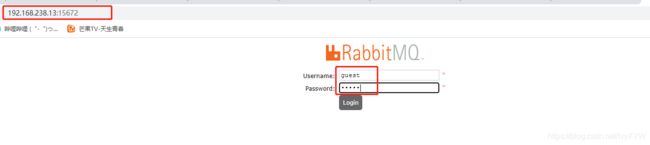
可访问192.168.238.11:15672
默认账号密码均为guest
3.4 安装memcached
● 作用:
安装memcached是用于存储session信息;服务身份验证机制(keystone)使用Memcached来缓存令牌 在登录openstack的dashboard时,会产生一些session信息,这些session信息会存放到memcached中
JWT
● 操作:
3.4.1 安装Memcached
yum install -y memcached python-memcached
#python-*模块在OpenStack中起到连接数据库的作用
3.4.2 修改Memcached配置文件
cat /etc/sysconfig/memcached
PORT="11211"
USER="memcached"
MAXCONN="1024"
CACHESIZE="64"
OPTIONS="-l 127.0.0.1,::1"
systemctl enable memcached
systemctl start memcached
netstat -nautp | grep 11211
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:11211 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 35746/memcached
tcp6 0 0 ::1:11211 :::* LISTEN 35746/memcached
3.4.3 安装etcd
yum -y install etcd
3.4.4 修改etcd配置文件
[root@ct ~]# cd /etc/etcd/
[root@ct etcd]# ls
etcd.conf
[root@ct etcd]# vim etcd.conf #数据目录位置
ETCD_DATA_DIR="/var/lib/etcd/default.etcd"
ETCD_LISTEN_PEER_URLS="http://192.168.86.11:2380" #监听其他etcd member的url(2380端口,集群之间通讯,域名为无效值)
ETCD_LISTEN_CLIENT_URLS="http://192.168.86.11:2379" #对外提供服务的地址(2379端口,集群内部的通讯端口)
ETCD_NAME="ct" #集群中节点标识(名称)
ETCD_INITIAL_ADVERTISE_PEER_URLS="http://192.168.86.11:2380" #该节点成员的URL地址,2380端口:用于集群之间通讯。
ETCD_ADVERTISE_CLIENT_URLS="http://192.168.86.11:2379"
ETCD_INITIAL_CLUSTER="ct=http://192.168.86.11:2380"
ETCD_INITIAL_CLUSTER_TOKEN="etcd-cluster-01" #集群唯一标识
ETCD_INITIAL_CLUSTER_STATE="new" #初始集群状态,new为静态,若为existing,则表示此ETCD服务将尝试加入已有的集群
若为DNS,则表示此集群将作为被加入的对象
#开机自启动、开启服务,检测端口
systemctl enable etcd.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/etcd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/etcd.service.
systemctl start etcd.service
netstat -anutp |grep 2379
tcp 0 0 192.168.86.13:2379 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 36063/etcd
tcp 0 0 192.168.86.13:2379 192.168.86.13:52808 ESTABLISHED 36063/etcd
tcp 0 0 192.168.86.13:52808 192.168.86.13:2379 ESTABLISHED 36063/etcd
netstat -anutp |grep 2380
tcp 0 0 192.168.86.13:2380 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 36063/etcd
#C1、C2安装OpenStack组件
yum -y install centos-release-openstack-train python-openstackclient openstack-selinux openstack-utils